![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
DECnet-Plus
Network Control Language Reference
Previous
| Contents
Argument:
|
NICE data
|
Phase IV event display
|
9.5 event dispatcher sink
An event dispatcher sink entity represents a sink. A sink
manages incoming connections and filters incoming events. Each sink
maintains a filter that is applied to all streams that are assigned to
that sink. The simple-name refers to the sink managed by this
command.
block [node node-id] event dispatcher sink
simple-name {global filter class-name, event-name |
specific filter instance-name, event-name }
create [node node-id] event dispatcher sink
simple-name maximum buffer size integer
delete [node node-id] event dispatcher sink
simple-name
disable [node node-id] event dispatcher sink
simple-name
enable [node node-id] event dispatcher sink
simple-name
ignore [node node-id] event dispatcher sink
simple-name {global filter class-name, event-name |
specific filter instance-name, event-name }
pass [node node-id] event dispatcher sink
simple-name {global filter class-name, event-name |
specific filter instance-name, event-name }
reset [node node-id] event dispatcher sink
simple-name
set [node node-id] event dispatcher sink
simple-name {catch-all filter action | client type
sinktype | device name filespec | description
latin1string | displayuids boolean | end user
end-user-spec | file name filespec | object name
full-name | template simple-name | user client
end-user-spec }
show [node node-id] event dispatcher sink
simple-name [all [attributes] | all characteristics | all
counters | all identifiers | all status ]
testevent [node node-id] event dispatcher
sink simple-name event instance-name, event-name
9.5.1 Commands
block
Sets the filters to block the specified events for the entity instance
or class. It causes the named events to be blocked.
ignore
Sets the filters to ignore the specified events for the entity instance
or class. The ignore directive causes the named events to be
ignored.
pass
Sets the filter to pass the specified events for the entity instance or
class. The pass directive causes the named events to be passed.
reset
Resets the catch-all, specific and global
filters to the default value. It causes these filters to be reset to
the values they had when the entity was created. It is equivalent to
setting the values for these filters to their defaults.
testevent
Tests the filter action state for the specified event. This directive
applies the filtering algorithm to the named event instance returning
the applicable FilterAction, and an indication of whether the
search was resolved by the SpecificFilter,
GlobalFilter, or CatchAllFilter attribute.
9.5.2 Arguments
class-name
Specifies the class name. The user may or may not include the node name.
event-name
Specifies all (for all events) or a specific event to be
filtered for the specified class or instance.
global filter
Specifies a class name, excluding all instance names (for example,
node, mop, circuit), and identifies the event to be blocked,
ignored, or passed. To block, ignore, or pass all events for the class,
specify all events instead of an individual event.
instance-name
Specifies a full entity name, including the node name and including a
specific instance.
maximum buffer size integer
This optional argument specifies the maximum number of octets to be
used for event processing of this sink. The current value is displayed
in the buffer size status attribute. You can specify a size
smaller than the implementation's default, provided it is still
sufficient to hold the events lost event. If the value
specified in this argument is inadequate for the events lost
event, an insufficient resources exception is returned.
specific filter
Specifies an entity, including instance names, and names of the event
to be blocked, ignored, or passed. To block, ignore, or pass all events
for this instance, specify all events instead of an individual
event.
9.5.3 Characteristic Attributes
catch all filter
|
Default: Pass
|
Value: Block or pass
|
Specifies the action to take if neither the specific filter setting nor
the global filter setting matches an event or if a filter setting that
does match an event is set to Ignore.
|
block
|
Discard the event.
|
|
pass
|
Report the event.
|
client type
|
Default: Console
|
Value: See description
|
Specifies the application to accept the events received by the sink.
This can only be set when the event dispatcher sink entity is
disabled (when the sink state is off).
|
console
|
Events go to the operator's console.
|
|
device
|
Events go to a device (refer to the
device name characteristic).
|
|
file
|
Events go to a file (refer to the
filename characteristic).
|
description
|
Default: Null
|
Value: Latin1String
|
Application description string.
device name
|
Default: Null
|
Value: Latin1String
|
Name of the device to which events are going to be logged, if the
client type of the sink is device.
displayuids
|
Default: True
|
Value: Boolean
|
A Boolean value indicating whether to include the UIDs when displaying
an event.
end user
|
Default: Number = 82
|
Value: End-user-specification
|
Sink Session Control end-user specification for this sink. For Digital
UNIX, do not modify this characteristic.
file name
|
Default for Digital UNIX: /usr/adm/event_file
|
Value: File specification
|
|
Default for OpenVMS:
SYS$MANAGER:NET$EVD_SINK_sinkname.LOG
|
Value: File specification
|
Name of the file to which events are going to be logged if the
client type of the sink is file.
global filter
Current global filter as it has been constructed by block,
ignore, and pass commands for this sink. By default,
the global filter is set to block all events for the following
entities: event dispatcher, event dispatcher sink,
and event dispatcher sink inbound stream. You cannot modify
this characteristic.
object name
|
Default: No sink object
|
Value: Full-name
|
Full DNS object name of the sink. Modifying this characteristic affects
only subsequent connect requests; existing connections are unaffected.
specific filter
|
Default: No specific filter
|
Current specific filter setting as constructed by block,
ignore and pass commands for this sink. You cannot modify
this characteristic.
template (Digital UNIX)
|
Default: No template
|
Value: Simple-name
|
Transport template (see the osi transport template entity) for
this sink's connections.
user client (Digital UNIX)
|
Default: Null
|
Value: End-user-specification
|
Session Control end-user specification for a user program that has been
set to receive events.
9.5.4 Counter Attributes
creation time
Time this entity was created.
connections accepted
Number of times a sink connection request was accepted by the sink
partner.
events filtered
Number of events for this sink that were filtered by its sink filter.
events lost
Number of events lost due to sink queue overflow.
filter changes
Number of times the filter has changed.
9.5.5 Identifier Attributes
name
Simple name assigned to the sink when it is created.
9.5.6 Status Attributes
buffer size
Maximum number of octets allowed for event processing of this sink.
This value is defined in the create command for the sink. This
value is limited by the value specified in the maximum buffer
size argument of the create command.
state
Status of the sink.
|
off
|
The sink is disabled.
|
|
on
|
The sink is enabled.
|
uid
Entity's unique identifier, which is generated when the entity is
created.
9.5.7 Event Messages
change filter
Generated each time the filter for a sink is changed, whether it is
changed by a block, ignore, or pass command
or by using set to change the value of the catch all
filter characteristic. The initial values of the filters for a
sink may be reported as arguments in the enable sink event. A
filter change event is filtered according to its new values.
Arguments: (for OpenVMS)
|
new catch all filter
|
Current catch-all filter setting.
|
|
new global filter
|
Current global filter setting.
|
|
new specific filter
|
Current specific filter setting.
|
|
old catch all filter
|
Previous catch-all filter setting.
|
|
old global filter
|
Previous global filter setting.
|
|
old specific filter
|
Previous specific filter setting.
|
events lost
Generated whenever the sink cannot allocate resources for event
transmission. The event-logging function guarantees that this event
cannot be lost. Also, you cannot block this event unless all events for
all modules are blocked.
This event is placed at the end of the queue. If another event cannot
be queued because of resource limitations while this event is still the
last event in the queue, the number argument is updated to reflect the
latest total of lost events.
Argument:
|
number
|
Number of consecutive events lost.
|
9.5.8 Exception Messages
For delete (Digital UNIX):
has children
Cannot delete while subentities exist.
wrong state
The attempt to delete the event dispatcher sink entity failed
because the sink must be disabled before deletion.
For block, pass, and ignore:
illegal element
The command did not include a class or instance
argument, or an argument contained one of the following illegal
elements: wildcard, node name, node class, illegal class.
For enable:
invalid name
Invalid name for DNA session.
9.6 event dispatcher sink inbound stream
The event dispatcher sink inbound stream entity is the
sink-side end of communication between an event dispatcher and a sink.
An inbound stream entity is dynamically created, enabled, disabled, and
deleted in tandem with the connection it represents.
disconnect [node node-id] event dispatcher
sink simple-name inbound stream simple-name
show [node node-id] event dispatcher sink
simple-name inbound stream simple-name [all
[attributes] | all counters | all identifiers | all status ]
9.6.1 Commands
disconnect
Requests the disconnection of the entity's stream connection. It
disconnects the entity's stream connection immediately. Event reports
in transit are lost and the sink cannot perform an orderly shutdown on
a stream.
9.6.2 Counter Attributes
creation time
Time at which this entity was created.
change confidence
Number of times the confidence variable has changed while connections
were in the on state.
9.6.3 Identifier Attributes
name
Local name assigned to the entity by its sink parent when it is
dynamically created.
9.6.4 Status Attributes
source end user
Source end-user specification, as provided by Session Control.
source node name
Name of the source node, as provided by Session Control.
state
Status of the inbound event stream.
|
off
|
The stream is disabled.
|
|
on connected
|
The stream is enabled and connected to the outbound stream.
|
uid
Entity's unique identifier, which is generated when the entity is
created.
9.6.5 Event Messages
change confidence
Generate when the underlying transport service detects that the
connection's confidence variable has changed to the new value reported
by the confidence parameter. This suggests a change in the connectivity
between the outbound stream and the sink.
Argument:
|
confidence
|
The new transport confidence value.
|
|
|
false
|
It is unlikely that a transmit operation would succeed under the
current circumstances.
|
|
|
true
|
It is likely that a transmit operation would succeed under the current
circumstances.
|
disconnect
Generated each time the sink detects that an inbound stream connection
has been closed. The disconnect can be caused by a management command,
a sink disconnect, a network failure, or by receiving notice that the
associated outbound stream entity has been shut down.
Arguments:
|
disconnect data
|
Identifies the cause of the disconnect.
|
|
reason
|
Specifies the Session Control layer reason for the disconnect.
|
|
shutdown received
|
Inbound stream disconnected because of a shutdown event.
|
Chapter 10
FDDI Module
This chapter describes all the commands you can use to manage the
entities that constitute the FDDI module. The FDDI module implements
one of multiple possible Link level/Network level modules in the OSI
layered architecture model.
The Digital Network Architecture (DNA) Fiber Distributed Data Interface
(FDDI) is the basis for the second generation of network interconnect
architecture for Digital. The FDDI module implements one of the
multiple possible Link level/Physical level modules in the OSI layered
architecture model. The FDDI Physical level includes high-speed,
125-megabaud, fiber-optic links that may be many kilometers in length.
The FDDI Link level provides a high-bandwidth, 100-megabit-per-second
local area network (LAN), and uses the ANSI standard FDDI Token Ring.
Figure 10-1 shows the hierarchical relationship of the entities that
constitute the FDDI module.
Figure 10-1 Hierarchy of FDDI Module Entities
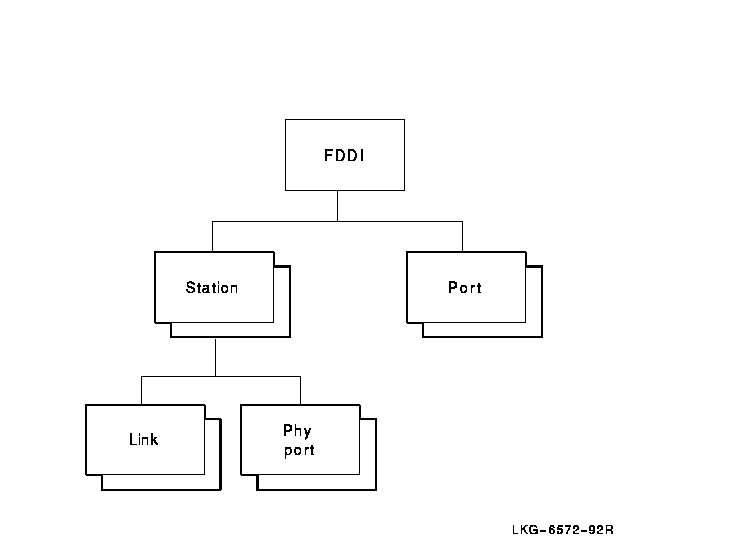
The FDDI module incorporates the functions and operations defined in
the ANSI FDDI Token Ring media access control (MAC), the ANSI FDDI
Token Ring Physical Layer Protocol (PHY), FDDI Physical Layer Medium
Dependent (PMD), Station Management (SMT) specifications, parts of the
ISO 8802-1 (IEEE 802.1) addressing, internetworking and network
management, and parts of the ISO 8802-2 (IEEE 802.2) logical link
control (LLC) specifications.
10.1 fddi
The fddi entity is the top-level entity in the hierarchy of
entities belonging to the FDDI module.
create [node node-id] fddi
delete [node node-id] fddi
show [node node-id] fddi [all [attributes] |
all characteristics ]
10.1.1 Characteristic Attributes
version
|
Default: Current version number
|
|
Version number of the FDDI architecture specification to which the
implementation conforms. You cannot modify this characteristic.
10.1.2 Exception Messages
For create:
already exists
An fddi entity already exists.
For delete:
has children
Cannot delete while subentities exist.
10.2 fddi station
An fddi station entity represents an access point to the
service offered by the FDDI module. The FDDI data link can be monitored
and controlled through DNA network management. The
station-name refers to the station managed by this command.
create [node node-id] fddi station
station-name communication port device-name
delete [node node-id] fddi station
station-name
disable [node node-id] fddi station
station-name
enable [node node-id] fddi station
station-name mode {normal | internal loopback }
show [node node-id] fddi station
station-name [all [attributes] | all characteristics | all
counters | all identifiers | all status ]
10.2.1 Arguments
communication port
The system device name assigned to this station.

The name must be in the format ddn, where dd is the
Digital UNIX device name prefix and n is the device
number.<>

The name must be in the format ddc, where dd is the
OpenVMS device name prefix and c is the controller
letter.<>
| Device Type |
Digital UNIX |
OpenVMS |
|
DEFAA
|
faa
|
fa
|
|
DEFEA
|
fta
|
fr
|
|
DEFTA
|
fta
|
fc
|
|
DEFPA
|
fta
|
|
|
DEFQA
|
|
fq
|
|
DEFZA
|
fza
|
fc
|
|
DEMFA
|
mfa
|
fx
|
|
FOCUS
|
|
fw
|
10.2.2 Characteristic Attributes
communication port
Name of the hardware port associated with this station, taken from the
corresponding argument in the create directive. You cannot
modify this characteristic.
smt maximum version id
Highest SMT version ID this station supports. You cannot modify this
characteristic.
smt minimum version id
Lowest SMT version ID this station supports. You cannot modify this
characteristic.
smt station id
SMT station ID for this station. You cannot modify this characteristic.
smt version id
Currently active SMT version ID for this station. You cannot modify
this characteristic.
type
SMT station type for this station. You cannot modify this
characteristic.
10.2.3 Counter Attributes
Unless stated otherwise, counts include both normal and multicast
traffic and all protocol types, service access points (SAPs), and
protocol identifiers.
configuration changes
Number of times the internal configuration of this station changed.
(Not present in single attached stations (SAS)).
creation time
Time at which the port was created.
selftest failures
Total number of times a self-test of the station detected an error.
traces received
Number of times the ECM state machine for this station entered the
trace state due to a received trace signal.
10.2.4 Identifier Attributes
name
Simple name assigned to the station when it is created.
10.2.5 Status Attributes
last set station id
The station ID of the station that last performed an SMT
Change/Add/Remove (PMF frame) operation.
state
|
Default: None
|
Value: Off, on or loopback
|
Operational state of the station.
uid
Entity's unique identifier, which is generated when the entity is
created.
10.2.6 Event Messages
configuration change
Internal configuration of the station changed.
selftest failure
An implementation-specific code giving the reason for the station
failure. Values are listed in the DNA registry.
trace received
ECM state machine of the station entered the trace state due
to a trace signal received on any PHY port.
10.2.7 Exception Messages
For create:
already exists
An fddi station entity already exists.
For enable:
communication port in use
Communication port already reserved by another entity.
invalid communication port
Cannot run FDDI data link on this communications port.
For delete:
wrong state
Failure to delete the fddi station entity because the station
must be disabled before deletion.
10.3 fddi station link
The fddi station link entity is a subentity of the fddi
station entity. The fddi station link subentity provides
the management view of LLC and the FDDI MAC. FDDI allows stations to be
either single MAC or dual MAC and therefore there can be up to two
link subentities for each station. In most cases, a station
has at least one link entity. Concentrators may have no
link entity and are not addressable on the FDDI, though they
may be using other communications channels.
disable [node node-id] fddi station
station-name link link-index
echo [node node-id] fddi station
station-name link link-index target lan
address timeout integer-16 data octet-string
enable [node node-id] fddi station
station-name link link-index
getnif [node node-id] fddi station
station-name link link-index target lan
address timeout integer-16
getsif [node node-id] fddi station
station-name link link-index target lan
address timeout integer-16 type {configuration |
operation }
show [node node-id] fddi station
station-name link link-index [all [attributes] | all
characteristics | all counters | all identifiers | all status ]
10.3.1 Commands (Digital UNIX)
echo
Causes the link subentity to transmit an SMT Echo request
frame and await the response. If a response is received, it is
displayed.
getnif
Causes the link subentity to transmit an SMT NIF (Neighbor
Information) request frame and await the response. If a response is
received, it is displayed.
getsif
Causes the link subentity to transmit an SMT SIF (Station
Information) request frame and await the response. If a response if
received, it is displayed.
10.3.2 Arguments
data
Data to transmit in echo request.
target
48-bit LAN address of the target.
timeout
|
Default: None
|
Value: 1--65535
|
Timeout in seconds.
type
|
Default: None
|
Value: Configuration or operation
|
SIF configuration or SIF operation request.
10.3.3 Characteristic Attributes
link address
MAC address assigned during manufacture of the communication hardware
that is associated with the station (read-only).
requested trt
|
Default: 8
|
Value: 1--65535
|
Requested token rotation timer. For OpenVMS, the default is determined
by the operating system, and this characteristic cannot be set.
restricted token timeout
|
Default: 1000
|
Value: 1--65535
|
Length limit of a restricted token dialog. For OpenVMS, the default is
determined by the operating system, and this characteristic cannot be
set.
ring purger enable
|
Default: True
|
Value: True or false
|
Controls whether this station is eligible to be a ring purger and
should participate in the ring purger election. For OpenVMS, the
default is determined by the operating system, and this characteristic
cannot be set.
valid transmission time
|
Default: 3.4
|
Value: 1--65535
|
Valid transmission time. For OpenVMS, the default is determined by the
operating system, and this characteristic cannot be set.
10.3.4 Counter Attributes
block check errors
Number of times a received frame containing an integral number of
octets failed the FCS check.
creation time
Time at which the station was created.
directed beacons received
Number of times the link detected the directed beacon process.
duplicate address test failures
Number of times the duplicate address test failed (detected that the
link address was a duplicate).
duplicate tokens detected
Number of times the MAC address test failed (detected that the link
address was a duplicate).
error count
Total number of frames that were in error with the E indicator
reset, indicating that the error occurred between the upstream
MAC and this one.
fci strip errors
Number of times a frame content independent strip operation
(bridge strip) was terminated by receipt of a token.
frame count
Total number of frames seen by this link, other than tokens.
frame status errors
Number of times a received frame had the E indicator in error (missing
or set) and the FCS was correct.
lost count
Counter lost count.
multicast octets received
Number of multicast data octets that were received successfully in
multicast frames of type LLC, implementer, reserved, or SMT. The count
does not include the MAC envelope.
multicast octets sent
Number of multicast data octets that were sent successfully in
multicast frames of type LLC, implementer, reserved, or SMT. The count
does not include the MAC envelope.
multicast pdus received
Number of multicast frames that were received successfully of type LLC,
implementer, reserved, or SMT.
multicast pdus sent
Number of multicast frames that were sent successfully of type LLC,
implementer, reserved, or SMT.
octets received
Number of octets received successfully in frames of type LLC,
implementer, reserved, or SMT. The count does not include the MAC
envelope.
octets sent
Number of octets sent successfully in frames of type LLC, implementer,
reserved, or SMT. The count does not include the MAC envelope.
pdu length errors
Number of times a received frame had an invalid length, either too long
or short for the type, or had an alignment error (odd number of
symbols).
pdus received
Number of frames received successfully in frames of type LLC,
implementer, reserved, or SMT.
pdus sent
Number of frames sent successfully in frames of type LLC, implementer,
reserved, or SMT.
receive data overruns
Number of times the hardware lost one or more consecutive, only
partially complete incoming frames because it was unable to keep up
with the medium rate. An example is overrun of a bit or octet FIFO
queue because of inability to copy data from adapter to host promptly.
In conjunction with total frames received, provides a measure of
hardware resource and bandwidth failures.
ring beacons initiated
Number of times the ring beacon process was initiated by this link.
ring initializations initiated
Number of times a ring reinitialization was initiated by this link.
ring initializations received
Number of times a ring reinitialization was initiated by some other
link.
ring purge errors
Number of times the ring purger received a token while still in the
ring purge state.
token count
Number of times a token has been seen by this link.
traces initiated
Number of times the pc_trace process was initiated by this
link.
transmit failures
Number of times a transmit error, other than underrun, occurred. This
does not include errors in transmitting MAC type frames.
transmit underruns
Number of times a transmit underrun occurred. This indicates the
transmit FIFO became empty during frame transmission.
unavailable link buffers
Number of times a complete, fully received frame was discarded because
no link buffer was available. In conjunction with total frames
received, provides a measure of station-buffer-related receive problems.
unavailable user buffers
Number of times no user buffer was available for an incoming frame that
passed all filtering for the port. These are the buffers supplied by
users on receive requests. In conjunction with total frames
received, provides a measure of user-buffer-related receive problems.
unrecognized individual destination pdus
Number of times a received LLC frame with an individual destination MAC
address was discarded because there was no port with the Ethernet
protocol type, SNAP protocol identifier, or LLC SAP address enabled.
Only frames containing individual destination MAC addresses are counted.
unrecognized multicast destination pdus
Number of times a received LLC frame with a multicast destination MAC
address was discarded because there was no port with the Ethernet
protocol type, SNAP protocol identifier, or LLC SAP address enabled.
Only frames containing multicast destination MAC addresses are counted.
10.3.5 Identifier Attributes
index
An integer that uniquely identifies this link to the parent
station entity.
10.3.6 Status Attributes
downstream neighbor
MAC address of the downstream neighbor, if known.
duplicate address flag
Summary output of the duplicate address test algorithm.
frame strip mode
Current frame-stripping mode of the MAC.
|
SA match
|
Source address match mode of the frame stripping algorithm matches the
source address of the frame with the MAC's MyLongAddress (MLA), and if
a match is found, the frame is removed from the token ring.
|
|
FCI strip
|
The FCI strip mode counts the number of frames transmitted since the
reception of a token, and strips equal number of frames.
|
loopback
This is true if the link has been set up to receive frames
transmitted by it. This allows loopback testing either on the ring or
with one of the PHY port loopback modes.
negotiated trt
Negotiated token rotation timer.
old downstream neighbor
Previous value of the downstream neighbor.
old upstream neighbor
Previous value of the upstream neighbor.
ring error reason
Reason code for the most recent link error.
|
directed beacon received
|
Link received particular beacon data.
|
|
duplicate address detected
|
Duplicate address algorithm detected a duplicate address.
|
|
duplicate token detected
|
A duplicate token was detected on the ring.
|
|
FCI strip error
|
Frame content independent strip operation was terminated by the receipt
of a token.
|
|
no error
|
No errors have occurred on this ring.
|
|
PC trace initiated
|
PC-trace was initiated by this link.
|
|
PC trace received
|
PC-trace was initiated by some other link.
|
|
ring beaconing initiated
|
Ring beaconing process was initiated by this link. This process is
initiated as a result of serious ring failure, such as loss of signal
or jabbering station transmitting in violation of the protocol. This
indicates to other links on the LAN that corrective action may be
required.
|
|
ring init initiated
|
Ring initialization was initiated by this link to initialize the ring
and create a token.
|
|
ring init received
|
Ring initialization was initiated by some other link to initialize the
ring and create a token.
|
|
ring op oscillation
|
Ring state has been changing continually from operational to
initializing.
|
|
ring purge error
|
Link received a token while performing a ring purge operation.
|
ring latency
Current ring latency as measured by this link entity.
ring purger state
State of the ring purger election process.
|
candidate
|
The link's ring purger process is participating in the ring purger
election algorithm as a candidate to become the ring purger.
|
|
nonpurger
|
The link's ring purger process is in an idle state listening for
periodic purger hello frames.
|
|
off
|
The link's ring purger process is disabled.
|
|
purger
|
The link's ring purger process is performing the function of removing
no owner frames and duplicate token from the ring. In this state, the
process transmits periodic purger hello frames.
|
state
State of the link entity.
|
broken
|
Attempt to turn the link on failed the initialization test, or link was
on, but failure was detected.
|
|
off-fault recovery
|
State entered when a
link entity detects conditions that indicate faulty ring.
|
|
off-ready
|
FDDI data link communication services are not available.
|
|
on-ring init
|
Physical layer service is available and the
link entity enabled.
|
|
on-ring run
|
Link detected that the ring initialization has been completed
successfully and the ring is operational.
|
uid
Entity's unique identifier, which is generated when the entity is
created.
upstream neighbor address
MAC address of the upstream neighbor, if known.
upstream neighbor duplicate address flag
|
Default: None
|
Value: True or false
|
Upstream neighbor's reported result of its duplicate address test.
Previous
| Next
| Contents
| [Home]
| [Comments]
| [Ordering info]
| [Help]
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
NCL_PROFILE_008.HTML
OSSG Documentation
2-DEC-1996 12:47:52.36
Copyright © Digital Equipment Corporation 1996. All Rights Reserved.
Legal
![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)



![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)