![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
Required Quota
None
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The specified buffer cannot be written. SS$_BADBUFLEN The specified buffer length is invalid or out of range.
On Alpha systems, gets information about a specified virtual region.This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$GET_REGION_INFO function_code ,region_id_64 ,start_va_64 , nullarg ,buffer_length ,buffer_address_64 ,return_length_64
int sys$get_region_info (unsigned int function_code, struct _generic_64 *region_id_64, void *start_va_64, void *reserved, unsigned int buffer_length, void *buffer_address_64, unsigned int *return_length_64);
function_code
OpenVMS usage: function code type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Function code specifying how the information you are requesting should be looked up. All function codes return region summary information in the return buffer in the format of the Region Summary Buffer. The Region Summary Buffer format is shown in Table SYS-12. If less buffer space is specified than the length of the Region Summary Buffer, only the amount of information requested is returned. If more buffer space is specified than the length of the Region Summary Buffer, the service will fill in the buffer. The return length will reflect the amount of useful information written to the buffer, the size of the Region Summary Buffer.The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro in STARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each function code. The following function codes are defined:
Symbolic Name Description VA$_REGSUM_BY_ID Return the region summary information for the region whose ID is specified in the region_id_64 argument. VA$_REGSUM_BY_VA Return the region summary information for the region that contains the virtual address specified in the start_va_64 argument. VA$_NEXT_REGSUM_BY_VA Return the region summary information for the region containing the starting address. If the starting address is not in a region, return the region summary information for the next region with a starting address higher than the specified address. Note: For the VA$_NEXT_REGSUM_BY_VA function, OpenVMS checks for a start_va_64 argument in the inaccessible address range in P2 space. If it finds one, OpenVMS adjusts the address to account for the discontinuity. For more information about the layout of the 64-bit virtual address space, see the OpenVMS Alpha Guide to 64-Bit Addressing and VLM Features.
This function code can be used for wildcard operations. See the description of the start_va_64 argument for information on how to program a wildcard operation on regions.
region_id
OpenVMS usage: region identifier type: quadword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
The region ID associated with the region about which information is requested. This argument is read only if the function code VA$_REGSUM_BY_ID is specified.The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro in STARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each of the three default regions in P0, P1, and P2 space. The following region IDs are defined:
Symbol Region VA$C_P0 Program region VA$C_P1 Control region VA$C_P2 64-bit program region Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can be specified.
start_va_64
OpenVMS usage: input address type: quadword address access: read only mechanism: by value
Virtual address associated with region about which information is requested. This argument is read only if the function_code argument is VA$_REGSUM_BY_VA or VA$_NEXT_REGSUM_BY_VA.If the function_code argument is VA$_REGSUM_BY_VA, this argument is a virtual address within the region about which you are requesting information.
To perform a wildcard search on all regions, specify VA$_NEXT_REGSUM_BY_VA as the function code and begin with the start_va_64 argument specified as -1. For subsequent calls, specify start_va_64 as the sum of the previous region's start address and length. Call the $GET_REGION_INFO service in a loop until the condition SS$_NOMOREREG is returned.
Note
Before performing the lookup function, OpenVMS sign-extends the 64-bit starting address so that it represents a properly formed virtual address for the CPU.
nullarg
OpenVMS usage: null_arg type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Placeholding argument reserved to Digital.buffer_length
OpenVMS usage: longword_unsigned type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Length of the buffer into which information is returned.buffer_address_64
OpenVMS usage: varying_arg type: unspecified access: write only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a quadword-aligned buffer into which to return information if the buffer_length argument is non-zero.This argument is ignored if the buffer_length argument is zero.
The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF MACRO in STARLET.MLB define the REGSUM structure.
Table SYS-12 Region Summary Buffer Format Field name Meaning Field Size (Bytes) Field Offset (Decimal) VA$L_FLAGS Flags used when region was created 4 8 VA$L_REGION_PROTECT Create and owner mode of region 4 12 VA$Q_REGION_ID Region identifier 8 0 VA$PQ_START_VA Starting (lowest) virtual address of region 8 16 VA$Q_REGION_SIZE Total length of region 8 24 VA$PQ_FIRST_FREE_VA First free virtual address in region 8 32 VA$C_REGSUM_LENGTH Length of Region Summary Buffer constant 40 return_length_64
OpenVMS usage: longword_unsigned type: longword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
The 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned longword into which the service returns the length of the information in bytes.
The Get Information About a Specified Virtual Region service is a kernel mode service that can be called from any mode. This service gets the requested information about the specified region or the next region in a wildcard search. If the returned value of this service is not a successful condition value, a value cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the buffer_address_64 or return_length_64 arguments.Required Privileges
Required Quota
Related Services
$CREATE_REGION_64, $DELETE_REGION_64
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The buffer_address_64 argument or the return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the caller. SS$_BADPARAM Unrecognized function code. SS$_IVREGID Invalid region ID specified in conjunction with the VA$_REGSUM_BY_ID function code. SS$_NOMOREREG No region at a higher address than specified in the start_va_64 argument, which was specified in conjunction with the wildcard function code VA$_NEXT_REGSUM_BY_VA. SS$_PAGNOTINREG The value specified in the start_va_64 argument is not within a region and was specified in conjunction with the function code VA$_REGSUM_BY_VA.
Retrieves the security characteristics of an object.
SYS$GET_SECURITY [clsnam] ,[objnam] ,[objhan] ,[flags] ,[itmlst] ,[contxt] ,[acmode]
int sys$get_security ( void *clsnam, void *objnam, unsigned int *objhan, unsigned int flags, void *itmlst, unsigned int *contxt, unsigned int *acmode);
Item Codes The following table provides a summary of item codes that are valid in an item descriptor in the itmlst argument. Complete descriptions of each item code are provided after the table.clsnam
OpenVMS usage: char_string type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by descriptor
Name of the object class. The clsnam argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to a string containing the name of the object class. The following is a list of protected object class names:
- CAPABILITY
- COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER
- DEVICE
- FILE
- GROUP_GLOBAL_SECTION
- LOGICAL_NAME_TABLE
- QUEUE
- RESOURCE_DOMAIN
- SECURITY_CLASS
- SYSTEM_GLOBAL_SECTION
- VOLUME
objnam
OpenVMS usage: char_string type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by descriptor
Name of the protected object whose associated security profile is going to be retrieved. The objnam argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to a string containing the name of the protected object.The format of an object name is class specific. The following table lists object names and describes their formats.
Object Class Object Name Format CAPABILITY A character string. Currently, the only capability object is VECTOR. COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER Name of the event flag cluster, as defined in the Associate Common Event Flag Cluster ($ASCEFC) system service. DEVICE Standard device specification, described in the OpenVMS User's Manual. FILE Standard file specification, described in the OpenVMS User's Manual. GROUP_GLOBAL_SECTION Section name, as defined in the Create and Map Section ($CRMPSC) system service. LOGICAL_NAME_TABLE Table name, as defined in the Create Logical Name Table ($CRELNT) system service. QUEUE Standard queue name, as described in the Send to Job Controller ($SNDJBC) system service. RESOURCE_DOMAIN An identifier or octal string enclosed in brackets. SECURITY_CLASS Any class name shown in column 1, or a class name followed by a period (.) and the template name. Use the DCL command SHOW SECURITY to display possible template names. SYSTEM_GLOBAL_SECTION Section name, as defined in the Create and Map Section ($CRMPSC) system service. VOLUME Volume name or name of the device on which the volume is mounted. objhan
OpenVMS usage: object_handle type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Data structure identifying the object whose associated characteristics are going to be retrieved. The objhan argument is an address of a longword containing the object handle. You can use the objhan argument as an alternative to the objnam argument; for example, channel number clearly specifies the file open on the channel and can serve as an object handle. The following table shows the format of the object classes.
Object Class Object Handle Format COMMON_EVENT_CLUSTER Event flag number DEVICE Channel number FILE Channel number RESOURCE_DOMAIN Resource domain identifier VOLUME Channel number
flags
OpenVMS usage: flags type: mask_longword access: read only mechanism: by value
Mask specifying processing options. The flags argument is a longword bit vector wherein a bit, when set, specifies the processing option. The flags argument requires the contxt argument. The following table describes each flag.
Symbolic Name Description OSS$M_RELCTX Release the context structure at the completion of this request. OSS$M_WLOCK Maintain a write lock on the security profile at the completion of this request. $GET_SECURITY ignores the flag if the context has already been established. These symbolic names are defined in the $OSSDEF macro. You construct the flags argument by specifying the symbolic names of each flag.
itmlst
OpenVMS usage: item_list_3 type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Item list specifying which information about the process or processes is to be returned. The itmlst argument is the address of a list of item descriptors, each of which describes an item of information. The list of item descriptors is terminated by a longword of 0.With the item list, the user retrieves the protected object's characteristics. The user defines which security characteristics to retrieve. If this argument is not present, only the flags argument is processed. Without the itmlst argument, you can only manipulate the security profile lock or release contxt resources.
The following diagram depicts a single item descriptor.
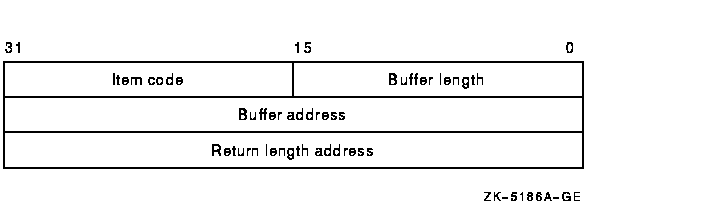
The following table describes the item descriptor fields.
Descriptor Field Definition Buffer length A word containing an integer specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer in which $GET_SECURITY is to write the information. The length of the buffer needed depends upon the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too small, $GET_SECURITY truncates the data. Item code A word containing a symbolic code specifying the item of information that $GET_SECURITY is to return. The $OSSDEF macro defines these codes. A description of each item code is given in the Item Codes section. Buffer address A longword containing the address of the buffer in which $GET_SECURITY is to write the information. Return length address A longword containing the address of a word in which $GET_SECURITY writes the length (in bytes) of the information it actually returns. contxt
OpenVMS usage: context type: longword (unsigned) access: modify mechanism: by reference
Value used to maintain the processing context when dealing with a single protected object across multiple $GET_SECURITY/$SET_SECURITY calls. Whenever the context value is nonzero, the class name, object name, or object handle arguments are disregarded. An input value of 0 indicates that a new context should be established.Because an active context block consumes process memory, be sure to release the context block by setting the RELCTX flag when the profile processing is complete. $GET_SECURITY sets the context argument to 0 once the context is released.
acmode
OpenVMS usage: access_mode type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Access mode to be used in the object protection check. The acmode argument is the address of a longword containing the access mode. The acmode argument defaults to kernel mode; however, the system compares acmode with the caller's access mode and uses the least privileged mode. The access modes are defined in the system macro $PSLDEF library. Digital recommends that this argument be omitted (passed as zero).
| Item Identifier | Description |
|---|---|
| OSS$_ACCESS_NAMES | Returns access bitname translation table for the class. |
| OSS$_ACCESS_NAMES_LENGTH | Returns the size (in bytes) of the access bitname translation table. |
| OSS$_ACL_FIND_ENTRY | Locates an access control entry (ACE). |
| OSS$_ACL_FIND_NEXT | Positions to the next ACE. |
| OSS$_ACL_FIND_TYPE | Locates an ACE of specified type. |
| OSS$_ACL_GRANT_ACE | Locates an ACE that either grants or denies access. |
| OSS$_ACL_LENGTH | Returns the length of the access control list (ACL). |
| OSS$_ACL_POSITION_BOTTOM | Sets a marker that points to the end of the ACL. |
| OSS$_ACL_POSITION_TOP | Sets a marker that points to the beginning of the ACL. |
| OSS$_ACL_READ | Reads the entire ACL. |
| OSS$_ACL_READ_ENTRY | Reads an ACE. |
| OSS$_CLASS_NAME | Returns the full object class name. |
| OSS$_FIRST_TEMPLATE | Returns the name of the first template profile of a Security_Class object. |
| OSS$_NEXT_OBJECT | Returns the name of the next Security_Class object. |
| OSS$_NEXT_TEMPLATE | Returns the name of the next template profile of a Security_Class object. |
| OSS$_OBJECT_NAME | Returns the name of the object. The FILE class does not return an object name. |
| OSS$_OWNER | Returns the UIC or general identifier of the object's owner. |
| OSS$_PROTECTION | Returns the protection code of the object. |
OSS$_ACCESS_NAMES
When you specify OSS$_ACCESS_NAMES, $GET_SECURITY returns the access name translation table in the buffer pointed to by the buffer address field of the item descriptor.The access name translation table is a 32-quadword vector followed by a variable section containing the access names. Each bit in the vector represents a single access type. The contents of the quadword is a string descriptor that corresponds to the ASCII bitname string. Undefined access types have zero-length names. The return length, if present, returns the length of the table.
OSS$_ACCESS_NAMES_LENGTH
When you specify OSS$_ACCESS_NAMES_LENGTH, $GET_SECURITY returns the length of the access name translation table.OSS$_ACL_FIND_ENTRY
When you specify OSS$_ACL_FIND_ENTRY, $GET_SECURITY locates an ACE pointed to by the buffer address. OSS$_ACL_FIND_ENTRY sets the position within the ACL for succeeding ACL operations; for example, for a deletion or modification of the ACE. If the buffer address is 0, it returns SS$_ACCVIO.OSS$_ACL_FIND_NEXT
When you specify OSS$_ACL_FIND_NEXT, $GET_SECURITY advances the current position to the next ACE in the ACL.OSS$_ACL_FIND_TYPE
When you specify OSS$_ACL_FIND_TYPE, $GET_SECURITY returns an ACE of a particular type if there is one in the buffer pointed to by the buffer address. OSS$_ACL_FIND_TYPE sets the position within the ACL for succeeding ACL operations. If the buffer address is 0, it returns SS$_ACCVIO.OSS$_ACL_GRANT_ACE
When you specify OSS$_ACL_GRANT_ACE, $GET_SECURITY returns the ACE in the object's ACL that grants or denies the user access to that object. OSS$_ACL_GRANT_ACE returns the ACE found in the buffer pointed to by the buffer address.OSS$_ACL_LENGTH
When you specify OSS$_ACL_LENGTH, $GET_SECURITY returns the size (in bytes) of the object's ACL. The buffer address field points to a longword that receives the size.OSS$_ACL_POSITION_BOTTOM
When you specify OSS$_ACL_POSITION_BOTTOM, $GET_SECURITY sets the ACL position to point to the bottom of the ACL.OSS$_ACL_POSITION_TOP
When you specify OSS$_ACL_POSITION_TOP, $GET_SECURITY sets the ACL position to point to the top of the ACL.OSS$_ACL_READ
When you specify OSS$_ACL_READ, $GET_SECURITY returns the portion of the object's ACL to the buffer pointed to by the buffer address.OSS$_ACL_READ_ENTRY
When you specify OSS$_ACL_READ_ENTRY, $GET_SECURITY reads the ACE pointed to by the buffer address.OSS$_CLASS_NAME
When you specify OSS$_CLASS_NAME, $GET_SECURITY returns the full object class name.OSS$_FIRST_TEMPLATE
When you specify OSS$_FIRST_TEMPLATE, $GET_SECURITY returns the name of the first template profile for the object named in the objnam argument. This item code is valid only for security class objects. If the clsnam is not Security_Class, SS$_INVCLSITM is returned.OSS$_NEXT_OBJECT
When you specify OSS$_NEXT_OBJECT, $GET_SECURITY returns the name of the next object. A return length of 0 indicates the end of the list. This item code is valid only for security class objects. If the clsnam is not Security_Class, SS$_INVCLSITM is returned.OSS$_NEXT_TEMPLATE
When you specify OSS$_NEXT_TEMPLATE, $GET_SECURITY returns the name of the next template. This item code allows you to step through a list of an object's templates. A return length of 0 indicates the end of the list. This item code is valid only for security class objects. If the clsnam is not Security_Class, SS$_INVCLSITM is returned.OSS_OBJECT_NAME
When you specify OSS$_OBJECT_NAME, $GET_SECURITY returns the name of the object.OSS$_OWNER
When you specify OSS$_OWNER, $GET_SECURITY returns the owner of the object.OSS$_PROTECTION
When you specify OSS$_PROTECTION, $GET_SECURITY returns the protection code of the object.
The Get Security service returns information about security characteristics of a selected object. Security characteristics include such information as the protection code, the owner, and the access control list (ACL). The security management services, $GET_SECURITY and $SET_SECURITY, maintain a single master copy of a profile for every security object in an OpenVMS Cluster environment. They also ensure that only one process at a time can modify an object's security profile.
Previous | Next | Contents | [Home] | [Comments] | [Ordering info] | [Help]
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
4527P048.HTM OSSG Documentation 22-NOV-1996 13:00:01.95Copyright © Digital Equipment Corporation 1996. All Rights Reserved.