![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
Because the rights database is an indexed file accessed with OpenVMS RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated with operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status codes, refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
Applies the hash algorithm you select to an ASCII password string and returns a quadword hash value that represents the encrypted password.
SYS$HASH_PASSWORD pwd ,alg ,[salt] ,usrnam ,hash
int sys$hash_password (void *pwd, unsigned char alg, unsigned short int salt, void *usrnam, struct _generic_64 *hash);
pwd
OpenVMS usage: char_string type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by descriptor---fixed-length string descriptor
ASCII password string to be encrypted. The pwd argument is the address of a character string descriptor pointing to the ASCII password. The password string can contain between 1 and 32 characters and use the uppercase characters A through Z, the numbers 0 through 9, the dollar sign ($), and the underscore (_).alg
OpenVMS usage: byte_unsigned type: byte (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Algorithm used to hash the ASCII password string. The alg argument is an unsigned byte specifying the hash algorithm. The operating system recognizes the following algorithms.
Symbolic Name Description UAI$K_AD_II Uses a CRC algorithm and returns a longword hash value. This algorithm was used in releases prior to VAX VMS Version 2.0. UAI$C_PURDY Uses a Purdy algorithm over salted input. It expects a blank-padded user name and returns a quadword hash value. This algorithm was used during VAX VMS Version 2.0 field test. UAI$C_PURDY_V Uses the Purdy algorithm over salted input. It expects a variable-length user name and returns a quadword hash value. This algorithm was used in releases prior to VMS Version 5.4. UAI$K_PURDY_S Uses the Purdy algorithm over salted input. It expects a variable-length user name and returns a quadword hash value. This algorithm is used to hash all new passwords in VMS Version 5.4 and later. UAI$C_PREFERED_ALGORITHM¹ Represents the latest encryption algorithm that the operating system uses to encrypt new passwords. Currently, it equates to UAI$C_PURDY_S. Digital recommends that you use this symbol in source modules because it always equates with the most recent algorithm.
¹ The value of this symbol might be changed in future releases if an additional algorithm is introduced.
Values ranging from 128 to 255 are reserved for customer use; the constant UAI$K_CUST_ALGORITHM defines the start of this range.
You can use the UAI$_ENCRYPT and UAI$_ENCRYPT2 item codes with the $GETUAI system service to retrieve the primary and secondary password hash algorithms for a user.
salt
OpenVMS usage: word_unsigned type: word (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Value used to increase the effectiveness of the hash. The salt argument is an unsigned word containing 16 bits of data that is used by the hash algorithms when encrypting a password for the associated user name. The $GETUAI item code UAI$_SALT is used to retrieve the SALT value for a given user. If you do not specify a SALT value, $HASH_PASSWORD uses the value of 0.usrnam
OpenVMS usage: char_string type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by descriptor---fixed-length string descriptor
Name of the user associated with the password. The usrnam argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to a character text string containing the user name. The current password encryption algorithm (UAI$C_PURDY_S) folds the user name into the ASCII password string to ensure that different users with the same password produce different hash values. This argument must be supplied for all calls to $HASH_PASSWORD but is ignored when using the CRC algorithm (UAI$C_AD_II).hash
OpenVMS usage: quadword_unsigned type: quadword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by reference
Output hash value representing the encrypted password. The hash argument is the address of an unsigned quadword to which $HASH_PASSWORD writes the output of the hash. If you use the UAI$C_AD_II algorithm, the second longword of the hash is always set to 0.
The Hash Password service applies the hash algorithm you select to an ASCII password string and returns a quadword hash value that represents the encrypted password.Required Access or Privileges
Required Quota
Related Services
$GETUAI, $SETUAI.
Use $GETUAI to get the values for the salt and alg arguments. Use $SETUAI to store the resulting hash using the item codes UAI$_PWD and UAI$_PWD2.
For more information, see the appendix on implementing site-specific security policies in the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The input or output buffer descriptors cannot be read or written to by the caller. SS$_BADPARAM The specified hash algorithm is unknown or invalid.
Allows a process to make itself inactive but to remain known to the system so that it can be interrupted; for example, to receive ASTs.
SYS$HIBER
int sys$hiber (void);
None.
The Hibernate service allows a process to make itself inactive but to remain known to the system so that it can be interrupted; for example, to receive ASTs. A hibernate request is a wait-for-wake-event request. When you call the Wake Process from Hibernation ($WAKE) service or when the time specified with the Schedule Wakeup ($SCHDWK) service occurs, the process continues execution at the instruction following the Hibernate call.In VAX MACRO, you can call the Hibernate service only by using the $name_S macro.
A hibernating process can be swapped out of the balance set if it is not locked into the balance set.
An AST can interrupt the wait state caused by $HIBER if the access mode at which the AST is to execute is equal to or more privileged than the access mode from which the hibernate request was issued and the process is enabled for ASTs at that access mode.
When the AST service routine completes execution, the system reexecutes the $HIBER service on behalf of the process. If a wakeup request has been issued for the process during the execution of the AST service routine (either by itself or another process), the process resumes execution. If a wakeup request has not been issued, it continues to hibernate.
If one or more wakeup requests are issued for the process while it is not hibernating, the next hibernate call returns immediately; that is, the process does not hibernate. No count of outstanding wakeup requests is maintained.
Although this service has no arguments, a Fortran function reference must use parentheses to indicate a null argument list, as in the following example:
ISTAT=SYS$HIBER()Required Access or Privileges
Required Quota
Related Services
$CANEXH, $CREPRC, $DCLEXH, $DELPRC, $EXIT, $FORCEX, $GETJPI, $GETJPIW, $PROCESS_SCAN, $RESUME, $SETPRI, $SETPRN, $SETPRV, $SETRWM, $SUSPND, $WAKE
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully.
Translates the specified identifier value to its identifier name.On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$IDTOASC id ,[namlen] ,[nambuf] ,[resid] ,[attrib] ,[contxt]
int sys$idtoasc (unsigned int id, unsigned short int *namlen, void *nambuf, unsigned int *resid, unsigned int *attrib, unsigned int *contxt);
id
OpenVMS usage: rights_id type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Binary identifier value translated by $IDTOASC. The id argument is a longword containing the binary value of the identifier. To determine the identifier names of all identifiers in the rights database, you specify id as --1 and call $IDTOASC repeatedly until it returns the status code SS$_NOSUCHID. The identifiers are returned in alphabetical order.namlen
OpenVMS usage: word_unsigned type: word (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit reference (VAX)
Number of characters in the identifier name translated by $IDTOASC. The namlen argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) of a word containing the length of the identifier name written to nambuf.nambuf
OpenVMS usage: char_string type: character-coded text string access: write only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor (VAX)
Identifier name text string returned when $IDTOASC completes the translation. The nambuf argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) of a descriptor pointing to the buffer in which the identifier name is written.resid
OpenVMS usage: rights_id type: longword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit reference (VAX)
Identifier value of the identifier name returned in nambuf. The resid argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) of a longword containing the 32-bit code of the identifier.attrib
OpenVMS usage: mask_longword type: longword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit reference (VAX)
Mask of attributes associated with the identifier returned in resid. The attrib argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) of a longword containing the attribute mask.Symbol values are offsets to the bits within the longword. You can also obtain the values as masks with the appropriate bit set using the prefix KGB$M rather than KGB$V. The following symbols for each bit position are defined in the system macro library ($KGBDEF).
Bit Position Meaning When Set KGB$V_DYNAMIC Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the process rights list using the DCL command SET RIGHTS_LIST. KGB$V_NAME_HIDDEN Allows holders of an identifier to have it translated---either from binary to ASCII or vice versa---but prevents unauthorized users from translating the identifier. KGB$V_NOACCESS Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem attribute. KGB$V_RESOURCE Allows holders of an identifier to charge disk space to the identifier. It is used only for file objects. KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in the subsystem. contxt
OpenVMS usage: context type: longword (unsigned) access: modify mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit reference (VAX)
Context value used when repeatedly calling $IDTOASC. The contxt argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) of a longword used while $IDTOASC searches for all identifiers. The context value must be initialized to the value 0, and the resulting context of each call to $IDTOASC must be presented to each subsequent call. After contxt is passed to $IDTOASC, you must not modify its value.
The Translate Identifier to Identifier Name service translates the specified binary identifier value to an identifier name. While the primary purpose of this service is to translate the specified identifier to its name, you can also use it to find all identifiers in the rights database. Owner or read access to the rights database is required. To determine all the identifiers, call $IDTOASC repeatedly until it returns the status code SS$_NOSUCHID. When SS$_NOSUCHID is returned, $IDTOASC has returned all the identifiers, cleared the context value, and deallocated the record stream.If you complete your calls to $IDTOASC before SS$_NOSUCHID is returned, use $FINISH_RDB to clear the context value and deallocate the record stream.
When you use wildcards with this service, the records are returned in identifier name order.
Required Access or Privileges
None, unless the id argument is NAME_HIDDEN, in which case you must hold the identifier or have read access to the rights list.
Required Quota
Related Services
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CHANGE_ACL, $CHECK_ACCESS, $CHKPRO, $CREATE_RDB, $ERAPAT, $FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $FORMAT_ACL, $FORMAT_AUDIT, $GRANTID, $HASH_PASSWORD, $MOD_HOLDER, $MOD_IDENT, $MTACCESS, $PARSE_ACL, $REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The namlen, nambuf, resid, attrib, or contxt argument cannot be written by the caller. SS$_INSFMEM The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights database. SS$_IVCHAN The contents of the context longword are not valid. SS$_IVIDENT The specified identifier is of invalid format. SS$_NOIOCHAN No more rights database context streams are available. SS$_NORIGHTSDB The rights database does not exist. SS$_NOSUCHID The specified identifier name does not exist in the rights database, or the entire rights database has been searched if the ID is --1.
Because the rights database is an indexed file that you access with OpenVMS RMS, this service can also return RMS status codes associated with operations on indexed files. For descriptions of these status codes, refer to the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
On Alpha systems, modifies the software IEEE floating-point control register and, optionally, returns the previous register value.The service provides the mechanism to set the specified bits in the IEEE floating-point control register, to clear the specified bits in the register, and to swap the values of the register.
SYS$IEEE_SET_FP_CONTROL [clrmsk] ,[setmsk] ,[prvmsk]
int sys$ieee_set_fp_control (struct _ieee *clrmsk, struct _ieee *setmsk, struct _ieee *prvmsk);
clrmsk
OpenVMS usage: mask_quadword type: quadword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Address of a quadword bit mask to be cleared in the IEEE floating-point control register.The $IEEEDEF macro defines symbols for the floating-point control register. Table SYS-13 shows the symbols, their corresponding masks, and their meaning.
Table SYS-13 Format of the IEEE Floating-Point Control Register (Alpha Only) Symbol Mask Meaning IEEE$M_TRAP_ENABLE_INV 2 Invalid operation IEEE$M_TRAP_ENABLE_DZE 4 Divide by 0 IEEE$M_TRAP_ENABLE_OVF 8 Overflow IEEE$M_TRAP_ENABLE_UNF 10 Underflow IEEE$M_TRAP_ENABLE_INE 20 Inexact IEEE$M_MAP_UMZ 4000 Underflows are mapped to 0.0 IEEE$M_INHERIT 8000 Inherit FP state on thread create IEEE$M_STATUS_INV 20000 Invalid operation IEEE$M_STATUS_DZE 40000 Divide by 0 IEEE$M_STATUS_OVF 80000 Overflow IEEE$M_STATUS_UNF 100000 Underflow IEEE$M_STATUS_INE 200000 Inexact setmsk
OpenVMS usage: mask_quadword type: quadword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Address of a quadword bit mask to be set in the IEEE floating-point control register.Table SYS-13 shows the format of the IEEE floating-point control register.
prvmsk
OpenVMS usage: mask_quadword type: quadword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by reference
Address of a quadword to receive the previous value of the IEEE floating-point control register.
The Set IEEE Floating-Point Control Register service updates the IEEE floating-point control register, maintained by the operating system, with the values supplied by the calling program.The following steps are used to update the register:
- If the prvmsk argument is specified, $IEEE_SET_FP_CONTROL first reads the previous value of the IEEE floating-point control register.
- If the clrmsk argument is specified, $IEEE_SET_FP_CONTROL then clears the specified bit masks in the clrmsk argument.
- If the setmsk argument is specified, $IEEE_SET_FP_CONTROL then sets the specified bit masks in the setmsk argument.
A program can swap the IEEE floating-point control register (that is, save the old value and specify a new value) by specifying the following:
- The clrmsk argument with the address of a quadword of all 1s
- The setmsk argument with the address of a quadword that holds the new register value
- The prvmsk argument with the address of a quadword to save the old register value
Required Access or Privilege
Required Quota
None
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The specified argument cannot be read or cannot be written.
On Alpha systems, initializes system process alignment fault reporting.This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT match_table ,buffer_size ,flags
int sys$init_sys_align_fault_report void *match_table, int buffer_size, unsigned int flags
;)
match_table
OpenVMS usage: address type: longword (unsigned) access: read mechanism: by 32-bit or 64-bit reference
Describes the system fault match table. The match_table argument is the 32-bit or 64-bit virtual address of an array of longwords describing the system fault match table. The first longword is the number of match entries; the remaining longwords are the match entries.The match table is used to restrict the number of alignment faults reported. Each entry in the table is a bit mask divided into three groups: mode bits, program counter (PC) space bits, and virtual address (VA) space bits.
The following table lists the symbols that can be used to define these bits.
Bit Type Symbols Mode bits AME$M_KERNEL_MODE Kernel mode AME$M_EXEC_MODE Executive mode AME$M_SUPER_MODE Supervisor mode AME$M_USER_MODE User mode Program counter bits AME$M_USER_PC PC in User space AME$M_SYSTEM_PC PC in System space Virtual address bits AME$M_SYSTEM_VA VA in System space AME$M_USER_VA_P0 VA in User P0 space AME$M_USER_VA_P1 VA in User P1 space AME$M_USER_VA_P2 VA in User P2 space The following diagram illustrates the data structure of the match table.
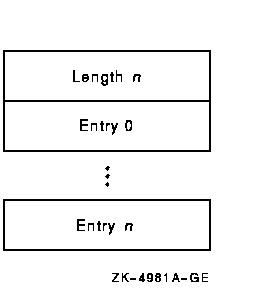
When an alignment fault occurs, a fault bit mask is created with one bit set in each group. The alignment fault handler then compares this fault bit mask against each entry in the match table. If the fault bit mask is a subset of an entry in the match table, the fault is reported.
buffer_size
OpenVMS usage: byte count type: longword (signed) access: read mechanism: by value
The number of bytes to allocate, from nonpaged pool, to save the alignment fault data. The buffer you allocate must be sufficient to accommodate one data item of the size specified in the flags argument.flags
OpenVMS usage: mask_longword type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Flag bit mask specifying options for the $GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA operation.
Previous | Next | Contents | [Home] | [Comments] | [Ordering info] | [Help]
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
4527P050.HTM OSSG Documentation 22-NOV-1996 13:00:05.18Copyright © Digital Equipment Corporation 1996. All Rights Reserved.