![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
DECnet-Plus
Network Control Language Reference
Previous
| Contents
Arguments:
|
reason
|
Specifies which characteristics have not been specified.
|
|
|
dte class
|
The DTE class characteristic has not been specified.
|
|
|
filters
|
The filters characteristic has not been specified.
|
For delete:
has active connections
One or more active connections exist on this client.
27.3 x25 relay pvc
An x25 relay pvc entity provides a set of default values to be
used to establish a connection to a client over a permanent virtual
circuit (PVC).
add [node node-id] x25 relay pvc
pvc-name rights identifiers simple-name
create [node node-id] x25 relay pvc
pvc-name type string
delete [node node-id] x25 relay pvc
pvc-name
disable [node node-id] x25 relay pvc
pvc-name
enable [node node-id] x25 relay pvc
pvc-name
remove [node node-id] x25 relay pvc
pvc-name rights identifiers simple-name
set [node node-id] x25 relay pvc
pvc-name {local pvc pvc-name | remote dte class
simple-name (connector nodes only) | relayed pvc
relayed-pvc-name | retry limit integer (connector
nodes only) | retry timer integer (connector nodes only) |
rights identifiers simple-name }
show [node node-id] x25 relay pvc
pvc-name [all [attributes] | all characteristics | all
counters | all identifiers | all status ]
27.3.1 Arguments
type string
Type of PVC, either local or remote.
27.3.2 Characteristic Attributes
local PVC
|
Default: No PVC name
|
Value: Simple-name
|
Name of the PVC entity that represents the local end of the connection.
remote dte class
|
Default: No dte class
|
Value: Simple-name
|
DTE class to be used when setting up the remote end of the connection.
It is only specified if the relayed PVC does not reside on the local
system. This attribute is only applicable to connector nodes, and will
not be visible in other implementations.
relayed PVC
|
Default: No PVC name
|
Value: Simple-name
|
Name of the PVC entity that represents the relayed end of the
connection.
retry limit
|
Default: 10
|
Value: 0--65535
|
Number of attempts that will be made to set up the PVC connection
following the failure of an enable command. This attribute is
only applicable to connector nodes, and will not be visible in other
implementations.
retry timer
|
Default: 60
|
Value: 1--65535
|
Interval, in seconds, between retries. This attribute is only
applicable to connector nodes, and will not be visible in other
implementations.
rights identifiers
|
Default: No rights identifiers
|
Value: Set of simple-names
|
Rights identifiers possessed by this entity. These rights are used to
access the local PVC and relayed PVC if it resides on the local system.
27.3.3 Counter Attributes
connections made
Number of successful connections made by this entity.
creation time
Time at which this entity was created.
times connections lost
Number of times that a successfully established PVC connection has been
abnormally terminated.
times retry limit exceeded
Number of times that the retry limit has been reached when trying to
set up a PVC connection.
27.3.4 Identifier Attributes
name
Simple name assigned to the PVC when it is created.
27.3.5 Status Attribute
state
State of the x25 relay pvc entity.
|
failed
|
The retry mechanism has failed to set up the connection.
|
|
off
|
The PVC is disabled.
|
|
on
|
The PVC is enabled.
|
|
retrying
|
The Retry timer is running.
|
uid
Entity's unique identifier, which is generated when the entity is
created.
27.3.6 Event Messages
connection lost
Generated when a successfully established PVC connection fails for some
other reason than being disabled.
Argument:
|
reason
|
Error returned by the X.25 Access module when notifying the X.25 Relay
module of the disconnection.
|
retry limit exceeded
Generated when an attempt to set up a PVC connection fails.
Arguments:
|
local pvc status
|
State of the local end of the PVC connection.
|
|
relayed pvc status
|
State of the relayed end of the PVC connection.
|
27.3.7 Exceptions
For enable:
insufficient information
One or more characteristics have not been specified.
Arguments:
|
reason
|
Specifies which characteristics have not been specified.
|
|
|
local pvc
|
The
local pvc characteristic has not been specified.
|
|
|
relayed pvc
|
The
relayed pvc characteristic has not been specified.
|
|
|
remote dte class
|
The
remote dte class characteristic has not been specified.
|
dte class not type remote
The DTE class specified is not of type remote (connector nodes only).
pvc error
An error has occurred attempting to open either the local or the
relayed PVC.
Arguments:
|
reason
|
Specifies the reason for failing to open the local or relayed pvcs.
|
|
|
local pvc in use
|
The specified
local pvc already has a client.
|
|
|
relayed pvc in use
|
The specified
relayed pvc already has a client.
|
|
|
local pvc security block
|
Attempt to open the
local pvc failed for security reasons.
|
|
|
relayed pvc security block
|
Attempt to open the
relayed pvc failed for security reasons.
|
|
|
no such local pvc
|
The specified
local pvc does not exist.
|
|
|
no such relayed pvc
|
The specified
relayed pvc does not exist.
|
Chapter 28
X.25 Server Module
This chapter describes all the commands you can use to manage the
entities that constitute the X.25 Server module. The X.25 Server module
resides in the Application layer of the Digital Network Architecture
(DNA). This module interfaces with the X.25 Access module to listen for
incoming calls for X.25 Client systems, and to make outgoing calls on
behalf of X.25 clients.
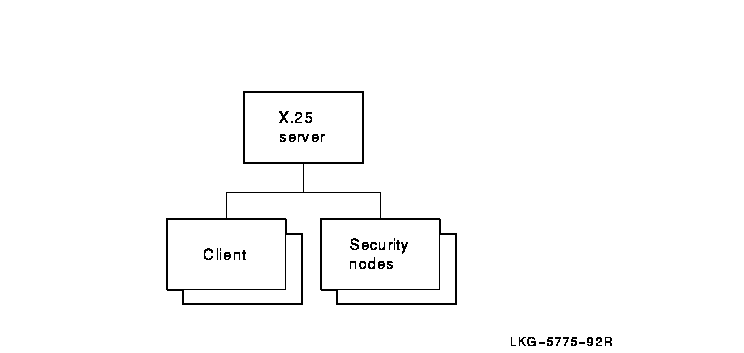
Figure 28-1 shows the hierarchical relationship of the entities that
constitute the X.25 Server module.
Figure 28-1 Hierarchy of X.25 Server Module Entities
28.1 x25 server
The x25 server entity represents the X.25 server that runs on
a gateway system. The X.25 server serves X.25 clients on accessing
systems, providing X.25 access to systems that do not have a direct
connection to a PSDN.
create [node node-id] x25 server {incoming
session template simple-name | maximum session connections
number ]
delete [node node-id] x25 server
disable [node node-id] x25 server
enable [node node-id] x25 server
show [node node-id] x25 server [all
[attributes] | all characteristics | all counters | all status ]
)
28.1.1 Arguments
incoming session template (Digital UNIX)
Optional argument that specifies the Session Control template used to
filter incoming Session Control connection requests.
maximum session connections
Optional argument that specifies the number of incoming and outgoing
connections that may be supported concurrently.
28.1.2 Characteristic Attributes
incoming session template (Digital UNIX)
The Session Control template specified on an OpenIncoming
invocation at the end user Session Control interface. You cannot modify
this characteristic.
maximum
session connections
|
Default: 512
|
Value: [1..65535]
|
Maximum number of Session Control connections with clients that the
entity can support. This includes both incoming and outgoing
connections. You cannot modify this characteristic.
version
|
Default: Current version number
|
|
Version number of the X.25 Gateway Access Protocol (GAP) to which the
implementation conforms. You cannot modify this characteristic.
28.1.3 Counter Attributes
connection attempts failed
Number of Session Control connection requests to clients that have
failed, due either to exceeding the maximum number of connections or
rejection by X.25 clients in accessing systems.
creation time
Time at which this entity was created.
times session control unavailable
Number of times the Session Control unavailable event was
raised.
28.1.4 Status Attributes
active inbound session connections
Current number of active inbound Session Control connections with
clients.
active outbound session connections
Current number of active outbound Session Control connections with
clients.
state
Current state of the x25 server entity.
|
off
|
The
x25 server entity is disabled.
|
|
on
|
The
x25 server entity is enabled.
|
uid
Specifies the entity's unique identifier, which is generated when the
entity is created.
28.1.5 Event Messages
client connect failed
Generated when the X.25 server is unable to make a connection to an
X.25 client (or to any of an alternative set of X.25 clients if the
service nodes characteristic is supported for the x25
server client entity).
Arguments:
|
client
|
Full name of the
x25 server client entity.
|
|
nodes
|
The node or set of nodes associated with the
x25 server client entity.
|
|
application
|
Application type in the client entity.
|
session control unavailable
Generated when the X.25 server detects the absence of the Session
Control module or when it detects that the state of Session Control is
not set to on.
Arguments:
|
module extent
|
true or
false. Set to
false when the X.25 server cannot detect the presence of
Session Control. When set to
false, the value of the
session control port state argument is always
null.
|
|
session control port state
|
null,
off,
shut, or
restricted. Reflects the state returned by the port state end
user interface when the value of the module
extent argument is set
true.
|
28.1.6 Exceptions
For enable:
session control no resources
The Session Control module does not have sufficient resources to handle
the call.
session control unavailable
The Session Control module either does not exist or is disabled.
28.2 x25 server client
An x25 server client entity provides a set of default values
to be used to establish a Session Control connection with an X.25
client when an incoming call arrives for that client. You should create
an x25 server client entity for each X.25 client with which
the gateway system is associated.
add [node node-id] x25 server client
simple-name filters [set]
create [node node-id] x25 server client
simple-name
delete [node node-id] x25 server client
simple-name
disable [node node-id] x25 server client
simple-name
enable [node node-id] x25 server client
simple-name
remove [node node-id] x25 server client
simple-name filters [set]
set [node node-id] x25 server client
simple-name {account string (OpenVMS) | application
end-user-specification | destination fullname
(OpenVMS) | filters [set] | node fullname | outgoing session
template simple-name (OpenVMS) | password string |
service nodes [set] | user string }
show [node node-id] x25 server client
simple-name [all [attributes] | all characteristics | all
identifiers | all status ]
28.2.1 Characteristic Attributes
account (OpenVMS)
|
Default: No service/account data
|
Value: String
|
Default service or account data to be used when connecting to the
system hosting the X.25 client.
application
|
Default: 36
|
Value: End-user-specification
|
Address information used by the destination Session Control module to
select the X.25 client that will receive the connection request.
destination (OpenVMS)
|
Default: No client name
|
Value: Fullname
|
Name of the X.25 client to which a connection is to be made when
delivering a "filtered" call.
filters
|
Default: No default
|
Value: Set of simple-names
|
Set of filters to be used by the server to filter calls for this X.25
client. Each name is the name of an x25 access filter entity.
node
|
Default: No node name
|
Value: Fullname
|
Name of the node that hosts the X.25 client to which connection is to
be made. This characteristic is supported only if the service
nodes characteristic is not supported.
outgoing session template (OpenVMS)
|
Default: Default template
|
Value: Simple-name
|
Transport template to be used by the X.25 server to set up a Session
Control connection to the X.25 client. The name is the name of an
osi transport template entity.
password
|
Default: No password
|
Value: String
|
Default password to be used for verification when connecting to the
system that hosts the X.25 client. You cannot display this
characteristic with the show command.
service nodes
|
Default: Empty set
|
Value: Set of candidate records
|
Set of nodes that host the x25 client entities to which
connections can be made.
user
|
Default: No user id
|
Value: String
|
Default user identification to be used in access verification when
connecting to the system that hosts the X.25 client.
28.2.2 Identifier Attributes
name
Simple name assigned to the client when it is created.
28.2.3 Status Attributes
state
Status of the x25 server client entity.
|
off
|
The
x25 server client entity is disabled.
|
|
on
|
The
x25 server client entity is enabled.
|
28.2.4 Exception Messages
For enable:
filter in error
One or more of the specified filters does not exist, or is in use.
filter in use
One or more of the specified filters is already being used by another
client.
insufficient information
Before enabling the client you must ensure that the following
characteristics have been given values of: application, filters,
nodes.
28.3 x25 server security nodes
An x25 server security nodes entity defines the set of rights
identifiers associated with calls issued by the X.25 Server module (on
behalf of the X.25 Client module at an accessing system) to the X.25
Access module at the gateway system. These rights identifiers are used
when making access control checks on the DTE class specified when a
call is made.
add [node node-id] x25 server security nodes
simple-name {nodes [set] | rights identifiers [set] }
create [node node-id] x25 server security
nodes simple-name
delete [node node-id] x25 server security
nodes simple-name
remove [node node-id] x25 server security
nodes simple-name {nodes [set] | rights identifiers [set] }
set [node node-id] x25 server security nodes
simple-name {nodes [set] | rights identifiers [set] }
show [node node-id] x25 server security nodes
simple-name [all [attributes] | all characteristics | all
counters | all identifiers | all status ]
28.3.1 Characteristic Attributes
nodes
|
Default: No node names
|
Value: Set of full names
|
DNS full names of accessing systems, or the wildcard full name.
rights identifiers
|
Default: No rights identifiers
|
Value: Set of simple-names
|
Set of rights identifiers to be associated with the set of nodes named
in the nodes characteristic for purposes of access control to
DTE classes at the gateway node.
28.3.2 Counter Attributes
creation time
Time at which this entity was created.
outgoing calls blocked
Number of times that an attempt to establish a call or use a PVC has
failed for security reasons.
28.3.3 Identifier Attributes
name
Simple name assigned to the security node when it is created.
28.3.4 Status Attributes
uid
Entity's unique identifier, which is generated when the entity is
created.
Appendix A
Interpreting NCL Error Messages
This appendix offers general guidelines for interpreting any NCL error
messages you may receive.
A.1 How Errors Are Reported
NCL uses error messages to report and describe errors that occur in
both the user interface and the entity.
For some errors, only one message is returned, even if a group of
entities was targeted by the directive. The requested entity name is
returned as part of the exception if specified. For other errors, if
the entities determine that none of the target entities can perform the
directive, the entity may return a single exception reply containing
the requested entity name. The entity may return an exception or
response for each target entity. In this case, the entity name returned
is that of the entity performing the directive. The entity may stop
forwarding the directive to further entities when an error occurs,
providing it responds for each entity performing the directive.
A.2 Standard Format for NCL Error Messages
This section describes the standard format for all NCL error messages.
For example:
# ncl set routing phaseiv prefix = 49:: (1)
Node 0 Routing (2)
AT 1995-09-08-13:28:43.800-04:00I0.178 (3)
FAILED IN DIRECTIVE: Set (4)
DUE TO: Attribute Could Not Be Modified Due To Constraint (5)
PhaseIV Prefix = /49 (6)
State = On
-
The NCL command in this example attempts to set the current node's
routing Phase IV prefix to 49.
-
This field includes the entity instance, which describes the specific
entity of the directive. In this example, the entity was the Routing
layer of the current node.
-
Each message includes a timestamp. The timestamp is taken by the entity
as soon as possible after the error occurs. Often this field includes
the note, "no timestamp from agent," indicating that the entity did not
supply the timestamp.
-
The FAILED IN DIRECTIVE field indicates the directive (or command
verb) that caused the error. In this example, the change could
not be set.
-
The DUE TO field lists the key phrase of the error message. When you
look through specific error messages, look for this key phrase. In this
example, "Attribute Could Not Be Modified Due To Constraint" indicates
that the command somehow violated a constraint built into the command.
Certain error messages also contain a secondary DUE TO line
pertaining to a particular attribute (or qualifier).
-
This describes the reason for the error. In this example, you cannot
set the Phase IV prefix to 49 because the Routing layer is enabled
(State = On). You must disable the Routing layer before attempting to
change the Phase IV prefix.
A.3 NCL Error Messages for Digital UNIX
The following is an alphabetized list of the NCL error messages. The
bolded key phrase appears in the DUE TO field of the error message
display.
- Access Denied
In general, you are only allowed to use show commands using
NCL. If you wish to issue commands such as set, add, remove,
and action, you must gain privileged access to the entities
you wish to manage.
When managing entities on the local Digital
UNIX system, you need only become a superuser before running NCL.
When managing remote entities, you need to connect to the remote
system as a privileged user. This can be done in one of two ways:
- Append the user name and password to the remote node name/address.
- Use the BY clause to specify the user name and password.
The latter form is a "portable" way to pass this information in any
NCL product, and is, therefore, recommended. See the relevant sections
on how to pass access control information.
- Attribute Can Only Be Modified, Not Read
Some attributes, such as passwords, are not readable for security
reasons, and may only be set. Of course, only a manager with privileged
access may set them (see Access Denied error).
- Attribute Can Only Be Read, Not Modified
The NCL user cannot modify counters, status, identifiers, and
some characteristic attributes. Characteristic attributes that
cannot be set are virtually constant over the lifetime of the entity
instance. The entity instance itself, however, can change status
and counter attributes. System managers can change status
attributes indirectly by using directives, such as enable.
- Attribute Could Not Be Modified Due to Constraint
Violation
Due to the state of the entity, it would not accept one of the
attribute values in a set, add, or remove command.
The entity indicates the violated constraint by returning the value of
one or more attributes. For example, if you attempt to issue the
command:
# ncl set routing inactive selector 34
and receive the following error:
Node 0 Routing
AT 1995-08-25-17:11:24.889-05:00I0.144
FAILED IN DIRECTIVE: Set
DUE TO: Attribute Could Not Be Modified Due To Constraint Violation
Inactive Selector = 34
State = = On
The display means this command could not be performed because the
state attribute was equal to on.
- Connection to Remote Entity Ended
The remote system has terminated the Session layer connection with NCL,
due to an unforeseen problem in executing the directive. This can also
mean that the system crashed between the time of the error and the time
of the previous NCL command. NCL maintains a Session layer connection
with the remote system until you issue a command to a different remote
system or exit NCL. If this kind of error occurs where the remote
system is a Digital UNIX system, the syslog(8) file may
contain additional information about the cause of the problem.
- Could Not Get All Requested Attributes
This error message actually states a partial success. The remote system
returns all attributes for which it has a value, and NCL displays the
attributes requested. If the remote system did not return an attribute
value for one of these attributes, NCL displays an appropriate error
message in its place. The possible per-attribute errors are:
- The entity instance does not currently have this attribute
- Attribute can only be modified, not read
- Access denied
- Duplicate attribute
- No such attribute group
- Could Not Modify Specified Attributes
When either NCL or the remote system detects a problem with any of the
attribute values in a set, add or remove command, the
command will not be executed. In other words, set, add and
remove commands cannot succeed partially for any single entity
instance. NCL rejects erroneous commands, identifies the first
erroneous attribute value encountered, and specifies the reason the
value was rejected. The possible reasons for rejection are:
- Entity instance does not currently have this attribute
- Attribute can only be read, not modified
- Access denied
- Invalid attribute value
- Duplicate attribute
- Entity Instance Does Not Support This Action
The directive (or verb) is known to both NCL and the remote system;
however, the entity management software does not implement it. Some
implementations may not support all of the action directives in the
entity specifications, but all implementations must support the
set, show, add, and remove directives.
- Entity Instance Does Not Currently Have This
Attribute
The value of a requested attribute is currently undefined within the
specified entity instance. Note that NCL knows about the attribute and,
therefore, by implication the remote system should as well. However, in
practice, there are two valid reasons why the remote system might not
have a defined value for the attribute:
- Attribute is not supported by this particular entity implementation.
- Attribute is not used by the entity in its current state.
An entity class represents the complete set of capabilities for all
known instances of the class. However, a software implementation may
not implement all of these capabilities for any of the following
reasons:
- Software is out of date and does not implement newer attributes.
- Software is not intended to provide a full-function entity.
For example, the Digital UNIX software does not perform inter-area
routing, even though inter-area routing is part of the DECnet-Plus
routing architecture. So a request to see an inter-area routing
attribute will fail when issued to a Digital UNIX routing entity
instance.
You should be able to tell whether an attribute should be
present by examining the values of other attributes.
This error
does not happen when the NCL user requests to see the values of an
attribute group, such as all characteristics. In this latter
case, the user sees only those values that the remote entity returns.
- Error Specific to This Entity's Class
The entity management software attempted to carry out the specified
command, and encountered an error specific to the verb and entity
class. See the entity documentation for a description of what these
errors are and what they mean.
- Failed to Get Connection to Remote Entity
The NCL was unable to get a Session layer connection to the remote
system. This kind of error usually means that the remote system is not
reachable, does not exist, or is not currently accepting connections
for network management. Issue the dls nodename::
command to further diagnose the problem.
- Invalid Use of Wildcarding
The entity name in the directive includes unsupported wildcarding. This
message includes the entity class, instance requested, and the reason
the request was invalid:
- Invalid create with wildcard
- Invalid directive for wildcarded class
- An attribute requested is not a universal group
- Filter used with wildcard class
- Wildcarding not at lowest level of entity name
- Invalid Attribute Value
The result of an attempt to modify an entity's attribute to a value
that is not allowed for that attribute. This error is particularly
likely to occur when the attribute value is valid for some members of
the entity class, but not for this particular entity instance.
Implementations of an entity may allow only a subset of the attribute's
specified values to be actually used.
- Invalid Argument Value
This error may occur if the NCL user specifies an invalid value for an
action directive's argument. Usually this error means that the
argument, while syntactically correct, was rejected by this particular
entity implementation for reasons that may be implementation specific.
This message includes the class, instance, and UID (or null UID) of the
entity that failed.
- Invalid Filter
The filter supplied was invalid for one or more entities named. This
message includes the entity class, instance, filter requested, and the
reason the filter was invalid:
- Access denied
- No such attribute
- Invalid value
- Invalid relational operator for filter attribute's data type
- Write-only attribute
- Filter used with create
- Management Protocol Version Is Not Supported
This error means the remote system is not running a management protocol
compatible with NCL. Usually this means that the remote system is a
Phase IV DECnet node that uses NICE (Network Information and Control
Exchange), not CMIP, as its management protocol. Use the ncl ncp
tell syntax to remotely manage such a node.
- Modify List Error
Applies only to all modify directives, and indicates that the entity
encountered an error while attempting to modify one or more attributes.
This message includes the class, instance, UID (or null UID) of the
entity that failed, and the status of each attribute in the request.
The status indicates whether the attribute could be modified as
requested, and if not, the reason why:
- Access denied
- No such attribute
- Invalid attribute value
- Read-only attribute
- Duplicate attribute
- No Such Action
The action is not supported by this entity. This message includes the
entity class, instance, and the unsupported action code.
- No Such Argument
One or more arguments supplied for the action are not supported by this
entity. This message includes the entity class, instance, UID (or null
UID) of the entity that failed, the action code, and a list of
arguments not supported.
- No Such Entity Class Is Known to the Remote Node
The remote system's management software does not recognize the entity
class specified. This could happen if the remote node's software was
released before the entity class was defined.
- No Such Entity Instance Exists
The remote system does not know of a particular entity with the
identifier (or name) used to select it. Replace the instance identifier
with a wildcard (*) to view all known instances. Show all the circuit
subentities of the routing entity to help determine what the
possible instance names are. Do this with the following command:
ncl> show routing circuit * [Return]
Remember that you (usually) cannot abbreviate instance identifiers,
unlike entity class and attribute names.
- No Resource Available
The entity management software was unable to carry out the command
because of a lack of some essential resource. Frequently that resource
is dynamic memory. Because this kind of error is so implementation
specific, the details of a particular error cannot be entirely
presented by NCL. If the remote system is Digital UNIX, more
information can be gained by looking at the syslog(8) file.
This message includes the class, instance, and UID (or null UID) of the
entity that failed.
- Relational Operator Not Valid for Filter Attribute's Data
Type
A specified filter attribute and relational operator do not make sense
together. Some data types do not support all of the relational (or
comparison) operators. For example, the following comparisons do not
make sense:
(TRUE < FALSE),
(number=25 <= name=fred).
- Required Argument Omitted
One or more required arguments of an action were omitted from the
argument list. This message includes the class, instance, UID (or null
UID) of the failed entity, the action code, and a list of arguments
that were omitted.
- Target Implementation Does Not Support This Entity
Class
The entity class is known to both NCL and the remote system; however,
the remote system cannot perform directives for this entity class. This
error frequently indicates that the software that implements the entity
is not (completely) installed on the target system. This message
includes the entity class and instance requested.
- Unrecognized Node Name
The NCL could not connect to the remote system because the node name
(the node's identifier attribute) was not recognized by the local
Digital UNIX system. Connect to the remote system using a different
application such as dlsnodename::, to further
diagnose the problem. Ensure that the remote system's name is in the
namespace. You can also enter an address for the remote system into
NCL, bypassing the name-to-address lookup feature of Digital UNIX.
- Unable to Decode Received Management PDU
The remote system sent a management protocol message that NCL was
unable to interpret. This is a software problem, usually caused by an
interoperability problem between different CMIP implementations. This
should not occur at all between properly tested implementations.
Determine the software implementation and version at both ends before
contacting your Digital Support representative.
A.4 NCL Error Messages for OpenVMS
This section describes NCL error messages that can be returned on a
command. Command-specific exception messages are described with
individual command descriptions.
ACCESSSTRINGTOOLLONG, access control string too long
Explanation: The username/password/account string is
longer than 255 characters.
User Action: Use shorter username/password/account
string.
ALLOCFAILURE, memory allocation failure
Explanation: NCL could not allocate the required
memory.
User Action: Increase the users' quotas or the values
for the system generation parameters to allow a larger virtual image.
The most likely parameters are BYTLIM, VIRTUALPAGENT, or MAXBUF.
AMBIGUOUS, ambiguous command
Explanation: A keyword in the command is not specified
with enough characters to distinguish it from another keyword
acceptable in this context. The offending keyword is displayed between
backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command using enough
characters to uniquely identify all keywords.
BADNCLENVIRONMENT, syntax error interpreting the NCL$ENVIRONMENT
variable
Explanation: The NCL$ENVIRONMENT logical name could
not be parsed because of a syntax error in its translation.
User Action: Redefine the NCL$ENVIRONMENT logical name
to correct the syntax.
BADPARSERFIELD, unknown datatype or corrupt parse tables
Explanation: The parser encountered corrupted parse
tables (NCL$GLOBALSECTION) or an unknown data type.
User Action: (1) If the NCL$GLOBALSECTION file is
fragmented (DUMP/HEADER/BLOCK=COUNT:0), try making it contiguous
(COPY/CONTIG). (2) Contact your Digital Support representative.
BADVALUE, bad command argument value
Explanation: The command contains an illegal argument
value. The illegal value is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command using a legal
argument value (if arguments are permitted).
BRACKETNESTING, brackets nested too deeply
Explanation: The command contains too many levels of
bracket nesting. The offending bracketed data is displayed between
backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command using fewer nested
brackets.
CMLINPUTOOSMALL, CML input itemlist too small
Explanation: The CML input itemlist buffer that is
passed to the internal CML interface is too small.
User Action: Contact your Digital Support
representative.
CMLRCVFAILED, error receiving command request
Explanation: The call to CML$ReceiveW failed.
User Action: Contact your Digital Support
representative.
CMLSENDFAILED, error sending command request
Explanation: The call to CML$SendW failed.
User Action: See Secondary Status for the reason for
the failure.
CMLTEMPLATETOOSMALL, CML template itemlist too small
Explanation: The CML template itemlist buffer that is
passed to the internal CML interface is too small.
User Action: Contact your Digital Support
representative.
DICTIONARYCORRUPT, NCL data dictionary is corrupt
Explanation: The NCL data dictionary returned corrupt
data.
User Action: Save NCL$GLOBALSECTION.DAT file. Restore
the file and contact your Digital Support representative with the bad
file and a description of what was done.
DISPLAYBUFFEROVERFLOW, display data too large for buffers
Explanation: The display data returned by CML is too
large for NCL's display buffer.
User Action: Contact your Digital Support
representative.
DTETOOLONG, DTE address string is longer than 15 characters
Explanation: The DTE address contains more than 15
characters. The offending address is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying no more
than 15 characters for the DTE address.
DUPLICATEARGUMENT, duplicate arguments not allowed
Explanation: The command contains duplicate arguments.
The duplicated argument is displayed in parentheses.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying each
argument only once.
FULLNAMETOOLONG, FullName string longer than 400 characters
Explanation: The full name string is longer than the
architected maximum length of 400 characters. The offending full name
is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying a full
name of 400 or fewer characters.
ILLEGALCHARACTER, illegal character in input command
Explanation: The command line contains an illegal
character. The illegal character is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command line using only legal
characters.
IMAGETOOLONG, end user specification image field is too long
Explanation: The image field in the end user
specification is too long. The offending data is displayed between
backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying data that
does not exceed the allowable limits. Allowable lengths for fields in
the end user specification are:
|
NUMBER = n
|
0
<= n
<= 255
|
|
NAME = "string"
|
string
<= 16 characters
|
|
UIC = [g,u]"string"
|
string
<= 12 characters
|
|
FULLNAME = fullname
|
fullname
<= 400 characters
|
INVALIDABSTIME, invalid absolute time, use DDDD-HH:MM:SS I SSS
Explanation: Absolute time format is invalid.
User Action: Reenter the time in correct format.
INVALIDACCESSCONTROL, invalid syntax for access control information
Explanation: The access control information is
formatted incorrectly. The offending data is displayed between
backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying the access
control information in the correct format.
INVALIDADDRESSPREFIX, invalid syntax for an address prefix string
Explanation: The address prefix string contains
illegal characters or invalid syntax. The offending data is displayed
between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying a correct
address prefix string.
INVALIDAREAADDRESS, invalid syntax for an area address
Explanation: The area address string contains illegal
characters or is incorrectly formatted. The offending data is displayed
between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying a correct
area address.
INVALIDCMLDATA, return data corrupt or incorrectly encoded
Explanation: The data returned by CML is incorrectly
formatted or corrupt.
User Action: Contact your Digital Support
representative.
INVALIDCOMMAND, unrecognized command
Explanation: NCL does not recognize the command. The
unrecognized command is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Correct the command and reenter it.
INVALIDDNSTS, invalid syntax for a name server timestamp
Explanation: The DECdns timestamp string is
incorrectly formatted.
User Action: Reenter in correct format.
INVALIDFULLNAME, invalid syntax for FullName string
Explanation: A full name string is incorrectly
formatted. The offending full name is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying the full
name string correctly.
INVALIDHEXSTRING, invalid syntax for a hex string
Explanation: A hexadecimal string contains illegal
characters. The offending data is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying only legal
characters for the hexadecimal string.
INVALIDIPADDRESS, invalid syntax for an IP address
Explanation: The IP address contains illegal
characters.
User Action: Reenter with correct syntax (length was
equal to zero or contained illegal characters). Valid characters are 0
to 9 and the period (.).
INVALIDLANADDRESS, invalid syntax for LAN Address
Explanation: A LAN address contains illegal
characters. The offending data is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying a legal
LAN address.
INVALIDLATIN1STRING, invalid characters in Latin1 String
Explanation: A Latin1 string contains invalid
characters (usually control characters). The offending data is
displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying only valid
characters in the Latin1 string.
INVALIDNET, invalid syntax for a Network Entity Title
Explanation: The network entity title (NET) string
contains illegal characters or is formatted incorrectly. The offending
network entity title is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying a legal
network entity title string.
INVALIDNSAP, invalid syntax for an NSAP Address string
Explanation: The NSAP address string contains illegal
characters or is formatted incorrectly. The offending data is displayed
between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying a legal
NSAP address.
INVALIDOCTETSTRING, invalid syntax for octet or octet string
Explanation: An octet does not contain two hexadecimal
digits. The offending data is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying two
hexadecimal digits for each octet.
INVALIDPHASE4ADDR, invalid syntax for a Phase IV node address
Explanation: A Phase IV node address has been
specified incorrectly. The invalid address is displayed between
backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying a correct
Phase IV node address.
INVALIDPHASE4NAME, invalid syntax for a Phase IV node name
Explanation: A Phase IV node-name string contains
illegal characters, does not contain at least one alpha character, or
is too long. The offending data is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying a legal
Phase IV node-name string.
INVALIDPID, invalid syntax for a process identifier
Explanation: The process identifier string does not
look like a hexadecimal PID or a process name string. The offending
process identifier is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying a valid
process identifier.
INVALIDRELOP, invalid syntax for an entity filter relational operator
Explanation: The relational operator in the entity
filter is invalid.
User Action: Reenter with valid operator. Valid
operators are =, <>, <, <=, >, and >=.
INVALIDSIMPLENAME, invalid syntax for SimpleName string
Explanation: A simple name string is incorrectly
formatted. The offending data is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying a valid
simple-name string.
INVALIDTIME, invalid syntax for a date/time
Explanation: The binary/character absolute/relative
time contains illegal characters or bad syntax.
User Action: Reenter correct absolute or relative time.
INVALIDUID, invalid syntax for an unique identifier
Explanation: The unique identifier contains illegal
characters or bad syntax.
User Action: Reenter hexadecimal string with "-"
separators.
INVALIDVERSION, invalid syntax for a version number
Explanation: The version number contains illegal
characters. The offending data is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying a valid
version number.
MISSINGARGUMENT, missing required command arguments
Explanation: The command line was terminated before
all required command arguments were specified.
User Action: Reenter the command including all of the
required arguments.
MISSINGEDITNUMBER, missing edit number for version number with edit
Explanation: The version number with edit is missing
the edit number. The offending data is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying the
required edit number.
MISSINGLEFTBKT, missing left bracket
Explanation: The left bracket character is missing.
The offending string is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command including the left
bracket character.
MISSINGRIGHTBKT, missing right bracket
Explanation: The right bracket character is missing.
The offending string is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command including the right
bracket character.
NOCONNECTION, cannot establish CMIP connection to remote node
Explanation: The call to CML$InitializeW failed.
User Action: See Secondary Status for the reason for
the failure.
NODENAMETOOLONG, node name and/or access control information too long
Explanation: The node name and access control string
are too long for NCL's parsed data buffer. The offending data is
displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying data that
does not exceed the allowable limits.
NOGLOBALENTITY, no global NODE entity found in the data dictionary
Explanation: The NCL$GLOBALSECTION.DAT file does not
have any entities in it.
User Action: Contact your Digital Support
representative.
NOGLOBALSECTION, cannot open and map the parse table global section file
Explanation: The NCL$GLOBALSECTION.DAT file could not
be opened.
User Action: See Secondary Status for the reason for
the failure.
NOLINKID, no LinkID returned by CML
Explanation: The call to CML$Initialize returned
successfully, but did not return a LinkID value.
User Action: Contact your Digital Support
representative.
NOSUCHPROCESS, no such process name or insufficient privilege
Explanation: Either the specified process does not
exist or you have insufficient privileges to use it. The process name
is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying a
different process name or retry the command from a privileged account.
PHASE4AREA, Phase IV area number is not between 1 and 63
Explanation: The Phase IV node address contains an
area number outside the legal range. The illegal data is displayed
between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying an area
number within the range 1 through 63.
PHASE4NODE, Phase IV node number is not between 1 and 1023
Explanation: The Phase IV node address contains a node
number outside the legal range. The illegal data is displayed between
backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying a node
number within the range 1 through 1023.
PROMPTNOTFOUND, prompt string not found in message file, using default
Explanation: The initial or continuation prompt string
was not found in the NCL message file. The default prompt is being used.
User Action: Contact your Digital Support
representative.
REQUESTFAILED, Command failed due to: 'reason code'
Explanation: The CMIP request failed for the reason
specified.
User Action: Correct the problem stated by the reason
code and retry the command.
SCRIPTNESTED, too many levels of nested NCL scripts
Explanation: Nested NCL scripts are not allowed.
User Action: Nest the scripts no more then 10 levels.
SCRIPTNOTFOUND, Cannot open script file, check spelling and/or file
specification.
Explanation: Cannot open the script file for input.
User Action: See the Secondary Status for the reason.
SIMPLENAMETOOLONG, SimpleName string longer than 255 characters
Explanation: The simple name string is longer than the
architected maximum length of 255 characters. The offending string is
displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying a simple
name of 255 characters or fewer.
TOKENTOOLONG, command line item too long
Explanation: A command line token is too long to fit
into the token buffer. The offending item is displayed between
backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying a shorter
command line token.
TSELTOOLONG, transport selector octet string is longer than 32 octets
Explanation: The transport selector string exceeds the
32-octet maximum. The illegal string is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying a
transport selector string that does not exceed the 32-octet maximum.
UNEXPECTEDRESPONSE, response function from CML does not match requested
function
Explanation: CML returned a response with a function
code that does not match that of the request.
User Action: Contact your Digital Support
representative.
UNKNOWNAFI, unknown authority and format identifier in NSAP
Explanation: The NSAP or address-prefix string
contains an illegal or unknown authority and format identifier (AFI)
value. The offending data is displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command specifying a valid
AFI value.
VERSIONMISMATCH, incompatible NCL parse table (Version !UL), expected
Version !UL
Explanation: The NCL parse table section
(NCL$GlobalSection.DAT) version number did not match that which NCL was
built for, and this version is not compatible.
User Action: Resinstall the kit with the proper
NCL.EXE and NCL$GlobalSection.DAT.
WRONGBRACKET, mismatched right bracket
Explanation: The right bracket character does not
match the corresponding left bracket character. The offending string is
displayed between backslashes.
User Action: Reenter the command using matching
bracket characters.
A.5 Common NCL Exception Messages
Access Denied
Explanation: You are not authorized to perform the
specified command.
Access Violation
Explanation: You have performed an illegal operation
for the specified command.
Already Exists
Explanation: You have tried to create an entity that
already exist.
Constraint Violation
Explanation: The setting of one or more attributes
violates a constraint defined for the entity.
Create With Wildcard
Explanation: You have used a wildcard to create an
entity name that is not supported.
Directive Not Supported
Explanation: You have entered an NCL command that is
not supported for this entity.
Duplicate Argument
Explanation: You have entered an NCL command with two
or more of the same argument.
Duplicate Attribute
Explanation: You have entered an NCL command with two
or more of the same attribute.
Entity Class Not Supported
Explanation: You have specified an entity class that
is not supported or has not been created.
Entity Is In The Wrong State
Explanation: Due to the state of the entity, it would
not accept one of the attribute values in the command.
Filter Invalid For Action
Explanation: You have specified a filter that is
invalid for the specified command.
Filter Specified With Wildcarded Class
Explanation: You have specified a filter by using a
wildcard. It is an invalid use of a wildcard.
Get List Error
Explanation: An error was detected while getting one
or more of the requested attributes.
Has Children
Explanation: You have attempted action on a parent
entity that requires you to delete the children entities first.
Invalid Argument Value
Explanation: You have specified one or more arguments
with values outside the permitted range.
Invalid Attribute Value
Explanation: You have specified one or more attributes
with values outside the permitted range.
Invalid Directive
Explanation: You have attempted to issue an
unsupported command.
Invalid Entity Name Format
Explanation: You have specified an illegal entity name.
Invalid Filter
Explanation: You have specifie a filter that is
invalid for one or more of the entities named.
Invalid Invocation Identifier
Explanation: You have specified an unsupported
identifier.
Invalid Item List Format
Explanation: You have specified an illegal item list
format.
Invalid Operator
Explanation: You have specified an unsupported
operator.
Invalid Use Of Wildcards
Explanation: You have specified wildcards in an entity
name where this is not supported.
No Resources Available
Explanation: The entity could not complete the
requested operation due to lack of resources. Typically, this refers to
memory or if a resource like maximum links has been exceeded. If you
receive this message on startup, try raising the PQL_MBYTLM SYSGEN
parameter.
No Responses Ready
Explanation: The entity could not complete the
requested operation because the entity received no response.
No Such Action Verb
Explanation: The specified action verb is not
supported by the entity.
No Such Argument
Explanation: You have specified one or more arguments
that are not supported by the entity for the specified action.
No Such Attribute ID
Explanation: You have specified one or more attribute
IDs that are not supported by the entity for the specified action.
No Such Entity
Explanation: The entity instance specified in the
command does not exist.
No Such Object Instance
Explanation: The object instance specified in the
command does not exist.
Not a Universal Attribute Group
Explanation: You have specified an unsupported
attribute group.
Operation Failure
Explanation: You have specified an illegal operation.
Operation Not Supported
Explanation: You have specified an operation that is
not supported by NCL.
Overflow While Filling Buffer
Explanation: The specified operation has resulted in a
buffer overrun. Try increasing MAXBUF or the process quota.
Process Failure
Explanation: The entity raised an action-specific
exception while attempting the specified action.
Read-only Attribute
Explanation: You have specified a non-read operation
on a read-only attribute.
Requested Attribute Is Not Active
Explanation: You have specified action on an attribute
that is not enabled.
Required Argument Omitted
Explanation: You have omitted one or more required
arguments in the specified command.
Set List Error
Explanation: An error was detected while setting one
or more of the requested attributes or a set value is improperly
specified. For further information, refer to Section 1.4.3 in the
Introduction of this manual.
Unknown CMIP Error Status
Explanation: The remote system is running a CMIP
protocol that is not compatible with NCL, and/or you have mismatched
versions of NCL, CML, or EMAA, or you are using an older version of
DECnet-Plus to manage a new one.
Unknown EMAA Error Status
Explanation: The remote system is running an EMAA that
is not supported by NCL, and/or you have mismatched versions of NCL,
CML, or EMAA, or you are using an older version of DECnet-Plus to
manage a new one.
Unknown Response Failure Code
Explanation: The operation has produced an error code
that NCL does not support, and/or you have mismatched versions of NCL,
CML, or EMAA, or you are using an older version of DECnet-Plus to
manage a new one.
Write-only Attribute
Explanation: You have specified a non-write operation
on a write-only attribute.
Wrong State
Explanation: The entity is in a state that is illegal
for the attempted operation. (For specific information on legal states,
see the command description for the specified entity.)
Appendix B
Common Data Types for NCL
B.1 Overview of Data Types
This appendix defines each supported NCL data type. The definitions
include the values allowed for the type, any relations defined on each
type (including equality and ordering relation), and any wildcard
symbols that are allowed. Before going into the details of each data
type, it is helpful to understand the ideas and terminology underlying
the definitions.
B.1.1 What Is a Data Type?
The term data type is used throughout the computer industry.
Commonly, a data type represents a set of values to which any given
value must belong. This set may be represented either explicitly, by
enumeration, or implicitly, by rules. For example, the data type
boolean may be represented explicitly as the set (true or
false). The data type latin1string, however, has an infinite
number of possible values and must be described as a set of rules. The
rules consist of restrictions on characters used and methods of
quotation.
Previous
| Next
| Contents
| [Home]
| [Comments]
| [Ordering info]
| [Help]
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
NCL_PROFILE_034.HTML
OSSG Documentation
2-DEC-1996 12:48:59.22
Copyright © Digital Equipment Corporation 1996. All Rights Reserved.
Legal
![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)

![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)