![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
In this example, the first three INITIALIZE/QUEUE commands set up printer queues. Both queue LPA0_PRINT and LPB0_PRINT are set up to put a flag page before each file within a job and a trailer page after only the last page in a job. In addition, LPB0_PRINT has a minimum block size of 1000. Thus only print jobs larger than 1000 blocks can execute on that queue. SYS$PRINT is established as a generic queue that can direct jobs to either LPA0_PRINT or LPB0_PRINT. Jobs that are too small to run on LPB0_PRINT will be queued from SYS$PRINT to LPA0_PRINT.
The last INITIALIZE/QUEUE command sets up a terminal queue on TXA5. A job queued with a form that has a stock type other than the stock type of form LETTER remains pending in the queue until a form with the same stock type is mounted on the queue, or until the entry is deleted from the queue or moved to another queue. LETTER has been established at this site to indicate special letterhead paper. The block size limit is 50, indicating that this queue is reserved for jobs smaller than 51 blocks.
Reads a value from SYS$COMMAND (usually the terminal in interactive mode or the next line in the main command procedure) and assigns it to a symbol.
INQUIRE symbol-name [prompt-string]
symbol-name
Specifies a symbol consisting of 1 to 255 alphanumeric characters.prompt-string
Specifies the prompt to be displayed at the terminal when the INQUIRE command is executed. String values are automatically converted to uppercase. Also, any leading and trailing spaces and tabs are removed, and multiple spaces and tabs between characters are compressed to a single space.Enclose the prompt in quotation marks (" ") if it contains lowercase characters, punctuation, multiple blanks or tabs, or an at sign (@). To denote an actual quotation mark in a prompt-string, enclose the entire string in quotation marks and use quotation marks (" ") within the string.
When the system displays the prompt string at the terminal, it generally places a colon (:) and a space at the end of the string. (See the /PUNCTUATION qualifier.)
If you do not specify a prompt string, the command interpreter uses the symbol name to prompt for a value.
The INQUIRE command displays the prompting message to and reads the response from the input stream established when your process was created. This means that when the INQUIRE command is executed in a command procedure executed interactively, the prompting message is always displayed on the terminal, regardless of the level of nesting of command procedures. Note that input to the INQUIRE command in command procedures will be placed in the RECALL buffer.When you enter a response to the prompt string, the value is assigned as a character string to the specified symbol. Lowercase characters are automatically converted to uppercase, leading and trailing spaces and tabs are removed, and multiple spaces and tabs between characters are compressed to a single space. To prohibit conversion to uppercase and retain space and tab characters, place quotation marks around the string.
To use symbols or lexical functions when you enter a response to the prompt string, use single quotation marks (` ') to request symbol substitution.
Note that you can also use the READ command to obtain data interactively from the terminal. The READ command accepts data exactly as the user types it; characters are not automatically converted to uppercase and spaces are not compressed. However, symbols and lexical functions will not be translated even if you use apostrophes to request symbol substitution.
When an INQUIRE command is entered in a batch job, the command reads the response from the next line in the command procedure; if procedures are nested, it reads the response from the first level command procedure. If the next line in the batch job command procedure begins with a dollar sign ($), the line is interpreted as a command, not as a response to the INQUIRE command. The INQUIRE command then assigns a null string to the specified symbol, and the batch job continues processing with the command on the line following the INQUIRE command.
/GLOBAL
Specifies that the symbol be placed in the global symbol table. If you do not specify the /GLOBAL qualifier, the symbol is placed in the local symbol table./LOCAL (default)
Specifies that the symbol be placed in the local symbol table for the current command procedure./PUNCTUATION (default)
/NOPUNCTUATION
Inserts a colon and a space after the prompt when it is displayed on the terminal. To suppress the colon and space, specify the /NOPUNCTUATION qualifier.
#1
$ INQUIRE CHECK "Enter Y[ES] to continue" $ IF .NOT. CHECK THEN EXIT
#2The INQUIRE command displays the following prompting message at the terminal:
Enter Y[ES] to continue:The INQUIRE command prompts for a value, which is assigned to the symbol CHECK. The IF command tests the value assigned to the symbol CHECK. If the value assigned to CHECK is true (that is, an odd numeric value, a character string that begins with a T, t, Y, or y, or an odd numeric character string), the procedure continues executing.
If the value assigned to CHECK is false (that is, an even numeric value, a character string that begins with any letter except T, t, Y, or y, or an even numeric character string), the procedure exits.
$ INQUIRE COUNT $ IF COUNT .GT. 10 THEN GOTO SKIP . . . $ SKIP:
#3The INQUIRE command prompts for a count with the following message:
COUNT:Then the command procedure uses the value of the symbol COUNT to determine whether to execute the next sequence of commands or to transfer control to the line labeled SKIP.
$ IF P1 .EQS. "" THEN INQUIRE P1 "FILE NAME" $ FORTRAN 'P1'
The IF command checks whether a parameter was passed to the command procedure by checking if the symbol P1 is null; if it is, it means that no parameter was specified, and the INQUIRE command is issued to prompt for the parameter. If P1 was specified, the INQUIRE command is not executed, and the FORTRAN command compiles the name of the file specified as a parameter.
Invokes the Install utility, which enhances the performance of selected executable and shareable images by making them "known" to the system and assigning them appropriate attributes. For a complete description of the Install utility, see the OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual.
INSTALL [subcommand] [filespec]
Identifies the beginning of a batch job submitted through a card reader. Each batch job submitted through the system card reader must be preceded by a JOB card.JOB cannot be abbreviated.
$ JOB user-name
user-name
Identifies the user name under which the job is to be run. Specify the user name as you would during the login procedure.
The JOB card identifies the user submitting the job and is followed by a PASSWORD card giving the password. (Although the PASSWORD card is required, you do not have to use a password on the card if the account has a null password.)The user name and password are validated by the system authorization file in the same manner as they are validated in the login procedure. The process that executes the batch job is assigned the disk and directory defaults and privileges associated with the user account. If a LOGIN.COM file exists for the specified user name, it is executed at the start of the job.
The end of a batch job is signaled by the EOJ command, by an EOF card (12-11-0-1-6-7-8-9 overpunch), or by another JOB card.
/AFTER=time
Holds the job until the specified time. If the specified time has already passed, the job is queued for immediate processing.The time can be specified as either absolute time or a combination of absolute and delta times. For complete information on specifying time values, see the OpenVMS User's Manual or the topic SPECIFY Date_Time in online help.
/CHARACTERISTICS=(characteristic[,...])
Specifies one or more characteristics required for processing the job. If you specify only one characteristic, you can omit the parentheses. Codes for characteristics are installation-defined. Use the SHOW QUEUE/CHARACTERISTICS command to see which characteristics are available on your system.All the characteristics specified for the job must also be specified for the queue that will execute the job. If not, the job remains pending in the queue until the queue characteristics are changed or the entry is deleted with the DELETE/ENTRY command. Users need not specify every characteristic of a queue with the JOB command as long as the ones they specify are a subset of the characteristics set for that queue. The job also runs if no characteristics are specified.
/CLI=filename
Specifies a different command language interpreter (CLI) with which to process the job. The filename parameter specifies that the CLI be SYS$SYSTEM:filename.EXE. The default CLI is that defined in the user authorization file (UAF)./CPUTIME=n
Specifies a CPU time limit for the batch job. Time can be specified as delta time, 0, NONE, or INFINITE. (For information on specifying time values, see the OpenVMS User's Manual or the topic SPECIFY Date_Time in online help.)When you need less CPU time than authorized, use the /CPUTIME qualifier to override the base queue value established by the system manager or the value authorized in your UAF. Specify 0 or INFINITE to request an infinite amount of time. Specify NONE when you want the CPU time to default to your UAF value or the limit specified on the queue. Note that you cannot request more time than permitted by the base queue limits or your UAF.
/DELETE (default)
/NODELETE
Controls whether the batch input file is deleted after the job is processed. If you specify the /NODELETE qualifier, the file is saved in the user's default directory under the default name INPBATCH.COM. If you specify the /NAME qualifier, the file name of the batch input file is the same as the job name you supply with the /NAME qualifier./HOLD
/NOHOLD (default)
Controls whether or not the job is to be made available for immediate processing.If you specify the /HOLD qualifier, the job is not released for processing until you specifically release it with the /NOHOLD or the /RELEASE qualifier of the SET QUEUE/ENTRY command.
/KEEP
/NOKEEP (default)
Controls whether the log file is deleted after it is printed. The /NOKEEP qualifier is the default unless you specify the /NOPRINTER qualifier./LOG_FILE=filespec
/NOLOG_FILE
Controls whether a log file with the specified name is created for the job or whether a log file is created.When you use the /LOG_FILE qualifier, the system writes the log file to the file you specify. If you use the /NOLOG_FILE qualifier, no log file is created. If you specify neither form of the qualifier, the log file is written to a file in your default directory that has the same file name as the first command file in the job and a file type of LOG. Using neither the /LOG_FILE nor the /NOLOG_FILE qualifier is the default.
You can use the /LOG_FILE qualifier to specify that the log file be written to a different device. Logical names that occur in the file specification are translated at the time the job is submitted. The process executing the batch job must have access to the device on which the log file will reside.
If you omit the /LOG_FILE qualifier and specify the /NAME qualifier, the log file is written to a file having the same file name as that specified by the /NAME qualifier and the file type LOG.
/NAME=job-name
Specifies a string to be used as the job name and as the file name for both the batch job log file and the command file. The job name must be 1 to 39 alphanumeric characters and must be a valid file name. The default log file name is INPBATCH.LOG; the default command file name is INPBATCH.COM./NOTIFY
/NONOTIFY (default)
Controls whether a message is broadcast to any terminal at which you are logged in, notifying you when your job completes or aborts./PARAMETERS=(parameter[,...])
Specifies 1 to 8 optional parameters that can be passed to the command procedure. The parameters define values to be equated to the symbols P1 to P8 in the batch job. The symbols are local to the specified command procedure.If you specify only one parameter, you can omit the parentheses.
The commas (,) delimit individual parameters. If the parameter contains any spaces, special characters or delimiters, or lowercase characters, enclose it in quotation marks (" "). Individual parameters cannot exceed 255 characters.
/PRINTER=queue-name
/NOPRINTER
Controls whether the job log file is queued to the specified queue for printing when the job is complete. The default print queue for the log file is SYS$PRINT.If you specify the /NOPRINTER qualifier, the /KEEP qualifier is assumed.
/PRIORITY=n
Requires OPER (operator) or ALTPRI (alter priority) privilege to raise the priority above the value of the system parameter MAXQUEPRI.Specifies the job scheduling priority for the specified job. The value of n is an integer from 0 to 255, where 0 is the lowest priority and 255 is the highest.
The default value for the /PRIORITY qualifier is the value of the system parameter DEFQUEPRI. No privilege is needed to set the priority lower than the MAXQUEPRI value.
The /PRIORITY qualifier has no effect on the process priority. The queue establishes the process priority.
/QUEUE=queue-name[:]
Specifies the name of the batch queue in which the job is to be entered. If you do not specify the /QUEUE qualifier, the job is placed in the default system batch job queue, SYS$BATCH./RESTART
/NORESTART (default)
Specifies whether the job restarts after a system failure or a STOP/QUEUE/REQUEUE command./TRAILING_BLANKS (default)
/NOTRAILING_BLANKS
Controls whether input cards in the card deck are read in card image form or input records are truncated at the last nonblank character. By default, the system does not remove trailing blanks from records read through the card reader. Use the /NOTRAILING_BLANKS qualifier to request that input records be truncated./WSDEFAULT=n
Defines a working set default for the batch job; the /WSDEFAULT qualifier overrides the working set size specified in the user authorization file (UAF).Specify the value of n as a number of 512-byte pagelets on Alpha or 512-byte pages on VAX. Note that OpenVMS rounds this value up to the nearest CPU-specific page so that actual amount of physical memory allowed may be larger than the specified amount on Alpha. For further information, see the OpenVMS System Manager's Manual. The value n can be any integer from 1 to 65,535, 0, or the keyword NONE.
Use this qualifier to impose a value lower than the base queue value established by the system manager or lower than the value authorized in your UAF. A value of 0 or the keyword NONE sets the default value to the value specified either in your UAF or by the working set quota established for the queue. You cannot request a value higher than your default.
/WSEXTENT=n
Defines a working set extent for the batch job; the /WSEXTENT qualifier overrides the working set extent in the UAF.Specify the value of n as a number of 512-byte pagelets on Alpha or 512-byte pages on VAX. Note that OpenVMS rounds this value up to the nearest CPU-specific page so that actual amount of physical memory allowed may be larger than the specified amount on Alpha. For further information, see the OpenVMS System Manager's Manual. The value n can be any integer from 1 to 65,535, 0, or the keyword NONE.
To impose a lower value, use this qualifier to override the base queue value established by the system manager rather than the value authorized in your UAF. A value of 0 or the keyword NONE sets the default value either to the value specified in the UAF or working set extent established for the queue. You cannot request a value higher than your default.
/WSQUOTA=n
Defines the maximum working set size (working set quota) for the batch job; the /WSQUOTA qualifier overrides the value in the UAF.Specify the value of n as a number of 512-byte pagelets on Alpha or 512-byte pages on VAX. Note that OpenVMS rounds this value up to the nearest CPU-specific page so that actual amount of physical memory allowed may be larger than the specified amount on Alpha. For further information, see the OpenVMS System Manager's Manual. The value n can be any integer from 1 to 65,535, 0, or the keyword NONE.
Use this qualifier to impose a value lower than the base queue value established by the system manager or lower than the value authorized in your UAF. Specify 0 or NONE if you want the working set quota defaulted to either your UAF value or the working set quota specified on the queue. You cannot request a value higher than your default.
#1
#2
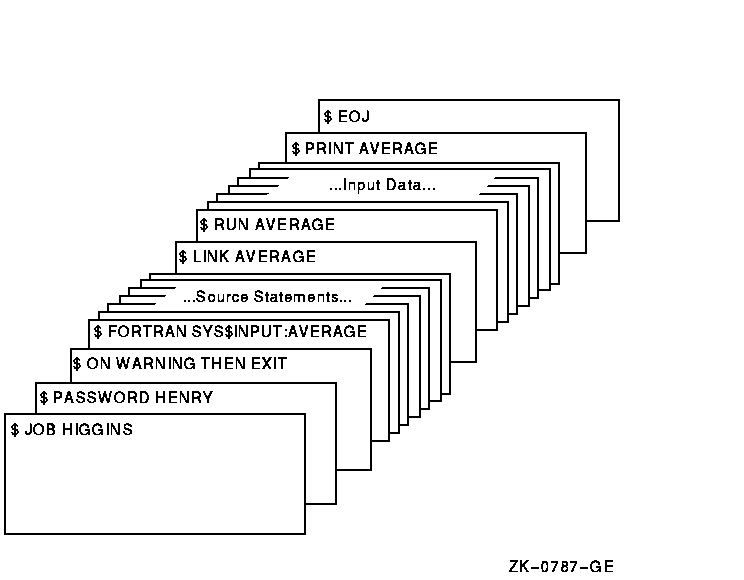
The JOB and PASSWORD cards identify and authorize the user HIGGINS to enter batch jobs. The command stream consists of a FORTRAN command and FORTRAN source statements to be compiled. The file name AVERAGE following the device name SYS$INPUT provides the compiler with a file name for the object and listing files. The output files are cataloged in user HIGGINS's default directory.
If the compilation is successful, the LINK command creates an executable image and the RUN command executes it. Input for the program follows the RUN command in the command stream. The last command in the job prints the program listing. The last card in the deck contains the EOJ (end of job) command.
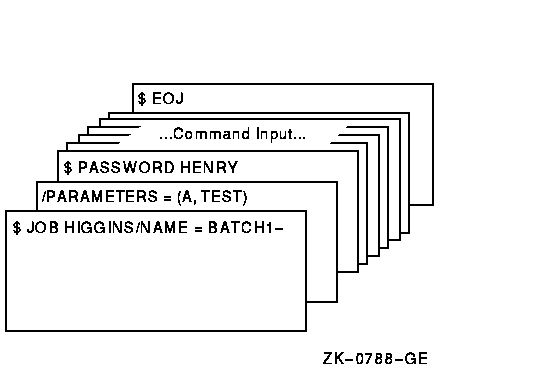
The /NAME qualifier on the JOB card specifies a name for the batch job. When the job completes, the printed log file is identified as BATCH1.LOG. The JOB command is continued onto a second card with the continuation character (-). The /PARAMETERS qualifier defines P1 as A and P2 as TEST. The last card in the deck contains the EOJ (end of job) command.
A set of functions that return information about character strings and attributes of the current process.
The command language includes constructs, called lexical functions, that return information about the current process and about arithmetic and string expressions. The functions are called lexical functions because the command interpreter evaluates them during the command input scanning (or lexical processing) phase of command processing.You can use lexical functions in any context in which you normally use symbols or expressions. In command procedures, you can use lexical functions to translate logical names, to perform character string manipulations, and to determine the current processing mode of the procedure.
The general format of a lexical function is as follows:
F$function-name([args,...])where:For more information on specifying expressions, see the OpenVMS User's Manual.
F$ Indicates that what follows is a lexical function. function-name A keyword specifying the function to be evaluated. Function names can be truncated to any unique abbreviation. () Enclose function arguments, if any. The parentheses are required for all functions, including functions that do not accept any arguments. args,... Specify arguments for the function, if any, using integer or character string expressions. Table DCLI-3 lists each lexical function and briefly describes the information that each function returns. A detailed description of each function, including examples, is given in the following pages.
Table DCLI-3 Summary of Lexical Functions Function Description F$CONTEXT Specifies selection criteria for use with the F$PID function. F$CSID Returns an OpenVMS Cluster identification number and updates the context symbol to point to the current position in the system's cluster node list. F$CVSI Extracts bit fields from character string data and converts the result, as a signed value, to an integer. F$CVTIME Retrieves information about an absolute, combination, or delta time string. F$CVUI Extracts bit fields from character string data and converts the result, as an unsigned value, to an integer. F$DEVICE Returns device names of all devices on a system that meet the specified selection criteria. F$DIRECTORY Returns the current default directory name string. F$EDIT Edits a character string based on the edits specified. F$ELEMENT Extracts an element from a string in which the elements are separated by a specified delimiter. F$ENVIRONMENT Obtains information about the DCL command environment. F$EXTRACT Extracts a substring from a character string expression. F$FAO Invokes the $FAO system service to convert the specified control string to a formatted ASCII output string. F$FILE_ATTRIBUTES Returns attribute information for a specified file. F$GETDVI Invokes the $GETDVI system service to return a specified item of information for a specified device. F$GETJPI Invokes the $GETJPI system service to return accounting, status, and identification information for a process. F$GETQUI Invokes the $GETQUI system service to return information about queues, batch and print jobs currently in those queues, form definitions, and characteristic definitions kept in the queue database. +On VAX, also returns information about a queue manager.
F$GETSYI Invokes the $GETSYI system service to return status and identification information about the local system, or about a node in the local cluster, if your system is part of a cluster. F$IDENTIFIER Converts an identifier in named format to its integer equivalent, or vice versa. F$INTEGER Returns the integer equivalent of the result of the specified expression. F$LENGTH Returns the length of a specified string. F$LOCATE Locates a character or character substring within a string and returns its offset within the string. F$MESSAGE Returns the message text associated with a specified system status code value. F$MODE Shows the mode in which a process is executing. F$PARSE Invokes the $PARSE RMS service to parse a file specification and return either the expanded file specification or the particular file specification field that you request. F$PID For each invocation, returns the next process identification number in sequence. F$PRIVILEGE Returns a value of TRUE or FALSE depending on whether your current process privileges match the privileges listed in the argument. F$PROCESS Returns the current process name string. F$SEARCH Invokes the $SEARCH RMS service to search a directory file, and returns the full file specification for a file you name. F$SETPRV Sets the specified privileges and returns a list of keywords indicating the previous state of these privileges for the current process. F$STRING Returns the string equivalent of the result of the specified expression. F$TIME Returns the current date and time of day, in the format dd-mmm-yyyy hh:mm:ss.cc. F$TRNLNM Translates a logical name and returns the equivalence name string or the requested attributes of the logical name. F$TYPE Determines the data type of a symbol. F$USER Returns the current user identification code (UIC). F$VERIFY Returns the integer 1 if command procedure verification is set on; returns the integer 0 if command procedure verification is set off. The F$VERIFY function also can set new verification states.
+VAX specific
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
9996P021.HTM OSSG Documentation 26-NOV-1996 11:17:25.79
Copyright © Digital Equipment Corporation 1996. All Rights Reserved.