![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
Changes the user capabilities associated with the specified CPUs.Requires ALTPRI and WORLD privileges.
SET CPU cpu-id[,...]
cpu-id
Specifies a decimal value representing the identity of a processor in an OpenVMS multiprocessing system. On a VAX 6000 system or an Alpha 7000 system, the CPU is the backplane slot number of the processor.
/ALL
Applies the specified operation to all CPUs in the active set./CAPABILITY
/NOCAPABILITY
Allows bits in the process user capability mask to be set or cleared individually, in groups, or all at once.
Note
The SET CPU/[NO]CAPABILITY command will fail if there is an active process that requires a capability that is not available on any remaining active CPU.
Specifying the /CAPABILITY qualifier has no direct effect, but merely indicates the target of the operations specified by the following secondary qualifiers:
/SET=( n[,...]) Sets all user capabilities defined by the position values n, where n has the range of 1 to 16. /CLEAR=( n[,...]) Clears all user capabilities defined by the position values n, where n has the range of 1 to 16. The secondary qualifiers can all be used at once as long as the user capability bits defined in the /SET and /CLEAR parameters do not overlap.
The /NOCAPABILITY qualifier clears all user capability bits.
/CLEAR=(n[,...])
Clears all user capabilities defined by the position values n specified by the /CAPABILITY qualifier./GLOBAL
Modifies the global cell SCH$GL_DEFAULT_CPU_CAP. This global cell is used to initialize the user capability mask of CPUs that are brought into the active set for the first time./SET=(n[,...])
Sets all user capabilities defined by the position values n specified by the /CAPABILITY qualifier.
#1
$ SET CPU/CAPABILITY/GLOBAL/SET=(2,4)
#2This command sets user capabilities 2 and 4 in the global cell SCH$GL_DEFAULT_CPU_CAP.
$ SET CPU/CAPABILITY/GLOBAL/SET=(2,4) 0
#3This command sets user capabilities 2 and 4 in the global cell SCH$GL_DEFAULT_CPU_CAP, as well in the active CPU 0.
$ SET CPU/CAPABILITY/SET=(1,2) 0
$ SHOW CPU/FULL
PIPERI, a DEC 3000 Model 500
Multiprocessing is ENABLED. Full checking synchronization image loaded.
Minimum multiprocessing revision levels: CPU = 1
System Page Size = 8192
System Revision Code =
System Serial Number =
Default CPU Capabilities:
System: QUORUM RUN
Default Process Capabilities:
System: QUORUM RUN
PRIMARY CPU = 00
CPU 00 is in RUN state
Current Process: VMSADU PID = 00000094
Serial Number:
Revision: F001
VAX floating point operations supported.
IEEE floating point operations and data types supported.
PALCODE: Revision Code = 5.48-01
PALcode Compatibility = 0
Maximum Shared Processors = 0
Memory Space: Physical address = 00000000 00054000
Length = 81920
Scratch Space: Physical address = 00000000 00104000
Length = 8192
Capabilities of this CPU:
System: PRIMARY QUORUM RUN
User bitmask: 00000003
Processes which can only execute on this CPU:
NETACP PID = 0000008F Reason: PRIMARY Capability
$ SET CPU/CAPABILITY/CLEAR=1 0
$ SHOW CPU/FULL
PIPERI, a DEC 3000 Model 500
Multiprocessing is ENABLED. Full checking synchronization image loaded.
Minimum multiprocessing revision levels: CPU = 1
System Page Size = 8192
System Revision Code =
System Serial Number =
Default CPU Capabilities:
System: QUORUM RUN
Default Process Capabilities:
System: QUORUM RUN
PRIMARY CPU = 00
CPU 00 is in RUN state
Current Process: VMSADU PID = 00000094
Serial Number:
Revision: F001
VAX floating point operations supported.
IEEE floating point operations and data types supported.
PALCODE: Revision Code = 5.48-01
PALcode Compatibility = 0
Maximum Shared Processors = 0
Memory Space: Physical address = 00000000 00054000
Length = 81920
Scratch Space: Physical address = 00000000 00104000
Length = 8192
Capabilities of this CPU:
System: PRIMARY QUORUM RUN
User bitmask: 00000002
Processes which can only execute on this CPU:
NETACP PID = 0000008F Reason: PRIMARY Capability
In this example, the first SET CPU command sets user capabilities 1 and 2 for CPU 0. The second SET CPU command clears capability 1.
Sets the default day type specified in the user authorization file (UAF) for the current day.Requires OPER (operator) privilege.
SET DAY
None.
The SET DAY command overrides the default primary and secondary day types that are used to control daily logins. These default day types are defined by the system manager in the user authorization file (UAF).The SET DAY command is useful when you need to override the day type because of a change in the work days of a particular week. For example, Monday, which is normally a work day, is occasionally a holiday. You can use the SET DAY command to override the normal day type for Monday and set it to a different day type.
/DEFAULT
Overrides any previous SET DAY specification and specifies that the normal UAF defaults are to be used to determine today's day type./LOG
/NOLOG (default)
Controls whether log information is displayed at the terminal to confirm that the new SET DAY information has been set./PRIMARY
Sets today until midnight to a primary day./SECONDARY
Sets today until midnight to a secondary day.
#1
$ SET DAY/PRIMARY
#2The SET DAY command in this example overrides the current default day type and sets today until midnight to a primary day.
$ SET DAY/DEFAULT
The SET DAY command in this example overrides the previous SET DAY command and sets today's day type to the UAF-defined default.
Sets your default device and directory specifications. The new default is applied to all subsequent file specifications that do not explicitly include a device or directory name.When you change the default device assignment, the system equates the specified device with the logical name SYS$DISK.
SET DEFAULT [device-name[:]][directory-spec]
device-name[:]
Specifies the name of the device you want to go to.directory-spec
Specifies the name of the directory you want to go to. A directory name must be enclosed in brackets ([ ]). Use the minus sign (-) to specify the next higher directory from the current default.You must specify either the device-name parameter or the directory-spec parameter. If you specify only the device name, the current directory is the default for the directory-spec parameter. If you specify only the directory name, the current device is the default for the device-name parameter.
You can use a logical name but it must constitute at least the device part of the specification. When you use a search list logical name as the parameter, the logical name is not translated by the SET DEFAULT command. Instead, the SET DEFAULT command retains the logical name so that OpenVMS Record Management Services (RMS) is able to access the entire search list. If you enter the SHOW DEFAULT command, the search list logical name is displayed as the default device, along with its equivalence strings.
#1
$ SET DEFAULT [CARPENTER]
#2The SET DEFAULT command in this example changes the default directory to [CARPENTER]. The default disk device does not change.
$ SET DEFAULT $FLOPPY1:[WATER.MEMOS]
#3The SET DEFAULT command in this example sets your default to the WATER.MEMOS subdirectory on $FLOPPY1.
$ SET DEFAULT $FLOPPY1:
#4The SET DEFAULT command in this example sets the default device to $FLOPPY1. The directory name does not change.
$ SET DEFAULT [-]
#5The SET DEFAULT command in this example changes the default directory to the parent directory of the one you are currently in. For example, if the current directory is $FLOPPY1:[WATER.MEMOS], this command sets your default to $FLOPPY1:[WATER]. If you are in $FLOPPY1:[WATER], this command sets your default to the master directory on the disk---$FLOPPY1:[000000].
$ SAVEDEF = F$ENVIRONMENT("DEFAULT")
$ SET DEFAULT [122001.JONES.APP10]
.
.
.
$ SET DEFAULT 'SAVEDEF'
#6The command procedure in this example uses the F$ENVIRONMENT lexical function to save the current default directory in the symbol named SAVEDEF. The SET DEFAULT command changes the default directory 122001.JONES.APP10. Later, the symbol SAVEDEF is used to restore the original default directory.
$ SHOW DEFAULT WORK:[TOP] $ DEFINE X WORK:[TOP.SUB1],WORK:[TOP.SUB2] $ SET DEFAULT X $ SHOW DEFAULT X:[TOP] = WORK:[TOP.SUB1] = WORK:[TOP.SUB2] $ DIRECTORY Directory WORK:[TOP.SUB1] KUDOS.TMP;1 Total of 1 file. Directory WORK:[TOP.SUB2] KUDOS.TMP;1 Total of 1 file. Grand total of 2 directories, 2 files. $ DIRECTORY [] Directory WORK:[TOP] KUDOS.TMP;1 NETSERVER.LOG;2 Total of 2 files.
In this example, the default directory is WORK:[TOP]. X is then defined to be a search list consisting of two subdirectories. When the SET DEFAULT X command is entered, the search list (X) is equated with the logical name SYS$DISK and is entered into the disk field. The subsequent SHOW DEFAULT command shows both the search list and the current default directory, followed by the expanded search list.
If a DIRECTORY command is entered, the directories searched are those contained in the logical name X. However, if the current default directory specification ([]) is explicitly entered, the current default directory, rather than SYS$DISK, is searched.
Establishes a print device or terminal as a spooled device or establishes the operational status for a device.Requires OPER (operator) privilege.
SET DEVICE device-name[:]
device-name[:]
Specifies the name of the device whose spooling or operational status is to change. The device must be a print device or a terminal if you want to change the spooling status; the device must be a disk or magnetic tape if you want to change the operational status.
When you specify the /SPOOLED qualifier, program output that uses OpenVMS Record Management Services (RMS) or file control system (FCS) and that specifies the print device name is written onto an intermediate disk rather than written directly to the print device or terminal.When you specify the /AVAILABLE, the /DUAL_PORT, or the /ERROR_LOGGING qualifier, the operational status of the drive is changed.
/AVAILABLE
/NOAVAILABLE
Controls whether the specified disk or magnetic tape is to be considered available. You must dismount the specified disk or magnetic tape before entering the SET DEVICE/[NO]AVAILABLE command. If you specify the /NOAVAILABLE qualifier, any attempt to allocate or mount the specified disk or magnetic tape is prevented. Devices are automatically set /AVAILABLE when brought online even if the device had been previously set /NOAVAILABLE./DUAL_PORT
/NODUAL_PORT
Controls whether the port seize logic in the device driver of the specified disk is to be enabled. This qualifier should be used only on disks that contain a dual port kit and have been dismounted./ERROR_LOGGING
/NOERROR_LOGGING
Controls whether device errors are logged in the error log file. When you specify the /ERROR_LOGGING qualifier, all error messages reported by the device on which error logging is enabled are recorded in the error log file. Use the SHOW DEVICE/FULL command to find out the current status./LOG
/NOLOG (default)
Controls whether log information is displayed at the terminal./SPOOLED[=(queue-name[:],intermediate-disk-name[:])]
/NOSPOOLED
Controls whether files are spooled to an intermediate disk.The queue name indicates the printer queue to which a file is queued. If a queue name is not supplied, the default is the name of either the printer or terminal.
The intermediate disk name identifies the disk to which the spooled files are written. If the intermediate disk name is not supplied, the default is SYS$DISK (the current default disk). The intermediate disk must be mounted before files can be written to it.
Once the device has been set spooled to a disk, that disk cannot be dismounted until the spooled device is set to /NOSPOOLED. All channels must be deassigned from a print device before its spooling characteristics can be changed. Also, the queue that is assigned to the device must be stopped.
#1
$ SET DEVICE/SPOOLED=(LPA0) LPA0:
#2In this example, the /SPOOLED qualifier requests that the printer queue LPA0 be spooled to an intermediate disk before files directed to the disk are printed. Because no intermediate disk was specified, the intermediate disk defaults to SYS$DISK.
$ SET DEVICE/ERROR_LOGGING DBB2:
#3The SET DEVICE command in this example requests that all device errors reported on device DBB2 be logged in the error log file.
$ SET DEVICE/NOAVAILABLE DRA0:
#4The SET DEVICE command in this example prevents any attempt to mount a disk on device DRA0.
$ SET DEVICE/DUAL_PORT DRA0:
The SET DEVICE command in this example enables the dual port seize logic in device DRA0.
Makes a disk on a local node available to all the nodes in an OpenVMS Cluster.Applies only to OpenVMS Cluster environments.
SET DEVICE/SERVED node-name$DDcu:
node-name$DDcu:
Specifies the device name of the device that you want to make available to the cluster.
The SET DEVICE/SERVED command is used in conjunction with the mass storage control protocol (MSCP) server to make a disk on a local node available to all nodes on the cluster. The local node must be a member of an OpenVMS Cluster, and the local MSCP server must have been invoked by the System Generation utility (SYSGEN).You cannot use the SET DEVICE/SERVED command under the following conditions:
- In service of a Phase II shadow set virtual unit
- On devices that are already mounted
- On system disks
- On quorum disks
The SET DEVICE/SERVED command string can be included as part of the local startup command file and entered before the Mount utility mounts the disk to be served (made available to the entire cluster).
$ SET DEVICE/SERVED DRA4:
The SET DEVICE/SERVED command in this example instructs the MSCP server to make the disk device DRA4 on your local node available to all other processors on your cluster.
Modifies the characteristics of one or more directories.See the qualifier descriptions for restrictions.
SET DIRECTORY [device-name[:]]directory-spec[,...]
device-name[:]
Specifies the device on which the directory that you want to modify is located. The device name parameter is optional.directory-spec[,...]
Specifies one or more directories to be modified. If you specify more than one directory, separate the directory specifications with commas. The asterisk (*) and the percent sign (%) wildcard characters are allowed.
/BACKUP
Modifies the time value specified with the /BEFORE or the /SINCE qualifier. The /BACKUP qualifier selects directories according to the dates of their most recent backups. This qualifier is incompatible with the /CREATED, /EXPIRED, and /MODIFIED qualifiers, which also allow you to select directories according to time attributes. If you specify none of these four time qualifiers, the default is the /CREATED qualifier./BEFORE[=time]
Selects only those directories dated prior to the specified time. You can specify time as absolute time, as a combination of absolute and delta times, or as one of the following keywords: BOOT, LOGIN, TODAY (default), TOMORROW, or YESTERDAY. Specify one of the following qualifiers with the /BEFORE qualifier to indicate the time attribute to be used as the basis for selection: /BACKUP, /CREATED (default), /EXPIRED, or /MODIFIED.For complete information on specifying time values, see the OpenVMS User's Manual or the topic SPECIFY Date_Time in online help.
/BY_OWNER[=uic]
Selects only those directories whose owner user identification code (UIC) matches the specified owner UIC. The default UIC is that of the current process.Specify the UIC by using standard UIC format as described in the OpenVMS Guide to System Security.
The /OWNER_UIC qualifier requires control access, a system UIC, or privilege.
/CONFIRM
/NOCONFIRM (default)
Controls whether a request is issued before each SET DIRECTORY operation to confirm that the operation should be performed on that file. The following responses are valid:
YES NO QUIT TRUE FALSE Ctrl/Z 1 0 ALL [Return] You can use any combination of uppercase and lowercase letters for word responses. Word responses can be abbreviated to one or more letters (for example, T, TR, or TRU for TRUE), but these abbreviations must be unique. Affirmative answers are YES, TRUE, and 1. Negative answers include: NO, FALSE, 0, and pressing the Return key. Entering QUIT or pressing Ctrl/Z indicates that you want to stop processing the command at that point. When you respond by entering ALL, the command continues to process, but no further prompts are given. If you type a response other than one of those in the list, DCL issues an error message and redisplays the prompt.
/CREATED (default)
Modifies the time value specified with the /BEFORE or the /SINCE qualifier. The /CREATED qualifier selects directories based on their dates of creation. This qualifier is incompatible with the /BACKUP, /EXPIRED, and /MODIFIED qualifiers, which also allow you to select directories according to time attributes. If you specify none of these four time qualifiers, the default is the /CREATED qualifier./EXCLUDE=(filespec[,...])
Excludes the specified directories from the SET DIRECTORY operation. You can include a directory but not a device in the file specification. The asterisk (*) and the percent sign (%) wildcard characters are allowed in the file specification. However, you cannot use relative version numbers to exclude a specific version. If you specify only one directory, you can omit the parentheses./EXPIRED
Modifies the time value specified with the /BEFORE or the /SINCE qualifier. The /EXPIRED qualifier selects directories according to their expiration dates. (The expiration date is set with the SET FILE/EXPIRATION_DATE command.) The /EXPIRED qualifier is incompatible with the /BACKUP, /CREATED, and /MODIFIED qualifiers, which also allow you to select directories according to time attributes. If you specify none of these four time qualifiers, the default is the /CREATED qualifier./LOG
/NOLOG (default)
Controls whether the system displays the directory specification of each directory that is modified as the command executes./MODIFIED
Modifies the time value specified with the /BEFORE or the /SINCE qualifier. The /MODIFIED qualifier selects directories according to the dates on which they were last modified. This qualifier is incompatible with the /BACKUP, /CREATED, and /EXPIRED qualifiers, which also allow you to select directories according to time attributes. If you specify none of these four time modifiers, the default is the /CREATED qualifier.
/OWNER_UIC[=uic]
Requires control access, a system UIC, or privilege.Specifies an owner UIC for the directory. The default UIC is that of the current process.
/SINCE[=time]
Selects only those directories dated after the specified time. You can specify time as absolute time, as a combination of absolute and delta times, or as one of the following keywords: BOOT, LOGIN, TODAY (default), TOMORROW, or YESTERDAY. Specify one of the following qualifiers with the /SINCE qualifier to indicate the time attribute to be used as the basis for selection: /BACKUP, /CREATED (default), /EXPIRED, or /MODIFIED.For complete information on specifying time values, see the OpenVMS User's Manual or the topic SPECIFY Date_Time in online help.
/VERSION_LIMIT[=n]
Specifies the total number of versions that a file in the specified directory can have. If you do not specify a version limit, a value of 0 is used, indicating that the number of versions of a file is limited only to the Files-11 architectural limit---32,767. If you change the version limit for the directory, the new value applies only to files created after the change has been made.The SET DIRECTORY version limit value refers to the number of files with the same file name and type that can exist in the directory at one time. It has no effect on the version number field of a particular file specification. Use the SET FILE command to set limits on file version numbers.
To find out the current version limit for a directory, use the DIRECTORY/FULL command on a directory file and look at the File Attributes component of the output.
#1
$ SET DIRECTORY/VERSION_LIMIT=5/CONFIRM [SMITH...]
#2The SET DIRECTORY command in this example sets a version limit of five for all files in the SMITH directory and all subdirectories of [SMITH]. The /CONFIRM qualifier requests that you confirm whether the specified directory should actually be modified. Note that it affects only the files created after the command is entered.
$ SET DIRECTORY/OWNER_UIC=[360,020] [DAVIDSON],[USERS]
The SET DIRECTORY command in this example modifies both the [DAVIDSON] and [USERS] directories, changing their owner UICs. Using the OWNER_UIC qualifier requires SYSPRV (system privilege).
Directs the output of an OpenVMS DECwindows application. Output can be directed from any processor running a DECwindows application, including workstations, to any DECwindows workstation.Both source and destination nodes must be part of the same network.
SET DISPLAY [display-device]
display-device
Specifies a logical name for the workstation display you are creating or modifying. If you are directing application output to multiple workstation displays, you can use different logical names to point to each display. If you do not specify a display-device parameter, the logical name DECW$DISPLAY is used. This means that, by default, application output will be displayed on the workstation display device referred to by DECW$DISPLAY.By entering the command SHOW DISPLAY, you can see the workstation node where applications will be displayed by default. If you specified your own logical name in the SET DISPLAY/CREATE command, include that logical name in the SHOW DISPLAY command.
DECwindows gives you the ability to run applications across a network. The SET DISPLAY command gives you the ability to perform the following tasks:
- Direct the output from applications running on your workstation to another workstation.
- Direct the output from applications running on remote processors to your workstation. Although the application runs on another processor, it looks the same as any other application running locally on your workstation.
By running applications on a remote processor for local display on your workstation monitor, you can take advantage of larger computers that might be better suited to a specific computing task. By default, applications running on your workstation are displayed on your workstation. While DECwindows must be available on both nodes, only the display node must be a workstation.
The SET DISPLAY command affects only those applications running from the process from which you enter the command. This means that although you might be running one application on your workstation and displaying it on another workstation, you can continue to run applications on your workstation for display in other windows on your workstation as illustrated in Figure DCLII-1.
Figure DCLII-1 Running Remote and Local Applications
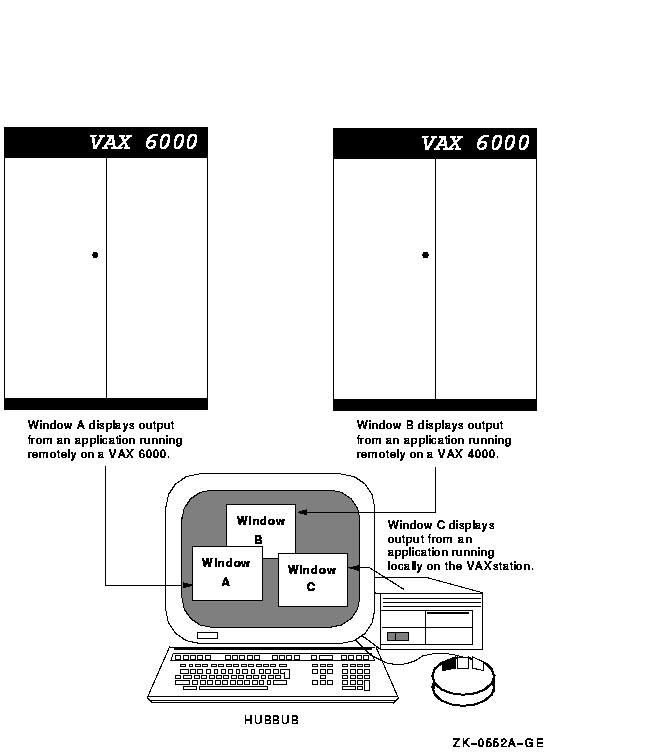
To initially direct application output to another DECwindows workstation, enter a DCL command in the following form:
SET DISPLAY/CREATE/NODE=workstation_display/TRANSPORT=DECNETSubsequently, you can redirect the display to other workstation devices by entering a DCL command in the following form:
SET DISPLAY/NODE=workstation_displayBy default, you are authorized to run applications locally on your workstation. You cannot log in to another node and direct applications to display on your workstation unless you explicitly authorize yourself to do so. This prevents unauthorized users on other nodes in the network from directing output to or receiving input from your workstation without your specific permission.
Make sure the node name you use in the SET DISPLAY command matches the node name from which you are authorized to display applications. For example, if you specify SET DISPLAY/CREATE/NODE=HUBBUB from your node ZEPHYR, and are not authorized to display applications on the DECwindows workstation HUBBUB, DECwindows reports that you are not authorized to use that display. For information about displaying applications on other workstation nodes and using the DECwindows Session Manager to authorize remote connections, see the DECwindows documentation.
Previous | Next | Contents | [Home] | [Comments] | [Ordering info] | [Help]
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
9996P041.HTM OSSG Documentation 26-NOV-1996 11:18:04.28Copyright © Digital Equipment Corporation 1996. All Rights Reserved.