![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
DECnet-Plus
Network Control Language Reference
Previous
| Contents
For example, if the Phase IV node address is 4.260:
4.260
=> 4 * 1024 + 260
=> 4356 (decimal)
=> 1104 (hex)
=> AA-00-04-00-04-11
circuit
|
Default: No circuit
|
Value: Circuit-id
|
Name of the MOP circuit that corresponds to the data link circuit that
is to be used for communicating with this client.
device types (OpenVMS)
|
Default: No device types
|
Value: Set of device types
|
Specifies one or more device types associated with this client. Use
device types and omit addresses if you want to set up
a generic client entity; the entity will be used for any incoming load
or dump requests that specify a matching communications device type.
To determine the communications device type for a particular network
server, consult the server documentation, or use the Configuration
Monitor function of the MOP.
diagnostic image
|
Default: No file
|
Value: Sequence of file specifications
|
Files to be loaded when the client requests a diagnostic image during a
downline load operation. File identifications are interpreted according
to the file system of the local system.
dump address
|
Default: 1
|
Value: 0 to 2^
32-1
|
Memory address at which to begin an upline dump.
dump file
|
Default: No file
|
Value: Sequence of file specifications
|
Files to write to when the client is upline dumped. File
identifications are interpreted according to the file system of the
local system.
management image
|
Default: No file
|
Value: Sequence of file specifications
|
Files to be loaded when the client requests a management image during a
downline load operation. File identifications are interpreted according
to the file system of the local system.
phase iv client address
|
Default: 0.0
|
Value: Phase IV address
|
Phase IV node address given to the client system when it is downline
loaded. This address is passed in a load parameters message; whether it
is needed depends on the software being loaded.
phase iv client name
|
Default: No name
|
Value: Phase IV name
|
Phase IV node name given to the client system when it is downline
loaded. This name is passed in a load parameters message; whether it is
needed depends on the software being loaded.
phase iv host address
|
Default: 0.0
|
Value: Phase IV address
|
Phase IV node address to be passed as the host node address when a
client is downline loaded. This address is passed in a load parameters
message; whether it is needed depends on the software being loaded.
phase iv host name
|
Default: No name
|
Value: Phase IV name
|
Phase IV node name that is passed as the host name when the client is
downline loaded. This name is passed in a load parameters message;
whether it is needed depends on the software being loaded.
script file
|
Default: No file
|
Value: Sequence of file specifications
|
Files to be loaded when the client requests a CMIP initialization
script during a downline load operation. File identifications are
interpreted according to the file system of the local system.
secondary loader
|
Default: No file
|
Value: Sequence of file specifications
|
Files to be loaded when the client requests a secondary loader during a
downline load operation. File identifications are interpreted according
to the file system of the local system.
system image
|
Default: No file
|
Value: Sequence of file specifications
|
Files to be loaded when the client requests an operating system image
during a downline load operation. File identifications are interpreted
according to the file system of the local system.
tertiary loader
|
Default: No file
|
Value: Sequence of file specifications
|
Files to be loaded when the client requests a tertiary loader during a
downline load operation. File identifications are interpreted according
to the file system of the local system.
verification
|
Default: %x00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00
|
Value: Hex-string
|
Verification string to be sent in a boot message to this client. The
value must have an even number of digits from 2 to 16.
17.5.4 Identifier Attributes
name
Simple name assigned to the client when it is created.
17.5.5 Exception Messages
For create:
already exists
The mop client subentity already exists.
For boot, load, loop, query and
test:
data link error
An error was reported by the Data Link layer.
unrecognized circuit
There is no circuit with the specified identification.
For load, loop, query and test:
timeout
The operation has timed out.
For load:
protocol error
A protocol error occurred during the load operation.
For loop:
invalid assistant
The assistant address is either a multicast address, or the assistant
system was specified, and the corresponding client subentity has the
default value for its address on the loop command.
unrecognized assistant
There is no assistant with the specified identification on the
loop command.
Chapter 18
NSP Module
This chapter describes all the commands you can use to manage the
entities that constitute the NSP module. The NSP module implements one
of the protocols in the DNA Transport layer.
Figure 18-1 shows the hierarchical relationship of the entities that
constitute the NSP module.
Figure 18-1 Hierarchy of NSP Module Entities
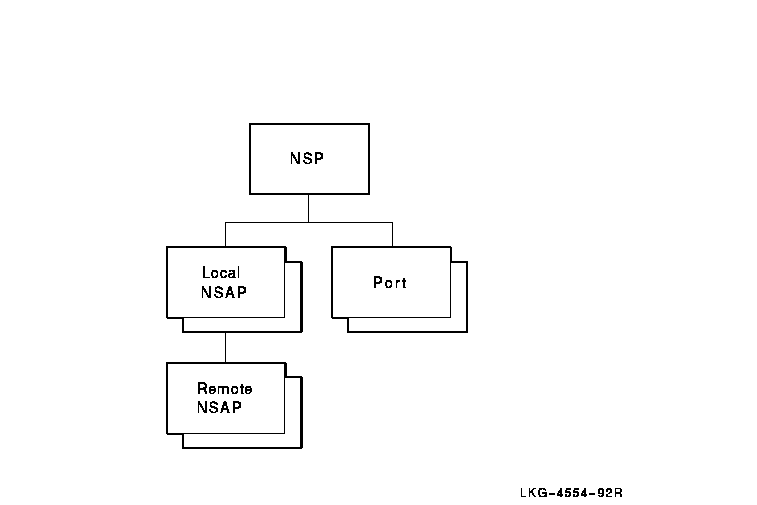
NSP performs the following functions:
- Enables the creation and destruction of transport connections used
for sending messages within a network node and between network nodes.
- Manages the movement of expedited and normal data from transmit
buffers to receive buffers, using flow control mechanisms.
- Breaks up normal data messages into segments that can be
transmitted individually, and reassembles these segments into correct
order after they have been received.
- Guarantees the delivery of data and control messages to a specified
destination using an error correction mechanism.
18.1 nsp
The nsp entity is the top-level entity in the hierarchy of
entities belonging to the NSP module.
create [node node-id] nsp
delete [node node-id] nsp
disable [node node-id] nsp
enable [node node-id] nsp
set [node node-id] nsp {congestion avoidance
boolean (Digital UNIX) | delay factor integer | delay
weight integer | flow control policy | keepalive time
seconds | maximum remote nsaps integer | maximum
receive buffers integer (OpenVMS) | maximum transport
connections integer | retransmit threshold integer }
show [node node-id] nsp [all [attributes] |
all characteristics | all status ]
18.1.1 Characteristic Attributes
acknowledgment delay time
|
Default: 3
|
Value for Digital UNIX: 3
|
|
Default: 3
|
Value for OpenVMS: 0--65
|
Maximum amount of time (in seconds) that an acknowledgment is to be
withheld. You cannot modify this characteristic.
congestion avoidance (Digital UNIX)
|
Default: True
|
Value: True or false
|
Enables the use of the automatic congestion avoidance mechanism. This
mechanism reduces the transport window size in response to an
indication from the Network layer.
delay factor
Factor by which to multiply the current value of the roundtrip
delay estimate status attribute in order to set a value for the
retransmission timer.
Note, the roundtrip delay estimate is an attribute of the
nsp port entity.
delay weight
Relative weighting to apply to the current estimate and to a new sample
when estimating round-trip delay.
dna version
|
Default: current version number
|
Version number of the DNA NSP architecture specification to which the
implementation conforms. You cannot modify this characteristic.
flow control policy
|
Default: Segment flow control
|
Value: Segment flow control, no flow control
|
Determines NSP flow control policy used. This attribute may not be
changed when NSP state is on.
Flow control is the mechanism that determines when to send a data or
expedited messages. Flow control is performed separately for normal and
expedited data. During transport connection formation, each end of the
connection determines the kind of flow control policy it expects when
acting as a data receiver. It is not required that both ends operate
with the same flow control policy.
keepalive time
|
Default for Digital UNIX: 30
|
Value: 1--65535
|
|
Default for OpenVMS: 60
|
Value: 1--65535
|
Time (in seconds) that NSP waits for data to be transmitted or received
before testing a transport connection. When this timer expires, NSP
sends a data request PDU to the remote NSP. This PDU does not change
the flow control parameters, but does require acknowledgment. For
Digital UNIX, you can modify this characteristic to a lower value only
when the entity is disabled.
maximum receive buffers (OpenVMS)
|
Default: 2000
|
Value: 1--65535
|
Maximum number of receive buffers that can store received transport
PDUs. You may not decrease the value while NSP is enabled.
maximum remote nsaps
|
Default for Digital UNIX: 160
|
Value: 1--65535
|
|
Default for OpenVMS: 201
|
Value: 1--65535
|
Maximum number of remote Network Services Access Points (NSAPs) that
can exist concurrently. Must be greater than the current value of
maximum transport connections. You can modify this
characteristic to a lower value only when the entity is disabled. For
Digital UNIX, this characteristic can be increased when enabled.
maximum transport connections
|
Default for Digital UNIX: 128
|
Value: 0--1023
|
|
Default for OpenVMS: 200
|
Value: 0--65535
|
Maximum number of active transport connections allowed at one time.
Must not be less than the current value of maximum remote NSAPs. You
may not decrease the value while NSP is enabled.
maximum window
|
Default for Digital UNIX: 32
|
Value: 1--65535
|
|
Default for OpenVMS: 8
|
Value: 1--2047
|
Maximum credit window that can be granted on a transport connection.
This is used for control of the number of data segments (PDUs) allowed
to be transmitted over a particular transport connection before at
least one acknowledgment must be returned from the destination system.
If the number of PDUs already transmitted equals the maximum
window and no corresponding acknowledgments have been received,
transport stops sending PDUs over the transport connection and waits
for an acknowledgment message. You cannot modify this characteristic.
nsap selector
|
Default: 32
|
Value: 0--255
|
NSAP selector used by the nsp entity when opening a port to a
network service. You cannot modify this characteristic.
retransmit threshold
|
Default: 12
|
Value: 1--65535
|
Maximum number of times a source nsp entity is to restart an
expired retransmission timer before the remote node is to be considered
unreachable. When the threshold is reached, NSP sets the confidence
variable to false.
18.1.2 Status Attributes
currently active connections
Number of active transport connections.
state
Status of the nsp entity.
|
off
|
The
nsp entity is disabled.
|
|
on
|
The
nsp entity is enabled.
|
uid
Entity's unique identifier, which is generated when the entity is
created.
18.1.3 Exception Messages
For create:
already exists
An nsp module already exists.
For delete:
wrong state
You cannot delete the entity while it is enabled.
For enable:
routing unavailable
You cannot enable the entity until routing has been created.
18.2 nsp local nsap
An nsp local nsap entity is created automatically for each
NSAP address used by the nsp entity. Local NSAPs are used
primarily to group together remote NSAPs (see the nsp local nsap
remote nsap entity). The nsap-address refers to the local
NSAP managed by this command.
show [node node-id] nsp local nsap
nsap-address [all [attributes] | all counters | all
identifiers | all status ]
18.2.1 Counter Attributes
creation time
Time this entity was created.
deleted remote nsaps
Number of times a remote NSAP has been deleted in order to reclaim
resources.
18.2.2 Identifier Attributes
name
Simple name assigned to the local NSAP when it is created.
nsap address
Address assigned to the local NSAP when it was created.
18.2.3 Status Attributes
uid
Entity's unique identifier, which is generated when the entity is
created.
18.2.4 Event Messages
deleted remote nsap
Generated each time a remote NSAP is deleted.
Arguments:
The event message lists all attributes for the deleted entity.
18.3 nsp local nsap remote nsap
An nsp local nsap remote nsap entity maintains the transport
counters and generates events resulting from interactions between its
superior local NSAP and a remote transport service. The local nsap
nsap-address refers to the local NSAP associated with the
specified remote NSAP. The remote nsap nsap-address refers to
the remote NSAP managed by this command.
show [node node-id] nsp local nsap
nsap-address remote nsap nsap-address [all
[attributes] | all counters | all identifiers | all status ]
18.3.1 Counter Attributes
connects received
Total number of connect initiated (CI) messages, regardless of their
disposition, that the local service provider has received from the
remote service provider.
connects sent
Total number of connect initiated (CI) messages sent by the local
service provider to the remote service provider, including
retransmissions.
creation time
Time this entity was created.
duplicate pdus received
Total number of all types of detected duplicate transport PDUs received
from the remote service provider.
pdus received
Total number of all types of transport PDUs received from the remote
service provider (excluding detected duplicates).
pdus sent
Total number of all types of transport PDUs sent to the remote service
provider (excluding retransmissions).
rejects received
Number of detected reject received events.
rejects sent
Number of detected reject sent events.
remote protocol errors
Number of detected remote protocol error events.
retransmitted pdus
Total number of all types of retransmitted transport PDUs sent to the
remote service provider.
total octets received
Total number of octets of all types of transport PDUs received from the
remote service provider, regardless of their disposition. This count
includes detected duplicates.
total octets sent
Total number of octets of all types of transport PDUs sent to the
remote service provider, including retransmissions.
user octets received
Total number of user data octets received from the remote service
provider, including normal, expedited, connect, accept, and disconnect
data. This count does not include duplicates such as data retransmitted
by the remote service provider.
user octets sent
Total number of user data octets sent to the remote service provider,
including normal, expedited, connect, accept, and disconnect data. This
count does not include data retransmitted by the local service provider.
user pdus discarded
Number of PDUs received from the remote service provider that were
discarded because of insufficient buffer space.
user pdus received
Total number of transport PDUs containing user data received from the
remote service provider, including normal, expedited, connect, accept,
and disconnect data. This count does not include duplicates such as
transport PDUs retransmitted by the remote service provider.
user pdus sent
Total number of transport PDUs containing user data sent to the remote
service provider, including normal, expedited, connect, accept, and
disconnect data. This count does not include retransmitted transport
PDUs.
18.3.2 Identifier Attributes
name
Simple name assigned to the remote NSAP when it is created.
nsap address
Address assigned to the remote NSAP when it was created.
18.3.3 Status Attributes
uid
Entity's unique identifier, which is generated when the entity is
created.
18.3.4 Event Messages
reject received
Generated when a connection attempt initiated by the local service
provider is rejected by the remote service provider. This does not
include rejects initiated by the remote user of the transport service.
The rejects received counter is incremented.
Arguments:
|
additional information
|
If applicable, contains additional information from the variable part
of the PDU.
|
|
reason
|
Reason why the event was generated.
|
|
|
no resources
|
Transport rejected the connection attempt because of insufficient
resources.
|
reject sent
Generated when a connection attempt initiated by the remote service
provider is rejected by the local service provider. This does not
include rejects requested by the local user of the transport service.
The rejects sent counter is incremented.
Arguments:
|
additional information
|
If applicable, contains additional information from the variable part
of the PDU.
|
|
reason
|
Reason why the event was generated.
|
|
|
no resources
|
Transport rejected the connection attempt because of insufficient
resources.
|
remote protocol error
Generated when a transport PDU received from the remote service
provider violates the NSP protocol. The remote protocol errors
counter is incremented.
Arguments:
|
erroneous transport data unit
|
Includes some, none, or all of the PDUs causing the event.
|
|
reason
|
Reason why the event was generated.
|
|
|
invalid flow control
|
A PDU was discarded because it contained flow control information that,
when used to compute the request count, would produce a result that
exceeds the limits. The entire PDU is provided in the
erroneous transport data unit argument.
|
|
|
invalid message format
|
A PDU was discarded because reserved bits or values were used in the
PDU. The beginning of the PDU is provided in the
erroneous transport data unit argument.
|
18.4 nsp port
An nsp port entity represents one end of a transport
connection and maintains status information about that connection. A
port is visible to the network only when it is assigned to a transport
connection. The port-name refers to the port managed by this
command.
show [node node-id] nsp port
port-name [all [attributes] | all counters | all identifiers |
all status ]
18.4.1 Counter Attributes
creation time
Time the port was assigned.
duplicate pdus received
Number of all types of detected duplicate transport PDUs received from
the remote service provider.
pdus received
Number of all types of transport PDUs received from the remote service
provider (excluding detected duplicates).
pdus sent
Number of all types of transport PDUs sent to the remote service
provider (excluding retransmissions).
retransmitted pdus
Number of all types of retransmitted transport PDUs sent to the remote
service provider.
total octets received
Number of octets of all types of transport PDUs received from the
remote service provider, regardless of their disposition. This count
includes detected duplicates.
total octets sent
Number of octets of all types of transport PDUs sent to the remote
service provider, including retransmissions.
user octets received
Number of user data octets received from the remote service provider,
including normal, expedited, connect, accept, and disconnect data. This
count does not include duplicates such as data retransmitted by the
remote service provider.
user octets sent
Number of user data octets sent to the remote service provider,
including normal, expedited, connect, accept, and disconnect data. This
count does not include data retransmitted by the local service provider.
user pdus received
Number of transport PDUs containing user data received from the remote
service provider, including normal, expedited, connect, accept, and
disconnect data. This count does not include duplicates such as
transport PDUs retransmitted by the remote service provider.
user pdus sent
Number of transport PDUs containing user data sent to the remote
service provider, including normal, expedited, connect, accept, and
disconnect data. This count does not include retransmitted transport
PDUs.
18.4.2 Identifier Attributes
name
Simple name assigned to the port when it is created.
18.4.3 Status Attributes
client name
|
Default: None
|
Value: Local-entity-name
|
Name designated by the port user when the port was opened.
incoming network priority (OpenVMS)
|
Default: None
|
Value: 0--255
|
Network priority encoded in NPDU header for all received packets.
local flow control policy
|
Default: None
|
Value: Segment flow control, no flow control
|
Local flow control policy selected when acting as a data receiver.
local nsap
|
Default: None
|
Value: NSAP address
|
Local NSAP address being used for the transport connection.
local reference
|
Default: None
|
Value: 0--65535
|
Unique reference number assigned to the transport connection by the
local transport service provider.
network port
|
Default: None
|
Value: Local-entity-name
|
Name of the port being used.
outgoing network priority (OpenVMS)
|
Default: None
|
Value: 0--255
|
Remote priority encoded in NPDU header for all transmitted packets.
remote flow control policy
|
Default: None
|
Value: Segment flow control, no flow control
|
Remote flow control policy selected when remote end is acting as a data
receiver.
remote nsap
|
Default: None
|
Value: NSAP address
|
Remote NSAP address being used for the transport connection.
remote reference
|
Default: None
|
Value: 0--65535
|
Reference number assigned to the transport connection by the remote
transport service provider.
round trip delay estimate
|
Default: None
|
Value: 0--65535
|
Amount of time, in milliseconds, of the round-trip delay on the
transport connection.
uid
Entity's unique identifier, which is generated when the entity is
created.
Chapter 19
OSAK Module
This chapter describes the commands you can use to manage the entities
that make up the OSAK (OSI Applications Kernel) module. The OSAK module
provides network control and management facilities for the OSAK
software. The OSAK software implements the ACSE (Association Control
Service Element) protocol of the Application layer, the Presentation
layer, and the Session layer of the OSI Reference Model.
Note
For Digital UNIX, you cannot modify any counter, identifier, or status
attributes within the OSAK module.
Previous
| Next
| Contents
| [Home]
| [Comments]
| [Ordering info]
| [Help]
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
NCL_PROFILE_016.HTML
OSSG Documentation
2-DEC-1996 12:48:12.58
Copyright © Digital Equipment Corporation 1996. All Rights Reserved.
Legal
![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)

![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)