![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
DECnet-Plus
Network Control Language Reference
Previous
| Contents
20.6 osi transport template
An osi transport template entity provides a collection of
characteristics that supply default values for certain parameters that
influence the operation of a port on a transport connection. One
template, with the reserved identifier default, is
automatically created when the osi transport entity is
created. This template is used by default when a user does not specify
a template identifier in a call to establish a connection. The
default template is deleted automatically when the osi
transport entity is deleted. Similarly, the initial values of the
attributes in a template are the same as the current values in the
default template. The template-name refers to the template
managed by this command.
For Digital UNIX, the only attributes that apply to CLTS are
checksum, network service, and local nsap.
add [node node-id] osi transport template
template-id classes bit-set
create [node node-id] osi transport template
template-id
delete [node node-id] osi transport template
template-id
remove [node node-id] osi transport template
template-id classes bit-set
set [node node-id] osi transport template
template-id {acknowledge delay time seconds |
checksums boolean | classes bit-set | CLNS inactive
area address set-of-area-address (OpenVMS) | CONS template
simple-name | cr timeout seconds | er timeout
seconds | expedited data boolean | extended format
boolean | inbound boolean (OpenVMS) | initial
retransmit time seconds | keepalive time seconds |
local nsap nsap-address | loopback boolean (OpenVMS)
| maximum nsdu size octets | network service type |
network priority (OpenVMS) | retransmit threshold integer |
RFC 1006 port number (OpenVMS) | security octet string | send
implementation id boolean | send preferred maximum TPDU size
boolean | send request acknowledgment boolean | use
CLNS error reports boolean }
show [node node-id] osi transport template
template-id [all [attributes] | all characteristics | all
identifiers ]
20.6.1 Characteristic Attributes
acknowledgment delay time
Maximum amount of time, in seconds, that an AK TPDU is to be withheld.
This attribute is valid for protocol class 4 only.
checksums
|
Default: False
|
Value: True or false
|
Specifies whether the use of checksums should be negotiated for a
transport connection. This attribute is valid for protocol class 4 only.
classes
|
Default: {4}
|
Value: Bit-set
|
Set of protocol classes that can be negotiated for use on a transport
connection. If the value of the network service attribute is CLNS, the
class must be a subset of the classes supported by the OSI transport
attribute clns classes supported. If the value is CONS, the
classes must be a subset of the classes supported by the OSI transport
attribute cons classes supported. If the value of the network
service attribute is ANY, the classes must be a subset of the combined
classes in the clns classes supported and cons classes
supported attributes.
CLNS inactive area address (OpenVMS)
|
Default: Empty set
|
Value: Set of area-address
|
Specifies the inactive area address to be used by transport connections
that use this template. This characteristic is relevant only for
connections that use CLNS with null internet. The set must contain no
more than one area address.
CONS template
|
Default: OSI transport
|
Value: Simple-name
|
Name of the X.25 Access module template to be used when establishing a
network connection over the CONS. Used only when the value of the
network service attribute is cons.
cr timeout
|
Default: 30
|
Value for Digital UNIX: 1-- (2 ^
31 - 1 )
|
|
Default: 30
|
Value for OpenVMS: 1-- (2 ^
32 - 1 )
|
During connection establishment, the amount of time, in seconds, to
wait for a response to a CR TPDU before assuming that the remote
transport service provider will not respond. This attribute is valid
for protocol classes 0 and 2 only.
er timeout
|
Default: 30
|
Value for Digital UNIX: 1-- (2 ^
31 - 1 )
|
|
Default: 30
|
Value for OpenVMS: 1-- (2 ^
32 - 1 )
|
The amount of time, in seconds, to wait for a response to an ER TPDU
before disconnecting the network connection. This attribute is used for
protocol classes 0 and 2 only.
expedited data
|
Default: True
|
Value: True or false
|
Specifies whether use of the expedited data option should be negotiated
for the transport connections. This attribute is not valid for protocol
class 0.
extended format
|
Default: None
|
Value: True or false
|
Specifies whether the use of extended TPDU format should be negotiated
for the transport connections. Normal format gives 7-bit sequence
numbers and 4-bit credit fields; extended format gives 31-bit sequence
numbers and 16-bit credit fields. This attribute is supported only for
class 2 and class 4 protocols.
inbound (OpenVMS)
|
Default: True
|
Value: True or false
|
Indicates whether this template may be used as the template for an
inbound transport connection. The algorithm of selection of the inbound
template is different depending on the type of network service over
which the transport connection is made. If an inbound template cannot
be found for an inbound transport connection, then the template called
default will be selected as the default. For the CLNS network
service, the inbound template selected is the first template found that
has the Inbound attribute set to true, the Network Service attribute
set to CLNS, and the CLNS Inactive Area Address attribute set to empty
set.
For the CLNS network service (using the inactive subset, that is, null
internet), the incoming template selected is the first template found
that has the Inbound attribute set to True, the Network Service
attribute set to CLNS and the CLNS Inactive Area Address attribute
matches the Inactive Area Address attribute of the Routing Circuit
entity that the transport connection is using. For the CONS network
service, the inbound template selected is the first template found that
has the inbound attribute set to true, the network service attribute
set to CONS and the CONS template attribute (that is, an X.25 Access
template name) matches the name of the X.25 Access filter that was used
to accept the inbound network connection.
initial retransmit time
|
Default: 5
|
Value for Digital UNIX: 1-- (2 ^
31 - 1 )
|
|
Default: 5
|
Value for OpenVMS: 1-- (2 ^
32 - 1 )
|
Amount of time, in seconds, to wait for an acknowledgment before
retransmitting the first TPDU over the transport connection.
keepalive time
|
Default: 60
|
Value: 1--16383
|
Time, in seconds, to be used for the window timer. When the transport
service provider has no TPDUs to send over a transport connection, it
retransmits the last AK TPDU at the specified frequency to prevent
expiration of the remote NSAP's inactivity timer. This attribute is
valid for protocol class 4 only.
local nsap
|
Default: System dependent, determined at run-time
|
Value: NSAP address
|
A local NSAP address to be used by default if one is not supplied
across the service interface.
loopback (OpenVMS)
|
Default: False
|
Value: True or false
|
Specifies whether transport connections using this template are looped
back locally in the Transport layer.
maximum nsdu size
|
Default: 2048
|
Value for Digital UNIX: 128-- (2 ^
32 - 1 )
|
|
Default: 2048
|
Value for OpenVMS: 2048
|
When operating over the CONS, the maximum NSDU size to use for transmit
and receive buffers. Expressed as a number of octets.
network priority (OpenVMS)
When operating over CLNS, indicates network priority encoded in NPDU
header for all transmitted packets. It may be used by intermediate
systems to assign the packets to queues of appropriate priority.
network service
|
Default: CLNS
|
Value: Any, CLNS, CONS, or RFC 1006 (OpenVMS)
|
Type of network service. On Digital UNIX, the default template
network service cannot be set to any. The
network service chosen must be compatible with the value of the
protocol class attribute.
|
any
|
Either
|
|
CLNS
|
Connectionless Network Service
|
|
CONS
|
Connection-Oriented Network Service
|
|
RFC 1006
|
ISO transport service on top of TCP
|
retransmit threshold
|
Default: 8
|
Value: 0-- (2 ^
32 - 1 )
|
Number of times a TPDU requiring acknowledgment is to be retransmitted
before it is assumed that network connectivity has failed. This
attribute is valid for protocol class 4 only.
RFC 1006 port number (OpenVMS)
|
Default: 102
|
Value: TCP port number
|
Specifies the TCP port number to use. Only applicable if the network
service is RFC 1006.
security
|
Default: Null value
|
Value: Octet string
|
An octet string to be transmitted in the security parameter of a CR or
CC TPDU. A null value causes the security parameter to be omitted from
the TPDU. For security reasons, this attribute cannot be displayed.
send implementation id
|
Default: True
|
Value: True or false
|
Indicates whether the implementation id should be sent in the CR if the
proposed protocol class is 2 or 4. It is always returned in the CC if
it is present in the CR.
send preferred maximum TPDU size
|
Default: True
|
Value: True or false
|
Indicates whether the preferred maximum TPDU size parameter should be
sent in the CR TPDU.
If the preferred maximum TPDU size parameter was present in the CR
TPDU, then it indicates whether the preferred maximum TPDU size
parameter should be sent in the CC TPDU.
Note
The default value of this characteristic should not be changed unless
the remote implementation does not conform to ISO 8073.
send request acknowledgment
|
Default: True
|
Value: True or false
|
Indicates whether the request acknowledgment parameter should be sent
in the CR TPDU.
If the request acknowledgment parameter was present in the CR TPDU,
then it indicates whether the request acknowledgment parameter should
be sent in the CC TPDU.
Note
The default of this characteristic should not be changed unless the
remote implementation does not conform to ISO 8073.
use CLNS error reports
|
Default: False
|
Value: True or false
|
Indicates whether the network Routing layer's error report facility
should be used when performing connection establishment. If set to
true, this may result in faster detection of an unreachable
node at the time of connection establishment. This characteristic
should not be set to true on an end system that is either
dual-railed or connected to a network that has a high probability of
duplication. This is valid only if network service equals CLNS.
20.6.2 Identifier Attributes
name
Simple name assigned to the template when it is created. The name
default is reserved.
20.6.3 Exception Messages
For create:
already exists
An osi transport template entity already exists.
For delete:
cannot delete default template
Attempt to delete the osi transport template entity failed
because the template named default cannot be deleted.
Chapter 21
Routing Module
This chapter describes all the commands you can use to manage the
entities that constitute the Routing module. The Routing module
implements the Network Routing layer described by the Digital Network
Architecture (DNA).
Figure 21-1 shows the hierarchical relationship of the entities that
constitute the Routing module.
Figure 21-1 Hierarchy of Routing Module Entities
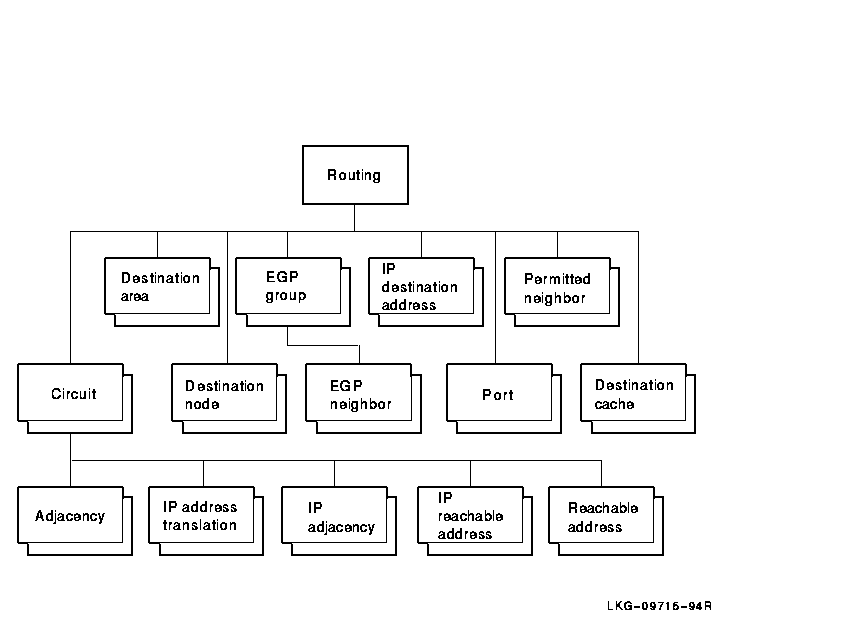
The Routing module routes messages in the network and manages the
message packet flow. The Routing module components provide the
following functions:
- Routing --- determines packet paths. A path is the sequence of
connected nodes and links between a source node and a destination node.
The combined knowledge of all the network Routing layer modules of all
the nodes in a network is used to determine the existence of a path,
and route the packet to its destination. The routing component at a
routing node has the following specific functions:
- Extracts and interprets the route header in a packet.
- Performs packet forwarding based on the destination address.
- Performs packet fragmentation where necessary.
- Manages the characteristics of the path and if a node or link fails
on a path, finds an alternate route.
- Interfaces with the Network Routing Subnetwork Dependent sublayer
to receive reports concerning a circuit or node that has failed or the
subsequent recovery of a circuit or node.
- Performs packet reassembly at the destination.
- Returns error reports to the source where necessary, for instance
when the destination is unreachable or when the packet would have
needed to be fragmented but segmentation permitted was not set
in the packet. Segmentation permitted is always set in data
packets generated by DNA nodes. However, non-DNA nodes may do otherwise.
- Congestion control --- manages the resources used at each packet
switching node (each node that permits route-through).
- Packet lifetime control---bounds the amount of time a packet can
exist in the network.
- Initialization --- identifies the adjacent node and the adjacent
node's network routing layer. It also performs node verification, if
required.
- Dynamic circuit management --- determines when to dial calls, when
to hang up calls, and (on dynamically assigned circuits) which DTE
address to dial. It exists only on dynamically established data links.
21.1 Support for Attributes and Events
Whether a particular attribute or event of a Routing module entity is
supported often depends on the type of node on which the Routing module
is operating. The description of an attribute or event indicates the
type of node for which the attribute or event is supported, using the
following key:
|
L1
|
The attribute is supported only for level 1 routers.
|
|
L2
|
The attribute is supported only for level 2 routers.
|
|
L1,L2
|
The attribute is supported only for level 1 or level 2 routers.
|
|
End
|
The attribute is supported only for end nodes.
|
|
IP
|
The attribute is supported only for routers that support dual routing
(that is, both OSI and IP routing).
|
|
All
|
The attribute is supported by all implementations.
|
21.2 routing
The routing entity is the top-level entity in the Routing
module hierarchy of entities. The Routing module controls the operation
of network routing within a node.
add [node node-id] routing {manual area
addresses [set] | manual network entity titles [set] }
create [node node-id] routing {type
routing-type | protocols protocol-set }
delete [node node-id] routing
disable [node node-id] routing
enable [node node-id] routing
ping [node node-id] routing {destination
ip-address | size integer | timeout integer }
remove [node node-id] routing {manual area
addresses [set] | manual network entity titles [set] }
set [node node-id] routing {area
authentication type none or simple | area receive passwords
hex-string | area send password hex-string |
autonomous system number | dna address format boolean | domain
authentication type none or simple | domain receive passwords
hex-string | domain send password hex-string |
generate checksums boolean | lifetime integer |
manual area addresses [set] | manual L1 algorithm string |
manual L2 algorithm string | manual network entity titles
[set] | maximum buffers integer | maximum path splits
integer | phaseiv address ph4-address | phaseiv
prefix address-prefix | phaseiv area maximum cost
integer | phaseiv area maximum hops integer | phaseiv
broadcast routing timer integer | phaseiv buffer size
integer | phaseiv maximum address integer | phaseiv
maximum area integer | phaseiv maximum cost integer |
phaseiv maximum hops integer | phaseiv maximum visits
integer | probe rate integer | protocols | routing
mode integrated or segregated | redirect holding time
integer | segment buffer size integer | send source
quench boolean | source quench interval boolean |
summary addresses set of summary-address | time to live
integer }
show [node node-id] routing [all [attributes]
| all characteristics | all counters | all status ]
21.2.1 Arguments
destination ip-address
Destination to which an ICMP Echo Request message is to be sent. This
argument is mandatory.
protocols protocol-set
Protocols supported by this router. The value of this argument is a set
containing either or both of the values IP or ISO 8473. This argument
determines the value of the protocols characteristic. The
default value of this argument depends on the value of the
type argument.
size integer
Size, in bytes, of the data part of the ICMP Echo Request message. The
default is 64 bytes.
timeout integer
Time, in seconds, for which the Routing module will wait for an ICMP
Echo Reply message. The default is 5 seconds.
type routing-type
Routing type for this node. This argument determines the value of the
type characteristic attribute. For information on the
available routing types, see the Characteristic Attributes section.
|
endnode
|
The node is an end system.
|
|
L1router
|
The node is a level 1 router.
|
|
L2router
|
The node is a level 2 router.
|
21.2.2 Characteristic Attributes
area authentication type
|
Support: L1,IP
|
|
|
Default: None
|
Value: None or simple
|
Type of authentication to be used for level 1 LSPs, PSNPs, and CSNPs.
area receive passwords
|
Support: L1,IP
|
|
|
Default: No passwords
|
Value: Set of hex-string
|
Set of passwords that are valid in level 1 LSPs, PSNPs, and CSNPs when
simple authentication is in use. You cannot use the show
command to display the value of this attribute.
area send password
|
Support: L1,IP
|
|
|
Default: No password
|
Value: Hex-string
|
Password to be sent in level 1 LSPs, PSNPs, and CSNPs when simple
authentication is in use. You cannot use the show command to
display the value of this attribute.
autonomous system number
|
Support: IP
|
|
|
Default: 0
|
Value: 0--65535
|
Autonomous system number of the local system. This characteristic is
supported only if the value of the routing protocols supported
characteristic includes EGP. You can modify this characteristic only
when the status attribute routing state is off.
dna address format
|
Support: End
|
|
|
Default: True
|
Value: True or false
|
If true, specifies that NSAP addresses are DNA structured, and
that NSAP address autoconfiguring is possible. If false,
specifies that NSAP addresses for this node are constructed from the
characteristic manual network entity titles and the
selectors supplied by the Transport Protocol module (NSP
and/or OSI transport).
The DNA address format attribute controls only the
interpretation of address structuring and no longer controls
autoconfiguration. To control autoconfiguration, you need to use the
manual network entity titles attribute by manually adding or
removing NETs.
domain authentication type
|
Support: L2,IP
|
|
|
Default: None
|
Value: None or simple
|
Type of authentication to be used for level 2 LSPs, PSNPs, and CSNPs.
domain receive passwords
|
Support: L2,IP
|
|
|
Default: No passwords
|
Value: Set of hex-string
|
Set of passwords that are valid in level 2 LSPs, PSNPs, and CSNPs when
simple authentication is in use. You cannot use the show
command to display the value of this attribute.
domain send password
|
Support: L2,IP
|
|
|
Default: No password
|
Value: Hex-string
|
Password to be sent in level 2 LSPs, PSNPs, and CSNPs when simple
authentication is in use. You cannot use the show command to
display the value of this attribute.
generate checksums
|
Support: All
|
|
|
Default: False
|
Value: True or false
|
If true, specifies that checksums are generated for data,
error report, and ES-IS PDUs initiated by this node. If false,
these checksums are not generated. It is strongly recommended that, for
performance reasons, you use the default value (indicating no checksum
generation).
ip reassembly time
|
Support: IP
|
|
|
Default: 10
|
Value: 1--255
|
Maximum time, in seconds, for which IP fragments are held while
awaiting reassembly.
lifetime
|
Support: All
|
|
|
Default: 63
|
Value: 2--255
|
Value to be placed in the "lifetime" field of originating
data packets. This value should be greater than the maximum number of
hops in any path in the network, plus the maximum packet lifetime in
half-seconds.
manual area addresses
|
Support: L1,L2
|
|
|
Default: No area addresses
|
Value: Set of area addresses
|
Area addresses to be used for this node. An area address cannot be a
Phase IV address or the address DefaultArea.
Previous
| Next
| Contents
| [Home]
| [Comments]
| [Ordering info]
| [Help]
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
NCL_PROFILE_020.HTML
OSSG Documentation
2-DEC-1996 12:48:22.62
Copyright © Digital Equipment Corporation 1996. All Rights Reserved.
Legal
![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)

![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)