![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
DECnet-Plus
Network Control Language Reference
Previous
| Contents
21.12 routing egp group egp neighbor
A routing egp group egp neighbor entity defines one of the
systems in the autonomous group defined by the owning egp
group entity. This entity is supported only on level 2 routers
that support dual routing (and, in particular, the EGP routing
protocol).
create [node node-id] routing egp group
group-name egp neighbor neighbor-name ip address
ip-address
delete [node node-id] routing egp group
group-name egp neighbor neighbor-name
disable [node node-id] routing egp group
group-name egp neighbor neighbor-name
enable [node node-id] routing egp group
group-name egp neighbor neighbor-name
show [node node-id] routing egp group
group-named egp neighbor neighbor-name [all
[attributes] | all characteristics | all counters | all identifiers |
all status ]
start [node node-id] routing egp group
group-name egp neighbor neighbor-name
stop [node node-id] routing egp group
group-name egp neighbor neighbor-name
21.12.1 Arguments
ip address ip-address
The IP address of the EGP neighbor.
21.12.2 Characteristic Attributes
circuit
|
Default: None
|
Value: Circuit name
|
Simple name of the circuit.
ip address
Internet address of this EGP neighbor. The value of this characteristic
is derived from the ip address argument of the create
command. You cannot modify this characteristic.
next hop
|
Default: 0.0.0.0
|
Value: IP address
|
IP address and the next routing node.
source network
|
Default: 0.0.0.0
|
Value: Network number
|
Network number to query.
21.12.3 Counter Attributes
creation time
Time at which this entity was created.
error messages received
Number of EGP error messages received from this neighbor.
error messages sent
Number of EGP error messages sent to this neighbor.
messages received
Number of EGP messages received without error from this neighbor.
messages sent
Number of EGP messages sent to this neighbor. Note that this value does
not include EGP messages counted by the counter send messages
discarded.
received messages discarded
Number of EGP messages received from this neighbor with any kind of
error.
send messages discarded
Number of EGP messages not sent to this neighbor because of resource
limitations within the egp entity.
start events
Number of times the EGP neighbor has been manually started.
stop events
Number of times the EGP neighbor has been manually stopped.
21.12.4 Identifier Attributes
name
Simple name assigned to the EGP neighbor when it is created.
21.12.5 Status Attributes
egp state
EGP state of the system with respect to this EGP neighbor.
|
acquisition
|
idle
|
|
cease
|
up
|
|
down
|
|
hello time
Interval, in hundredths of a second, between retransmissions of EGP
Hellos. This value represents the t1 timer defined in RFC 904.
last event
Specifies whether the last event issued on this EGP neighbor was a
start or a stop event.
|
start
|
The last event was a start.
|
|
stop
|
The last event was a stop. This is the value with which an EGP neighbor
is created, before either a
start or
stop command has been issued.
|
polling mode
Polling mode of the EGP entity with respect to this neighbor as either
active or passive.
poll time
Interval, in hundredths of a second, between retransmissions of EGP
polls. This value represents the t3 timer defined in RFC 904.
state
State of the routing egp group egp neighbor entity.
|
off
|
The entity is disabled.
|
|
on
|
The entity is enabled.
|
uid
Entity's unique identifier, which is generated when the entity is
created.
21.12.6 Event Messages
error message received
Generated when an EGP error response message is received.
Arguments:
|
neighbor ip address
|
IP address of this neighbor.
|
|
reason
|
Reason why the error message occurred:
|
|
|
autonomous system number rejected
|
|
|
bad EGP data field format
|
|
|
bad EGP header format
|
|
|
excessive polling rate
|
|
|
no response
|
|
|
reachability information unavailable
|
error message sent
Generated when an EGP error response message is sent.
Arguments:
|
neighbor ip address
|
IP address of this neighbor.
|
|
reason
|
Reason why the error message occurred. See the description of the
Reason argument of the Error Message Received event.
|
received message discard
Generated when a received EGP message is discarded for some reason.
Arguments:
|
neighbor ip address
|
IP address of this neighbor.
|
|
reason
|
Reason why the error message occurred. See the description of the
Reason argument of the Error Message Received event.
|
send message discard
Generated when an EGP message for transmission is discarded for some
reason.
Arguments:
|
neighbor ip address
|
IP address of this neighbor.
|
|
reason
|
Reason why the error message occurred. See the description of the
Reason argument of the Error Message Received event.
|
start
Generated when a start command completes successfully.
Argument:
|
neighbor ip address
|
IP address of this neighbor.
|
state change
Generated when the status attribute egp state changes to some
other state.
Argument:
|
neighbor ip address
|
IP address of this neighbor.
|
stop
Generated when a stop command completes successfully.
Argument:
|
neighbor ip address
|
IP address of this neighbor.
|
21.12.7 Exception Messages
For create:
duplicate ip address
An EGP neighbor with this IP address already exists in this EGP group.
21.13 routing ip destination address
A routing ip destination address entity describes IP routing
information in the shortest paths database. This entity is supported
only on routers that support dual routing.
show [node node-id] routing ip destination
address address-name [all [attributes] | all identifiers | all
status ]
21.13.1 Identifier Attributes
name
Subnet address of a destination subnetwork.
21.13.2 Status Attributes
level
Level at which the shortest path exists in the shortest paths database:
|
Level 1
|
|
|
Level 2 External
|
|
|
Level 2 Internal
|
|
metric
Default metric value for the shortest path to the destination
subnetwork.
paths
Equal cost paths for this route. The following information appears for
each path:
- The name of the entity pair that represents the forwarding decision
for this path (circuit and one of adjacency, IP adjacency, or IP
reachable address).
- The routing mechanism through which the route was learned:
- Local --- the route is derived from the subnet address or
alternative subnet addresses characteristics of a local
circuit.
- Netmgnt --- the route is derived from manually configured
information on the local system.
- The number of seconds since the route was last updated.
21.14 routing permitted neighbor
A routing permitted neighbor entity represents a neighboring
node on a nonbroadcast circuit that is permitted to connect to this
node. The neighbor-name is the name of the permitted neighbor
managed by this command.
create [node node-id] routing permitted
neighbor neighbor-name id node-id
delete [node node-id] routing permitted
neighbor neighbor-name
set [node node-id] routing permitted neighbor
neighbor-name
show [node node-id] routing permitted
neighbor neighbor-name [all [attributes] | all characteristics
| all identifiers ]
21.14.1 Characteristic Attributes
id
|
Support: All
|
|
|
Default: No default
|
Value: Node ID
|
Node ID of a potential neighbor node. You cannot modify this
characteristic. This characteristic is set by means of an argument to
the create command.
verifier
|
Support: All
|
|
|
Default: No verifier
|
Value: Hex-string, length 0--38
|
Verifier to be checked from this neighbor. You may change this
characteristic at any time; however, the change will not take effect
until the circuit is next initialized. You cannot display this
characteristic.
If the verifier is not set, then a connection to the neighboring node
whose ID matches the ID in this entry is allowed. If the verifier is
set, the connection is allowed only if the verifier sent by the remote
node matches the one in this entry.
21.14.2 Identifier Attributes
name
Simple name assigned to the permitted neighbor when it is created.
21.14.3 Exception Messages
For create:
duplicate node id
A routing permitted neighbor entity with the specified node ID
already exists.
Argument:
|
name
|
The name of the permitted neighbor that already has this node ID.
|
permitted neighbor already exists
A routing permitted neighbor entity with the specified name
already exists.
21.15 routing port
A routing port entity represents a client of the Routing
module, and presents information associated with that client. The
port-name refers to the port managed by this command.
show [node node-id] routing port
port-name [all [attributes] | all counters | all identifiers |
all status ]
21.15.1 Counter Attributes
creation time
Time the entity was created.
data sdus received
Number of data NSDUs delivered across transport interface (after
reassembly).
error reports received
Number of error report PDUs delivered across transport interface.
expired segments discarded
Number of segments discarded because lifetime expired during reassembly.
ip packets reassembled
Number of IP packets reassembled successfully from fragments.
sdus transmitted
Number of data NSDUs requested for transmission across transport
interface.
segments discarded
Number of segments (data- or error-report) discarded before delivery
across the Transport interface, including segments discarded for any
reason other than lifetime expiration during reassembly.
segments received
Number of data- and error-report NPDUs received before reassembly.
21.15.2 Identifier Attributes
name
Simple name assigned to the port when it is created.
21.15.3 Status Attributes
client
Name given by the user of the port when the port was opened.
nsap addresses
Set of NSAP addresses to be received at this port. This attribute is
supported only if the status attribute type is not set to
IP.
nsap selector
Network service access point (NSAP) selector octet supplied by the
client. This attribute is supported only if the status attribute
type is not set to ip.
protocol type
Value of the IP protocol field specified by the client.
type
Type of connectionless network service to be used: IP or ISO 8473.
uid
Entity's unique identifier, which is generated when the entity is
created.
Chapter 22
Session Control Module
This chapter describes all of the commands you can use to manage the
entities that constitute the Session Control module. The Session layer
implements the user interface to the network.
Figure 22-1 shows the hierarchical relationship of the entities that
constitute the Session Control module.
Figure 22-1 Hierarchy of Session Control Module
Entities
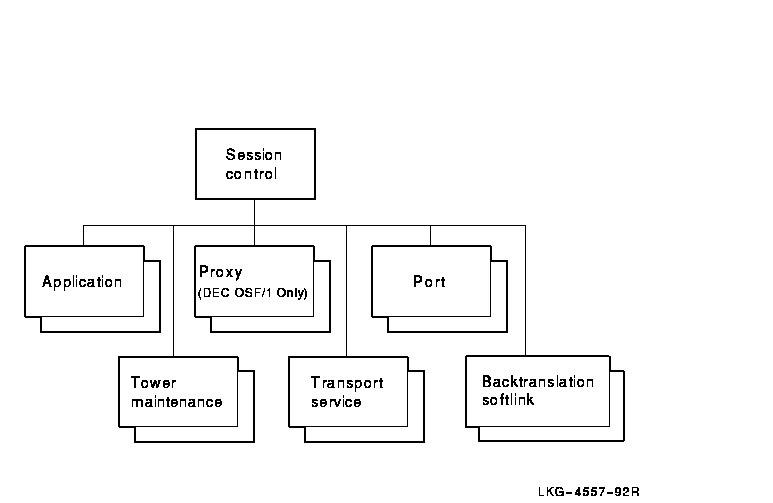
The Session layer is responsible for connection negotiation and
establishment. The Session Control module performs the following
functions:
- Manages transport connections on behalf of Session Control users.
- Enforces access control policies to restrict communication between
users and between Session Control modules.
- Maps from a DNA Naming Service object name to protocols and
addresses.
- Selects from the set of protocols supporting Session Control to
attempt connection establishment.
- Maintains in the namespace the protocol and address information
corresponding to objects that reside in the same node as the local
Session Control module.
22.1 session control
The session control entity is the top-level entity in the
hierarchy of entities belonging to the Session Control module.
create [node node-id] session control
delete [node node-id] session control
(Digital UNIX)
disable [node node-id] session control
enable [node node-id] session control
flush [node node-id] session control naming
cache entry "*" (OpenVMS)
restrict [node node-id] session control
set [node node-id] session control {address
update interval integer | backtranslation search path
search-path-information | decnet-internet gateway enabled
(Digital UNIX) | decnet-internet gateway user (Digital UNIX) | incoming
proxy boolean | incoming timer integer | maintain
backward soft links boolean | naming cache checkpoint interval
integer (OpenVMS) | naming cache entry (OpenVMS) | naming
cache timeout integer (OpenVMS) | naming search path
search-path-information | modify acs boolean | node
synonym directory full-name (Digital UNIX) | non privileged
user session-control (OpenVMS) | outgoing proxy
boolean | outgoing timer integer | soft link timer
binary-relative-time (Digital UNIX) | update retry interval
integer | transport precedence [set] }
show [node node-id] session control [all
[attributes] | all characteristics | all counters | all status ]
shut [node node-id] session control
22.1.1 Commands
flush (OpenVMS)
Removes one or more entries from the in-memory, local naming cache. Use
the syntax parenthesis-asterisk-parenthesis.
restrict
Places the module in the restrict state. In this state,
outgoing connection requests are accepted. Incoming connection requests
are not accepted, unless the client has sufficient privilege to
override.
shut
Places session control in the shut state. In this state, no
further connection requests are honored. It continues to service
existing connections. When all connections have been closed by their
clients, it is placed in the off state.
22.1.2 Characteristic Attributes
address update interval
|
Default: 10
|
Values: 1--4294967296
|
Minimum time, in seconds, allowed between updates of address
information. More frequent modification to the set of local towers is
prohibited.
backtranslation search path
|
Default: None
|
Value: Search-path-information
|
Describes the order in which name services will be searched for
address-to-node-name translation requests (when more than one name
service is in use on a node) and any associated naming templates for
each directory service.
decnet-internet gateway enabled (Digital UNIX)
|
Default: False
|
Value: True or false
|
If true, the DECnet-Internet Gateway is enabled.
decnet-internet gateway user (Digital UNIX)
Name of a user under whose account to run gateway applications.
incoming proxy
|
Default: True
|
Value: True or false
|
Specifies whether to honor incoming proxy requests. If this attribute
is set to false, requests to invoke proxies on incoming
requests are ignored.
incoming timer
|
Default: 45
|
Values: 0--65535
|
Time, in seconds, to wait for a user module to issue an
accept/reject call after a port enters a state indicating that
a connection request was received. If the timer expires, Session
Control aborts the transport connection with a timed out
error. For OpenVMS, a zero (0) value directs Session Control to wait
indefinitely without aborting the connection.
maintain backward soft links
|
Default: False
|
Value: True or false
|
Specifies whether Session Control should attempt to update the backward
translation soft links when it detects an address change. If this
attribute is set to false, Session Control will add no new
backward translation soft links and it may delete any that it has
created.
modify acs
|
Default: True
|
Value: True or false
|
Specifies whether Session Control should attempt to update the ACS
(access control set) of the node object whenever it attempts to update
the towers attribute for the node in the namespace.
naming cache checkpoint interval (OpenVMS)
Amount of time, in hours, between times when the address and node name
information is checkpointed to disk from the in-memory, local naming
cache.
naming cache entry (OpenVMS)
|
Default: None
|
Value: Name
|
Address and node name information for a node that has been retrieved
from a name service and is currently stored in the in-memory, local
naming cache.
naming cache timeout (OpenVMS)
Amount of time, in days, after which the address and node name
information for a node is deleted from the in-memory, local naming
cache.
naming search path
|
Default: None
|
Value: Search-path-information
|
Describes the order in which name services will be searched for
node-name-to-address translation requests (when more than one name
service is in use on a node), and any associated naming templates for
each name service.
node synonym directory (Digital UNIX)
|
Default: .DNA_NodeSynonym
|
Value: Full-name
|
Full name of a DECdns directory that contains node synonyms.
non privileged user (OpenVMS)
Specifies the Session Control on a non-privileged user account.
outgoing proxy
|
Default: True
|
Value: True or false
|
Specifies whether to invoke a proxy on outgoing connection requests
when the user does not explicitly specify to do so. If this attribute
is set to false, no proxy is invoked.
outgoing timer
|
Default: 60
|
Values: 0--65535
|
Time, in seconds, to wait for an outgoing transport connection to be
accepted before Session Control aborts the connection with a timed
out error. For OpenVMS, a zero (0) value directs Session Control
to wait indefinitely without aborting the connection.
soft link timer (Digital UNIX)
|
Default: 30 days
|
Value: Binary relative time
|
Interval of time, in days, DECdns checks that an object pointed to by a
backward translation soft link still exists.
update retry interval
|
Default: 60
|
Values: 1--4294967296
|
Time to wait before Session Control retries a failed attempt to update
information in the namespace. The default is 60 minutes.
transport precedence
|
Default: OSI
|
Value: Set of OSI or NSP
|
Note: On the DECnet/OSI for ULTRIX and DECnet/OSI for Digital UNIX V1.0
products, the default was tp4 rather than OSI.
Previous
| Next
| Contents
| [Home]
| [Comments]
| [Ordering info]
| [Help]
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
NCL_PROFILE_026.HTML
OSSG Documentation
2-DEC-1996 12:48:39.13
Copyright © Digital Equipment Corporation 1996. All Rights Reserved.
Legal
![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)

![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)