![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
For detailed information, see the OpenVMS License Management Utility Manual.
In addition, the displays of the SHOW LICENSE command are updated to
show any new options that you enter. For more information, see the
OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.
3.10 Networking Support
OpenVMS Version 7.1 provides you with the flexibility to choose the network protocol of your choice. Whether you require TCP/IP, OSI, or DECnet, OpenVMS enables you to simply choose the protocol or combination of protocols that work best for your network.
If you are installing OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.1, you will be able to easily choose from among the following network options now integrated into the operating system installation procedure:
If you are upgrading to DECnet-Plus from an earlier version of OpenVMS, the network upgrade is performed automatically as part of the operating system upgrade procedure.
Note
DECnet-Plus has replaced DECnet for OpenVMS Phase IV in both the installation and upgrade procedures for OpenVMS. To install or upgrade to DECnet Phase IV, follow the instructions in the OpenVMS Upgrade and Installation Manual on how to install DECnet Phase IV as a layered product.
With DECnet-Plus for OpenVMS Version 7.1 software, OpenVMS systems can communicate with each other and with systems produced by other vendors. DECnet-Plus provides true network independence: you get the full functionality of DECnet Phase IV, additional DECnet enhancements, and the ability to use DECnet over a variety of network protocols, such as Phase IV, TCP/IP, and OSI.
All OpenVMS Version 7.1 customers will receive a complimentary DECnet-Plus Starter Kit, which includes media and selected documentation. The starter kit documentation received will be in either online or printed format depending on the OpenVMS offering purchased. In future versions of OpenVMS, customers who do not receive the OpenVMS CD-ROM must purchase the media and documentation for Digital's networking products (such as DECnet Phase IV, DECnet-Plus, and Digital TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS) separately.
For complete information about the benefits of using DECnet-Plus
software, see the DECnet-Plus Introduction and User's Guide.
3.10.1.1 New Features of DECnet-Plus
The new features of DECnet-Plus for OpenVMS introduced in Version 7.1 are:
Host-based routing allows an OpenVMS system to operate as a DECnet-Plus intermediate system (IS) in a routing vector domain. This feature is useful for those configurations where you need to route from a local area network (LAN) to a wide area network (WAN) and want to use an existing system to do the routing rather than investing in a dedicated router. Host-based routing is not intended to be used in network configurations that have high-throughput requirements.
For upgrades from DECnet Phase IV to DECnet-Plus, the fast-configuration option allows system or network managers to use the NET$CONFIGURE.COM procedure to configure DECnet-Plus quickly.
For complete information about the DECnet-Plus new features and functionality, see the DECnet-Plus for OpenVMS Release Notes.
3.10.1.2 Upgrading to DECnet-Plus
You can upgrade a network node or system from DECnet Phase IV to
DECnet-Plus software in less than 1 hour. The Network Command Protocol
(NCP) emulator makes the upgrade easy without disrupting your network's
day-to-day operations.
Upgrading to DECnet-Plus brings significant enhancements to your DECnet network as well as global communication between independent networks. The software allows DECnet Phase IV applications to run over DECnet-Plus and TCP/IP without modification.
For DECnet-Plus upgrade and installation information, see the
DECnet-Plus Installation and Basic Configuration manual.
3.10.2 Digital TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS
Digital TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS provides you with the following features as part of the Version 4.1 product:
For detailed information about these features, see the Digital TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS Release Notes.
3.11 OpenVMS Cluster Features
The following OpenVMS Cluster features are included in OpenVMS Version
7.1.
These features further enhance the performance, availability, and
functionality of OpenVMS Clusters. The following sections describe
these features in more detail.
3.11.1 MEMORY CHANNEL Interconnect
MEMORY CHANNEL is a new, high-performance cluster interconnect for PCI-based Alpha systems. MEMORY CHANNEL provides node-to-node communications and is used with one or more other interconnects which provide storage and network communications.
MEMORY CHANNEL enables a system to write data very quickly to the memory of other systems, delivering up to 100 Mb/s aggregate bandwidth. MEMORY CHANNEL supports a maximum of 4 nodes in a 10 foot radial topology.
MEMORY CHANNEL improves throughput in high-performance databases and other applications that generate heavy OpenVMS Lock Manager traffic. With the current MEMORY CHANNEL adapters, the achievable Lock Manager performance with MEMORY CHANNEL is approximately two to three times that of a CI (depending on CPU type). Note that acheiving such performance will consume approximately three to four times the compute overhead of a CI.
MEMORY CHANNEL can be used to offload internode cluster traffic (such as lock management communication) from existing interconnects---CI, DSSI, FDDI, and Ethernet---so that they can process storage and network traffic more effectively.
For a detailed description of MEMORY CHANNEL, see Guidelines for OpenVMS Cluster Configurations.
3.11.2 New CI-to-PCI Adapter, CIPCA
With the release of OpenVMS Alpha Version 6.2--1H2, Digital introduced a CI-to-PCI adapter (CIPCA) that allows PCI-based AlphaServer systems to connect directly to CI-based OpenVMS Clusters. For CI-based clusters, OpenVMS Version 7.1 supports up to 26 CIPCA adapters per system, and a combination of CIXCD and CIPCA adapters on the AlphaServer 8400.
CIPCA support for Alpha servers provides the following features and benefits to customers:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Lower entry cost and more configuration choices | If you require midrange compute power for your business needs, CIPCA enables you to integrate midrange Alpha servers into your existing CI cluster. |
| High-end Alpha speed and power | If you require maximum compute power, you can use the CIPCA with both the AlphaServer 8200 systems and AlphaServer 8400 systems that have PCI and EISA I/O subsystems. |
| Cost-effective Alpha migration path | If you want to add Alpha servers to an existing CI VAXcluster, CIPCA provides a cost-effective way to start migrating to a mixed-architecture cluster in the price/performance range that you need. |
| Advantages of the CI |
The CIPCA connects to the CI, which offers the following advantages:
|
For more information about CIPCA, see the Guidelines for OpenVMS Cluster Configurations.
3.11.3 New LAN$POPULATE Support
The LAN$POPULATE command now provides support for migrating satellite Maintenance Operations Protocol (MOP) booting from DECnet-Plus to LANCP.
LANCP is the preferred service for MOP downline loading to boot satellites in an OpenVMS Cluster. LAN$POPULATE generates command procedures that assist in migration from DECnet MOP loading to LANCP MOP loading.
Note
If you plan to use LANCP in place of DECnet, and you also plan to move from DECnet Phase IV to DECnet-Plus, Digital recommends that you do so in the following order:
- Replace DECnet with satellite booting (MOP downline load service), using LAN$POPULATE.COM.
- Migrate from DECnet Phase IV to DECnet-Plus.
For more information about LAN$POPULATE, see OpenVMS Cluster Systems.
3.11.4 Lock Manager: Increased Quotas and Limits
The OpenVMS lock manager has been enhances for OpenVMS Version 7.1. Some internal restrictions on the number of locks and resources available on the system have been eased and a method to allow enqueue limit quota (ENQLM) of greater than 32767 has been added. No application changes are required to take advantage of these increases.
Specifically, the OpenVMS lock manager includes the following additions:
While most processes do not require very many locks simultaneously
(typically less than 100), large scale database or server applications
can easily exceed the previous thresholds. For more information about
these enhancements, see the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
3.11.5 New CLUSTER_CREDITS System Parameter
The CLUSTER_CREDITS parameter specifies the number of per-connection buffers a node allocates to receiving VMS$VAXcluster communications. This system parameter is provided to support lock-intensive applications, such as large scale-databases, which may require more per-connection buffers. Prior to this release, it was not possible to change the default setting.
This system parameter is not dynamic; that is, if you change the value, you must reboot the node on which you changed it.
A shortage of credits affects performance, since message transmissions are delayed until free credits are available. These are visible as credit waits in the SHOW CLUSTER display.
For instructions for using this system parameter, see OpenVMS Cluster Systems.
3.11.6 New Cluster Configuration Options
Two new options, Make Root and Delete Root, have been added to the main menu of both CLUSTER_CONFIG.COM and CLUSTER_CONFIG_LAN.COM, as shown in the following example. These options replace the MAKEROOT.COM command procedure.
MAIN MENU 1. ADD an Alpha node to the cluster. 2. REMOVE a node from the cluster. 3. CHANGE a cluster member's characteristics. 4. CREATE a duplicate system disk for node-name. 5. MAKE a directory structure for a new root on a system disk. 6. DELETE a root from a system disk. 7. EXIT from this procedure.
In addition to these new options, you will now get a shortened main
menu when you execute either CLUSTER_CONFIG.COM or
CLUSTER_CONFIG_LAN.COM on a node that does not already belong to a
cluster.
3.11.7 New SCSI Adapter Support
The KZPSA and KZTSA adapters are SCSI adapters that connect a PCI bus (KZPSA) or a TURBOchannel bus (KZTSA) to a single 16-bit fast-wide differential SCSI bus. With the Version 6.2--1H3 release of the OpenVMS operating system, you can share access to storage by configuring the KZPSA or KZTSA adapters on a multihost SCSI bus.
Note
The minimum adapter firmware revision that supports the KZPSA in a SCSI cluster is A10. The minimum adapter firmware revision that supports the KZTSA in a SCSI cluster is A10_1.
The KZPSA and KZTSA adapters are supported in multihost configurations on all Alpha computers that support them in single-host configurations. You can configure up to three SCSI host adapters on the same SCSI bus, using any combination of KZPSA, KZTSA, and KZPAA adapters. Each system can be connected with up to six shared buses. The KZPSA and KZTSA adapters use fast and wide SCSI data transfers when interacting with storage devices that support those modes.
For more information about OpenVMS multihost SCSI configurations, see
Guidelines for OpenVMS Cluster Configurations. Refer to the OpenVMS SPD (25.01.xx) for the list of
systems that support the KZPSA and KZTSA adapters in single-host
configurations and for detailed configuration rules.
3.11.8 New SCSI Device Naming Scheme
Port allocation classes provide a new method for naming SCSI devices attached to Alpha systems in an OpenVMS Cluster. Devices that use the new naming scheme are also accessible on OpenVMS VAX systems via the MSCP server.
Port allocation classes are designed to solve the naming and configuration conflicts that can occur when configuring a large OpenVMS Cluster that includes multiple hosts sharing one or more storage interconnects and multiple disks, some connected to the shared interconnect and some connected to single-host SCSI systems.
Note
This optional feature is intended primarily for changing or creating a new cluster configuration that contains multiple SCSI buses.
For more information about port allocation classes, see OpenVMS Cluster Systems.
3.11.9 SCSI Support for 16 Devices
Wide adapters enable the use of 16 data lines for device
identification. SCSI wide adapter support enables the configuration and
use of up to 16 devices per SCSI bus. For more information, see
Section 3.7.
3.11.10 OpenVMS Cluster Compatibility Kit
The OpenVMS Cluster Compatibility Kit is required for customers with mixed-version and mixed-architecture clusters that include systems running OpenVMS Version 7.1 and OpenVMS Version 6.2. It provides OpenVMS Version 7.1 Volume Shadowing, Mount, lock manager, and other quality improvements for Version 6.2 systems.
This kit also includes limited support for port allocation classes for Version 6.2 systems. Port allocation classes are a naming option for SCSI devices on systems running OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.1. OpenVMS Version 6.2 systems that have installed the Cluster Compatibility Kit can access SCSI disks, named with port allocation classes, that are connected to OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.1 systems.
For more information about the OpenVMS Cluster Compatibility Kit, see
the OpenVMS Version 7.1 Release Notes.
3.11.11 Warranted and Migration Support for OpenVMS Cluster Configurations
OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.1 and OpenVMS VAX Version 7.1 provide two levels of support, warranted and migration, for mixed-version and mixed-architecture OpenVMS Cluster systems.
Warranted support means that Digital has fully qualified the two versions coexisting in an OpenVMS Cluster and will answer all problems identified by customers using these configurations.
Migration support is a superset of the Rolling Upgrade support provided in earlier releases of OpenVMS and is available for mixes that are not warranted. Migration support means that Digital has qualified the versions for use together in configurations that are migrating in a staged fashion to a newer version of OpenVMS VAX or to OpenVMS Alpha. Problem reports submitted against these configurations will be answered by Digital. However, in exceptional cases Digital may request that you move to a warranted configuration as part of answering the problem.
Migration support will help customers move to warranted OpenVMS Cluster version mixes with minimal impact on their cluster environments.
Figure 3-1 shows the level of support provided for all possible version pairings.
Figure 3-1 OpenVMS Cluster Version Pairings
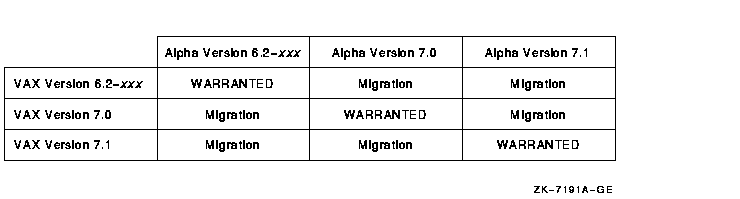
Note that Digital does not support the use of Version 7.1 with Version
6.1 (or earlier versions) in an OpenVMS Cluster. In many cases, mixing
Version 7.1 with versions prior to Version 6.2 will successfully
operate, but Digital cannot commit to resolving problems experienced
with such configurations.
3.12 OpenVMS Management Station: Offers Enhanced Printer Management
OpenVMS Management Station now makes it easy for you to manage a wide range of printers and print queues across multiple OpenVMS Cluster systems and OpenVMS nodes. Plus, the printer monitoring feature allows you to detect and correct printer problems quickly and efficiently.
You no longer need to maintain complicated command files to control your printer environment. You can create, delete, and manage a printer and its related queues, as well as perform print job management for those printers, from an easy-to-use Windows interface.
Some of the tasks you can now perform include:
For more information about this feature, see the OpenVMS Management Station Overview and Release Notes.
3.13 OpenVMS Volume Shadowing: Minimerge Capability for System Disks
OpenVMS Volume Shadowing Version 7.1 has been enhanced to permit system disk shadow sets to be minimerged. This provides much faster merge operations for shadowed system disks, eliminating the I/O overhead associated with a full merge operation. Minimerge is an MSCP feature that is available for cluster configurations with DSSI- and CI-based shadow sets. Note that non-system disks have benefited from the minimerge feature for several releases.
To take advantage of this feature, it is necessary to use another new feature in OpenVMS Version 7.1 --- the ability to write system crash dump files off the system disk. When the crash dump file is written to a non-system disk, the system disk minimerge feature can be enabled.
For more information on volume shadowing and the OpenVMS Cluster
Compatibility Kit, see the OpenVMS Version 7.1 Release Notes.
3.14 POLYCENTER Software Installation Utility: New Subcommands and Displays
The POLYCENTER Software Installation Utility PRODUCT command has the following new subcommands:
In addition, the format and content of the display has changed for the following PRODUCT subcommands:
For PRODUCT FIND, a /FULL qualifier has been added. Many improvements have also been made to the interactive dialog for several PRODUCT subcommands, especially PRODUCT INSTALL. More detailed examples are in the PRODUCT command section of the OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual.
Following are brief explanations of the new subcommands. More detailed
explanations and examples are in the POLYCENTER section of the
OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual.
3.14.1 EXTRACT FILE Subcommand
The EXTRACT FILE subcommand retrieves a user-specified file or files
from a sequentially formatted software product kit. A file type of
.PCSI denotes a sequential kit. The original name of the file is
preserved when it is extracted.
3.14.2 EXTRACT PDF Subcommand
The EXTRACT PDF subcommand retrieves the product description file (PDF)
from a sequentially formatted software product kit. A file type of
.PCSI denotes a sequential kit. The file type of the extracted PDF file
is .PCSI$DESCRIPTION.
3.14.3 EXTRACT PTF Subcommand
The EXTRACT PTF subcommand retrieves the product text file (PTF) from a
sequentially formatted software product kit. A file type of .PCSI
denotes a sequential kit. The PTF is stored in a product kit as a text
library file. The file type of the extracted PTF file is .PCSI$TLB. In
addition, a text file version of this text library file is created with
a file type of .PCSI$TEXT.
3.14.4 LIST Subcommand
The LIST subcommand lists the names of the files contained in a
sequentially formatted software product kit. A file type of .PCSI
denotes a sequential kit. All files in a kit are listed unless you use
the /SELECT qualifier to specify a subset of the files.
3.14.5 SHOW UTILITY Subcommand
The SHOW UTILITY subcommand displays the version of the POLYCENTER
Software Installation utility that implements the PRODUCT command.
3.15 SYSMAN Utility: New Qualifiers
New qualifiers make several SYSMAN commands more usable by allowing you to do the following:
The following sections describe the commands and each new qualifier.
3.15.1 DO/CONFIRM Qualifier
You can use the /CONFIRM qualifier to verify that you want to perform a DO command on each node you have specified with the SYSMAN command SET ENVIRONMENT.
Example
The following example shows how to control whether the system displays time for each node in a cluster.
$ MCR SYSMAN SYSMAN> SET ENVIRONMENT/CLUSTER
%SYSMAN-I-ENV, current command environment:
Clusterwide on local cluster
Username KIERSTEIN will be used on nonlocal nodes
SYSMAN> DO/CONFIRM SHOW TIME Execute command for node EXPERT? [N]: Y [Return] %SYSMAN-I-OUTPUT, command execution on node EXPERT 22-MAR-1996 09:40:28 Execute command for node MODERN [N]: Y [Return] %SYSMAN-I-OUTPUT, command execution on node MODERN 22-MAR-1996 09:40:56 Execute command for node IMPOSE? [N]: N [Return] Execute command for node ADU26A? [N]: Y [Return] . . .
You can use the /PAUSE qualifier to control the rate at which the system displays information. Using the /PAUSE qualifier causes the system to display information about one node at a time, prompting you to press Return when you are ready to display the information about the next node. For example:
SYSMAN> DO/PAUSE SHOW TIME %SYSMAN-I-OUTPUT, command execution on node EXPERT 22-MAR-1996 09:40:13 Press return to continue [Return] %SYSMAN-I-OUTPUT, command execution on node MODERN 22-MAR-1996 09:40:41 Press return to continue [Return] %SYSMAN-I-OUTPUT, command execution on node IMPOSE 22-MAR-1996 09:39:46 Press return to continue [Return] . . .
The IO REBUILD command reconstructs device configuration tables in preparation for using the IO AUTOCONFIGURE command to reconfigure the system.
You must have CMKRNL privilege to use this command.
/VERIFY Qualifier
The /VERIFY qualifier with the IO REBUILD command causes SYSMAN to read
and process the files SYS$SYSTEM:SYS$USER_CONFIG.DAT and
SYS$SYSTEM:CONFIG.DAT, but not to apply the files to the I/O database.
Messages will be displayed for any errors that are encountered.
Developers can use the IO REBUILD/VERIFY command to test new changes to
SYS$SYSTEM:SYS$USER_CONFIG.DAT without modifying the current system.
3.15.4 PARAMETERS SHOW/PAUSE Qualifier
You can use the /PAUSE qualifier to control the rate at which the system displays information about parameters. Using the /PAUSE qualifier causes the system to display information about one node at a time, prompting you to press Return when you are ready to display information about the next node. For example:
SYSMAN> PARAMETERS SHOW/PAUSE MAXPROCESSCNT
Node EXPERT: Parameters in use: ACTIVE Parameter Name Current Default Minimum Maximum Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- MAXPROCESSCNT 160 32 12 8192 Processes
Press return to continue [Return]
Node MODERN: Parameters in use: ACTIVE Parameter Name Current Default Minimum Maximum Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- MAXPROCESSCNT 157 32 12 8192 Processes
Press return to continue [Return]
Node IMPOSE: Parameters in use: ACTIVE Parameter Name Current Default Minimum Maximum Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- MAXPROCESSCNT 50 32 12 8192 Processes
Press return to continue [Return]
The following sections describe the new and changed system parameters
for OpenVMS Version 7.1.
3.16.1 CLUSTER_CREDITS Parameter
CLUSTER_CREDITS specifies the number of per-connection buffers a node allocates to receiving VMS$VAXcluster communications.
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
6480P003.HTM OSSG Documentation 5-DEC-1996 13:49:36.64
Copyright © Digital Equipment Corporation 1996. All Rights Reserved.