![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table SYS-14.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table SYS-14.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table SYS-14.
The process name string is blank-padded for the comparison unless the item-specific flag PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH is present.
Because the information is a character string, the selection value is passed by reference. The length of the selection value is placed in the first word of the item descriptor and the address of the buffer is placed in the second longword.
Although the current length of the process name field is 15 bytes, the PSCAN$_PRCNAM buffer can be up to 64 bytes in length. If the buffer length is 0 or greater than 64, the SS$_IVBUFLEN error is returned.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table SYS-14.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table SYS-14.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table SYS-14.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table SYS-14.
This bit mask item code uses an immediate value descriptor; the selection value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table SYS-14.
Because the information is a character string, the selection value is passed by reference. The length of the selection value is placed in the first word of the item descriptor and the address of the buffer is placed in the second longword.
Although the current length of the terminal name field is 8 bytes, the PSCAN$_TERMINAL buffer can be up to 64 bytes in length. If the buffer length is 0 or greater than 64, the SS$_IVBUFLEN error is returned.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table SYS-14.
This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table SYS-14.
The user name string is blank-padded for the comparison unless the item-specific flag PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH is present.
Because the information is a character string, the selection value is passed by reference. The length of the selection value is placed in the first word of the item descriptor and the address of the buffer is placed in the second longword.
Although the current length of the user name field is 12 bytes, the PSCAN$_USERNAME buffer can be up to 64 bytes in length. If the buffer length is 0 or greater than 64, the SS$_IVBUFLEN error is returned.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table SYS-14. Item-Specific Flags Table SYS-14 lists the flags and the item codes that can be used together. The flags are described in the section following the table.
| Item-Specific Flag | Description | Common to the Following $PROCESS_SCAN Item Codes |
|---|---|---|
| PSCAN$M_BIT_ALL | All bits set in pattern set in target | _CURPRIV |
| PSCAN$M_BIT_ANY | Any bit set in pattern set in target | _STS |
| PSCAN$M_CASE_BLIND | Match without regard to case of letters | _ACCOUNT |
| PSCAN$M_EQL | Match value exactly (the default) |
All except
_BUFFER_SIZE |
| PSCAN$M_GEQ | Match if value is greater than or equal to | _AUTHPRI |
| PSCAN$M_GTR | Match if value is greater than | _GRP |
| PSCAN$M_LEQ | Match if value is less than or equal to | _JOBPRCCNT |
| PSCAN$M_LSS | Match if value is less than | _PRI |
| _PRIB | ||
| PSCAN$M_NEQ | Match if value is not equal |
All except
_BUFFER_SIZE |
| PSCAN$M_OR | Match this value or the next value |
All except
_BUFFER_SIZE |
| PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH | Match on leading substring | _HW_NAME |
| PSCAN$M_WILDCARD | Match a wildcard pattern |
_NODENAME
_PRCNAM _TERMINAL _USERNAME |
PSCAN$M_BIT_ALL
If the PSCAN$M_BIT_ALL flag is used, all bits set in the pattern mask specified by the item descriptor must also be set in the process mask. Other bits in the process mask can also be set.For item codes that describe bit masks, such as privilege masks and status words, this flag controls how the pattern bit mask specified by the item descriptor is compared with that in the process. By default, the bit masks are compared for equality.
The PSCAN$M_BIT_ALL flag is used only with bit masks.
PSCAN$M_BIT_ANY
If the PSCAN$M_BIT_ANY flag is used, a match occurs if any bit in the pattern mask is also set in the process mask.For item codes that describe bit masks, such as privilege masks and status words, this flag controls how the pattern bit mask specified by the item descriptor is compared with that in the process. By default, the bit masks are compared for equality.
The PSCAN$M_BIT_ANY flag is used only with bit masks.
PSCAN$M_CASE_BLIND
When you specify PSCAN$M_CASE_BLIND to compare the character string specified by the item descriptor with the character string value from the process, $PROCESS_SCAN does not distinguish between uppercase and lowercase letters.The PSCAN$M_CASE_BLIND flag is used only with character-string item codes. The PSCAN$M_CASE_BLIND flag can be specified with either the PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH flag or the PSCAN$M_WILDCARD flag.
PSCAN$M_EQL
When you specify PSCAN$M_EQL, $PROCESS_SCAN compares the value specified by the item descriptor with the value from the process to see if there is an exact match.PSCAN$M_EQL and PSCAN$M_NEQ are used with bit masks, character strings, and integers to control how the item is interpreted. Only one of the flags can be specified; if more than one of these flags is used, the SS$_BADPARAM error is returned. If you want to specify that bits not set in the pattern mask must not be set in the process mask, use PSCAN$M_EQL.
PSCAN$M_GEQ
When you specify PSCAN$M_GEQ, $PROCESS_SCAN selects a process if the value from the process is greater than or equal to the value specified by the item descriptor.PSCAN$M_GEQ, PSCAN$M_GTR, PSCAN$M_LEQ, and PSCAN$M_LSS are used with integer item codes only. Only one of these four flags can be specified; if more than one of these flags is used, the SS$_BADPARAM error is returned.
PSCAN$M_GTR
When you specify PSCAN$M_GTR, $PROCESS_SCAN selects a process if the value from the process is greater than the value specified by the item descriptor.PSCAN$M_GEQ, PSCAN$M_GTR, PSCAN$M_LEQ, and PSCAN$M_LSS are used with integer item codes only. Only one of these four flags can be specified; if more than one of these flags is used, the SS$_BADPARAM error is returned.
PSCAN$M_LEQ
When you specify PSCAN$M_LEQ, $PROCESS_SCAN selects a process if the value from the process is less than or equal to the value specified by the item descriptor.PSCAN$M_GEQ, PSCAN$M_GTR, PSCAN$M_LEQ, and PSCAN$M_LSS are used with integer item codes only. Only one of these four flags can be specified; if more than one of these flags is used, the SS$_BADPARAM error is returned.
PSCAN$M_LSS
When you specify PSCAN$M_LSS, $PROCESS_SCAN selects a process if the value from the process is less than the value specified by the item descriptor.PSCAN$M_GEQ, PSCAN$M_GTR, PSCAN$M_LEQ, and PSCAN$M_LSS are used with integer item codes only. Only one of these four flags can be specified; if more than one of these flags is used, the SS$_BADPARAM error is returned.
PSCAN$M_NEQ
When you specify PSCAN$M_NEQ, $PROCESS_SCAN selects a process if the value from the process is not equal to the value specified by the item descriptor.PSCAN$M_EQL and PSCAN$M_NEQ are used with bit masks, character strings, and integers to control how the item is interpreted. Only one of the flags can be specified; if more than one of these flags is used, the SS$_BADPARAM error is returned.
PSCAN$M_OR
When you specify PSCAN$M_OR, $PROCESS_SCAN selects processes whose values match the current item descriptor or the next item descriptor. The next item descriptor must have the same item code as the item descriptor with the PSCAN$M_OR flag. Multiple items are chained together; all except the last item descriptor must have the PSCAN$M_OR flag.The PSCAN$M_OR flag can be specified with any other flag and can be used with bit masks, character strings, and integers. If the PSCAN$M_OR flag is used between different item codes, or if it is missing between identical item codes, the SS$_BADPARAM error is returned.
PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH
When you specify PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH, $PROCESS_SCAN compares the character string specified in the item descriptor to the leading characters of the requested process value.For example, to find all process names that start with the letters AB, use the string AB with the PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH flag. If you do not specify the PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH flag, the search looks for a process with the 2-character process name AB.
The PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH flag also allows either the PSCAN$M_EQL or the PSCAN$M_NEQ flag to be specified. If you specify PSCAN$M_NEQ, the service matches those names that do not begin with the specified character string.
The PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH flag is used only with character string item codes. The PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH flag cannot be specified with the PSCAN$M_WILDCARD flag; if both of these flags are used, the SS$_BADPARAM error is returned.
PSCAN$M_WILDCARD
When you specify PSCAN$M_WILDCARD, the character string specified by the item descriptor is assumed to be a wildcard pattern. Acceptable wildcard characters are the asterisk (*), which allows the match to substitute any number of character in place of the asterisk, and the percent sign (%), which allows the match to substitute any one character in place of the percent sign. For example, if you want to search for all process names that begin with the letter A and end with the string ER, use the string A*ER with the PSCAN$M_WILDCARD flag. If the PSCAN$M_WILDCARD flag is not specified, the search looks for the 4-character process name A*ER.The PSCAN$M_WILDCARD is used only with character string item codes. The PSCAN$M_WILDCARD flag cannot be specified with the PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH flag; if both of these flags are used, the SS$_BADPARAM error is returned. The PSCAN$M_NEQ flag can be used with PSCAN$M_WILDCARD to exclude values during a wildcard search.
The following restrictions apply to the flags above:
The Process Scan system service creates and initializes a process context that is used by $GETJPI to scan processes on the local system or across the nodes in an OpenVMS Cluster system. An item list is used to specify selection criteria to obtain information about specific processes, for example, all processes owned by one user or all batch processes.The output of the $PROCESS_SCAN service is a process context longword named pidctx. This process context is then provided to $GETJPI as the pidadr argument. The process context provided by $PROCESS_SCAN enables $GETJPI to search for processes across the nodes in an OpenVMS Cluster system and to select processes that match certain selection criteria.
The process context consumes process dynamic memory. This memory is deallocated when the end of the context is reached. For example, when the $GETJPI service returns SS$_NOMOREPROC or when $PROCESS_SCAN is called again with the same pidctx longword, the dynamic memory is deallocated. If you anticipate that a scan might be interrupted before it runs out of processes, $PROCESS_SCAN should be called a second time (without an itmlst argument) to release the memory. Dynamic memory is automatically released when the current image terminates.
$PROCESS_SCAN copies the item list and user buffers to the allocated dynamic memory. This means that the item lists and user buffers can be deallocated or reused immediately; they are not referenced during the calls to $GETJPI.
The item codes referenced by $PROCESS_SCAN are found in data structures that are always resident in the system, primarily the process control block (PCB) and the job information block (JIB). A scan of processes never forces a process that is swapped out of memory to be brought into memory to read nonresident information.
Required Access or Privileges
Required Quota
See the description for the PSCAN$_GETJPI_BUFFER_SIZE item.
Related Services
$CANEXH, $CREPRC, $DCLEXH, $DELPRC, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW, $HIBER, $RESUME, $SETPRI, $SETPRN, $SETPRV, $SETRWM, $SUSPND, $WAKE
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The pidctx argument cannot be written by the caller; the item list cannot be read by the caller; or a buffer for a reference descriptor cannot be read. SS$_BADPARAM The item list contains an invalid item identifier, or an invalid combination of item-specific flags is present. Or, an item list containing both 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries was found. SS$_IVBUFLEN The buffer length field is invalid. For immediate value descriptors, the buffer length must be 0. For reference descriptors, the buffer length cannot be 0 or longer than the maximum for the specified item code. This error is also returned if the total length of the item list plus the length of all of the buffer fields is too large to process. SS$_IVSSRQ The pidctx argument was not supplied, or the item list is improperly formed (for example, multiple occurrences of a given item code were interspersed with other item codes).
Removes a specified range of pages from the current working set of the calling process to make room for pages required by a new program segment.
SYS$PURGWS inadr
int sys$purgws (struct _va_range *inadr);
inadr
OpenVMS usage: address_range type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Starting and ending virtual addresses of the range of pages to be purged. The inadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual addresses. The addresses are adjusted up or down to fall on CPU-specific page boundaries. Only the virtual page number portion of each virtual address is used; the low-order byte-within-page bits are ignored.
The Purge Working Set service removes a specified range of pages from the current working set of the calling process to make room for pages required by a new program segment. However, the Adjust Working Set Limit ($ADJWSL) service is the preferred mechanism for controlling a process's use of physical memory resources.The $PURGWS service locates pages within the specified range and removes them if they are in the working set.
If the starting and ending virtual addresses are the same, only that single page is purged.
To purge the entire working set, specify a range of pages from 0 through 7FFFFFFF; in this case, the image continues to execute and pages are faulted back into the working set as they are needed.
Required Access or Privileges
Required Quota
Related Services
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRETVA, $CRMPSC, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET, $MGBLSC, $SETPRT, $SETSTK, $SETSWM, $ULKPAG, $ULWSET, $UPDSEC, $UPDSECW
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The input address array cannot be read by the caller.
On Alpha systems, removes a specified range of pages from the current working set of the calling process to make room for pages required by a new program segment.This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$PURGE_WS start_va_64 ,length_64
int sys$purge_ws (void *start_va_64, unsigned __int64 length_64);
start_va_64
OpenVMS usage: address type: quadword address access: read only mechanism: by value
The starting virtual address of the pages to be purged from the working set. The specified virtual address will be rounded down to a CPU-specific page boundary.length_64
OpenVMS usage: byte count type: quadword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Length of the virtual address space to be purged from the working set. The specified length will be rounded up to a CPU-specific page boundary so that it includes all CPU-specific pages in the requested range.
The Purge Working Set service removes a specified range of pages from the current working set of the calling process to make room for pages required by a new program segment. However, the Adjust Working Set Limit ($ADJWSL) service is the preferred mechanism for controlling a process's use of physical memory resources.The $PURGE_WS service locates pages within the specified range and removes them if they are in the working set. To purge the entire working set, specify a range of pages from 0 through FFFFFFFF.FFFFFFFF (or to the highest possible process private virtual address, available from $GETJPI); in this case, the image continues to execute, and pages are faulted back into the working set.
Required Privileges
Required Quota
Related Services
$ADJWSL, $LCKPAG_64, $LKWSET_64, $PURGWS, $ULKPAG_64, $ULWSET_64
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully.
Writes informational and error messages to processes.On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$PUTMSG msgvec ,[actrtn] ,[facnam] ,[actprm]
int sys$putmsg (void *msgvec, void (*actrtn)(__unknown_params), void *facnam, unsigned __int64 actprm);
msgvec
OpenVMS usage: cntrlblk type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit reference (VAX)
Message argument vector specifying the message or messages to be written and options that $PUTMSG is to use in writing the message or messages. The msgvec argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) of the message vector.The message vector consists of one longword followed by one or more message descriptors, one descriptor per message. The following diagram depicts the contents of the first longword.
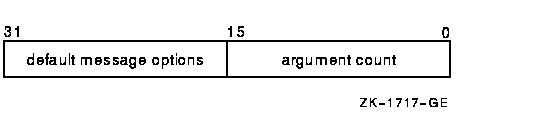
The following table describes the message vector fields.
Descriptor Field Definition Argument count This word-length field specifies the total number of longwords in the message vector, not including the first longword (of which it is a part). Default message options This word-length field specifies which message component or components are to be written. The default message options field is a word-length bit vector wherein a bit, when set, specifies that the corresponding message component is to be written. For a description of each of these components, refer to the Description section. The following table shows the significant bit numbers. Note that the bit numbers shown (0, 1, 2, 3) are the bit positions from the beginning of the word; however, because the word is the second word in the longword, you should add the number 16 to each bit number to specify its exact offset within the longword.
Bit Value Description 0 1
0Include message text
Do not include message text1 1
0Include mnemonic name for message text
Do not include mnemonic name for message text2 1
0Include severity level indicator
Do not include severity level indicator3 1
0Include facility prefix
Do not include facility prefixBits 4 through 15 must be 0.
You can override the default setting specified by the default message options field for any or all messages by specifying different options in the new message options field of any subsequent message descriptor. When you specify new message options, the options it specifies become the new default settings for all remaining messages until you specify new message options again.
The $PUTMSG service passes the default message options field to the $GETMSG service as the flags argument.
If you specify the default message options field as 0, the default message options for the process are used; you can set the process default message options by using the DCL command SET MESSAGE.
The Description section shows the format that $PUTMSG uses to write these message components.
Message Descriptors
Following the first longword of the message vector are one or more message descriptors. A message descriptor can have one of four possible formats, depending on the type of message it describes. There are four types of messages:The following diagrams depict the message descriptors for each type of message.
- User-supplied
- System
- OpenVMS RMS
- System exception
Previous | Next | Contents | [Home] | [Comments] | [Ordering info] | [Help]
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
4527P060.HTM OSSG Documentation 22-NOV-1996 13:00:20.80Copyright © Digital Equipment Corporation 1996. All Rights Reserved.