![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
To determine all the members of a shadow set, first specify the virtual unit to $GETDVI. Then, on subsequent calls, specify the member name returned by the previous $GETDVI call until it returns a null member name.
When the shadow set members have a nonzero allocation class, the device name returned by $GETDVI contains the allocation class; the name has the form $allocation-class$device. For example, if a shadow set has an allocation class of 255 and the device name is DUS10, $GETDVI returns the string $255$DUS10.
Note
Shadow set members must have a nonzero allocation class to operate in an OpenVMS Cluster system. See Volume Shadowing for OpenVMS for more information.
Because a device name can include up to 64 characters, the buffer length field of the item descriptor should specify 64 (bytes).
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| UCB$V_TIM | Timeout is enabled. |
| UCB$V_INT | Interrupt is expected. |
| UCB$V_ERLOGIP | Error log is in progress on unit. |
| UCB$V_CANCEL | I/O on unit is canceled. |
| UCB$V_ONLINE | Unit is on line. |
| UCB$V_POWER | Power failed while unit busy. |
| UCB$V_TIMOUT | Unit timed out. |
| UCB$V_INTTYPE | Receiver interrupt. |
| UCB$V_BSY | Unit is busy. |
| UCB$V_MOUNTING | Device is being mounted. |
| UCB$V_DEADMO | Deallocate at dismount. |
| UCB$V_VALID | Volume is software valid. |
| UCB$V_UNLOAD | Unload volume at dismount. |
| UCB$V_TEMPLATE | Template UCB from which other UCBs for this device type are made. |
| UCB$V_MNTVERIP | Mount verification is in progress. |
| UCB$V_WRONGVOL | Wrong volume detected during mount verification. |
| UCB$V_DELETEUCB | Delete this UCB when reference count equals 0. |
The $GETDVI service returns the name in the format of the remote system. If the remote system is a LAT terminal server, $GETDVI returns the name as server_name/port_name. The names are separated by the slash (/) character. If the remote system is an X.29 terminal, the name is returned as network.remote_DTE.
When writing applications, you should use the string returned by DVI$_ACCPORNAM, instead of the physical device name, to identify remote terminals.
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| TTC$V_HANGUL | DEC Korean |
| TTC$V_HANYU | DEC Hanyu |
| TTC$V_HANZI | DEC Hanzi |
| TTC$V_KANA | DEC Kana |
| TTC$V_KANJI | DEC Kanji |
| TTC$V_THAI | DEC Thai |
Each of these item codes requires that the buffer specify a longword into which $GETDVI will write a 0 or 1: 0 if the terminal does not have the specified characteristic, and 1 if the terminal does have it. The one exception is the DVI$_TT_PAGE item code, which when specified causes $GETDVI to return a decimal longword value that is the page size of the terminal.
You can also obtain this terminal-specific information by using the DVI$_DEVDEPEND and DVI$_DEVDEPEND2 item codes. Each of these two item codes specifies a longword bit vector wherein each bit corresponds to a terminal characteristic; $GETDVI sets the corresponding bit for each characteristic possessed by the terminal.
Following is a list of the item codes that return information about terminal characteristics. For information about these characteristics, refer to the description of the F$GETDVI lexical function in the OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.
| DVI$_TT_NOECHO | DVI$_TT_NOTYPEAHD |
| DVI$_TT_HOSTSYNC | DVI$_TT_TTSYNC |
| DVI$_TT_ESCAPE | DVI$_TT_LOWER |
| DVI$_TT_MECHTAB | DVI$_TT_WRAP |
| DVI$_TT_LFFILL | DVI$_TT_SCOPE |
| DVI$_TT_CRFILL | DVI$_TT_SETSPEED |
| DVI$_TT_EIGHTBIT | DVI$_TT_MBXDSABL |
| DVI$_TT_READSYNC | DVI$_TT_MECHFORM |
| DVI$_TT_NOBRDCST | DVI$_TT_HALFDUP |
| DVI$_TT_MODEM | DVI$_TT_OPER |
| DVI$_TT_LOCALECHO | DVI$_TT_AUTOBAUD |
| DVI$_TT_PAGE | DVI$_TT_HANGUP |
| DVI$_TT_MODHANGUP | DVI$_TT_BRDCSTMBX |
| DVI$_TT_DMA | DVI$_TT_ALTYPEAHD |
| DVI$_TT_ANSICRT | DVI$_TT_REGIS |
| DVI$_TT_AVO | DVI$_TT_EDIT |
| DVI$_TT_BLOCK | DVI$_TT_DECCRT |
| DVI$_TT_EDITING | DVI$_TT_INSERT |
| DVI$_TT_DIALUP | DVI$_TT_SECURE |
| DVI$_TT_FALLBACK | DVI$_TT_DISCONNECT |
| DVI$_TT_PASTHRU | DVI$_TT_SIXEL |
| DVI$_TT_PRINTER | DVI$_TT_APP_KEYPAD |
| DVI$_TT_DRCS | DVI$_TT_SYSPWD |
| DVI$_TT_DECCRT2 | |
| DVI$_TT_DECCRT3 | |
| DVI$_TT_DECCRT4 |
In the description of the DVI$_DEVCHAR item code is a list of symbol names in which each symbol represents a device characteristic. To construct the $GETDVI item code for each device characteristic, substitute for yyyy that portion of the symbol name that follows the underscore character. For example, the DVI$_REC item code returns the same information as the DEV$V_REC bit in the DVI$_DEVCHAR longword bit vector.
The buffer for each of these item codes must specify a longword value, which is interpreted as Boolean. The $GETDVI service writes the value 1 into the longword if the device has the specified characteristic and the value 0 if it does not.
The Get Device/Volume Information service returns primary and secondary device characteristics information about an I/O device. You can use the chan argument only if (1) the channel has already been assigned, and (2) the caller's access mode is equal to or more privileged than the access mode from which the original channel assignment was made.The caller of $GETDVI does not need to have a channel assigned to the device about which information is desired.
The $GETDVI service returns information about both primary device characteristics and secondary device characteristics. By default, $GETDVI returns information about the primary device characteristics only.
To obtain information about secondary device characteristics, you must perform a logical OR operation on the item code specifying the information desired with the code DVI$C_SECONDARY.
You can obtain information about primary and secondary devices in a single call to $GETDVI.
In most cases, the two sets of characteristics (primary and secondary) returned by $GETDVI are identical. However, the two sets provide different information in the following cases:
- If the device has an associated mailbox, the primary characteristics are those of the assigned device and the secondary characteristics are those of the associated mailbox.
- If the device is a spooled device, the primary characteristics are those of the intermediate device (such as the disk) and the secondary characteristics are those of the spooled device (such as the printer).
- If the device represents a logical link on the network, the secondary characteristics contain information about the link.
Unless otherwise stated in the description of the item code, $GETDVI returns information about the local node only.
Required Access or Privileges
Required Quota
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The device name string descriptor, device name string, or itmlst argument cannot be read; or the buffer or return length longword cannot be written by the caller. SS$_BADPARAM The item list contains an invalid item code, or the buffer address field in an item descriptor specifies less than four bytes for the return length information. SS$_EXASTLM The process has exceeded its AST limit quota. SS$_IVCHAN You specified an invalid channel number, that is, a channel number larger than the number of channels. SS$_IVDEVNAM The device name string contains invalid characters, or neither the devnam nor chan argument was specified. SS$_IVLOGNAM The device name string has a length of 0 or has more than 63 characters. SS$_NONLOCAL The device is on a remote system. SS$_NOPRIV The specified channel is not assigned or was assigned from a more privileged access mode. SS$_NOSUCHDEV The specified device does not exist on the host system.
Same as those returned in R0.
The Get Device/Volume Information and Wait service returns information about an I/O device; this information consists of primary and secondary device characteristics.The $GETDVIW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to the caller with the requested information. Digital recommends that you use an IOSB with this service. An IOSB prevents the service from completing prematurely. In addition, the IOSB contains additional status information.
For asynchronous completion, use the Get Device/Volume Information ($GETDVI) service; $GETDVI returns to the caller after queuing the information request, without waiting for the information to be returned. In all other respects, $GETDVIW is identical to $GETDVI. For all other information about the $GETDVIW service, refer to the description of $GETDVI.
For additional information about system service completion, refer to the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
SYS$GETDVIW [efn] ,[chan] ,[devnam] ,itmlst [,iosb] [,astadr] [,astprm] [,nullarg]
int sys$getdviw (unsigned int efn, unsigned short int chan, void *devnam, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned __int64 *nullarg);
Returns information about one or more processes on the system or across the OpenVMS Cluster system.The $GETJPI service completes asynchronously. For synchronous completion, use the Get Job/Process Information and Wait ($GETJPIW) service.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$GETJPI [efn] ,[pidadr] ,[prcnam] ,itmlst ,[iosb] ,[astadr] ,[astprm]
int sys$getjpi (unsigned int efn, unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), unsigned __int64 astprm);
efn
OpenVMS usage: ef_number type: quadword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Number of the event flag to be set when $GETJPI returns the requested information. The efn argument is a quadword containing this number; however, $GETJPI uses only the low-order byte.Upon request initiation, $GETJPI clears the specified event flag (or event flag 0 if efn was not specified). Then, when $GETJPI returns the requested information, it sets the specified event flag (or event flag 0).
pidadr
OpenVMS usage: process_id type: longword (unsigned) access: modify mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit reference (VAX)
Process identification (PID) of the process about which $GETJPI is to return information. The pidadr argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a longword containing the PID. The pidadr argument can refer to a process running on the local node or a process running on another node in the cluster.If you give pidadr the value --1, $GETJPI assumes a wildcard operation and returns the requested information for each process on the system that it has the privilege to access, one process per call. To perform a wildcard operation, you must call $GETJPI in a loop, testing for the condition value SS$_NOMOREPROC after each call and exiting from the loop when SS$_NOMOREPROC is returned.
If you use $GETJPI with $PROCESS_SCAN you can perform wildcard searches across the cluster. In addition, with $PROCESS_SCAN you can search for specific processes based on many different selection criteria.
You cannot abbreviate a PID. All significant digits of a PID must be specified; only leading zeros can be omitted.
prcnam
OpenVMS usage: process_name type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor (VAX)
Name of the process about which $GETJPI is to return information. The prcnam argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a character string descriptor pointing to this name string.A process running on the local node can be identified with a 1- to 15-character string. To identify a process on a cluster, you must specify the full process name, which includes the node name as well as the process name. The full process name can contain up to 23 characters.
A local process name can look like a remote process name. Therefore, if you specify ATHENS::SMITH, the system checks for a process named ATHENS::SMITH on the local node before checking node ATHENS for a process named SMITH.
You can use the prcnam argument only if the process identified by prcnam has the same UIC group number as the calling process. If the process has a different group number, $GETJPI returns no information. To obtain information about processes in other groups, you must use the pidadr argument.
itmlst
OpenVMS usage: 32-bit item_list_3 or 64-bit item_list_64b type: longword (unsigned) for 32-bit; quadword (unsigned) for 64-bit access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit reference (VAX)
Item list specifying which information about the process or processes is to be returned. The itmlst argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a list of item descriptors, each of which describes an item of information. An item list in 32-bit format is terminated by a longword of 0; an item list in 64-bit format is terminated by a quadword of 0. All items in an item list must be of the same format---either 32-bit or 64-bit.The following diagram depicts the 32-bit format of a single item descriptor.
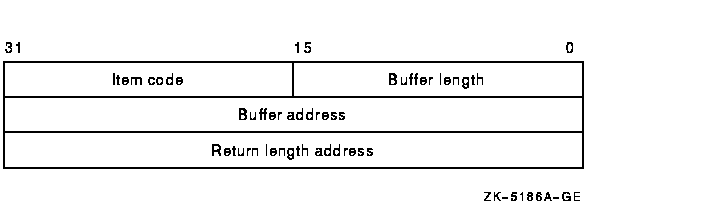
The following table defines the item descriptor fields for 32-bit item list entries.
Descriptor Field Definition Buffer length A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer in which $GETJPI is to write the information. The length of the buffer needed depends upon the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too small, $GETJPI truncates the data. Item code A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of information that $GETJPI is to return. The $JPIDEF macro defines these codes. Each item code is described in the Item Codes section. Buffer address A longword containing the user-supplied 32-bit address of the buffer in which $GETJPI is to write the information. Return length address A longword containing the user-supplied 32-bit address of a word in which $GETJPI writes the length (in bytes) of the information it actually returned. The following diagram depicts the 64-bit format of a single item descriptor.
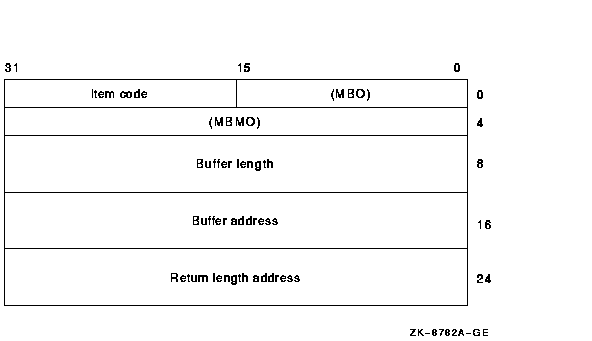
The following table defines the item descriptor fields for 64-bit item list entries.
Descriptor Field Definition MBO The field must contain a 1. The MBO and MBMO fields are used to distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries. Item code A word containing a symbolic code that describes the information in the buffer or the information to be returned to the buffer, pointed to by the buffer address field. The item codes are listed in the Item Codes section. MBMO The field must contain a --1. The MBMO and MBO fields are used to distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries. Buffer length A quadword containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer in which $GETJPI is to write the information. The length of the buffer needed depends upon the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too small, $GETJPI truncates the data. Buffer address A quadword containing the user-supplied 64-bit address of the buffer in which $GETJPI is to write the information. Return length address A quadword containing the user-supplied 64-bit address of a word in which $GETJPI writes the length (in bytes) of the information it actually returned. iosb
OpenVMS usage: io_status_block type: quadword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit reference (VAX)
I/O status block that is to receive the final completion status. The iosb argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of the quadword I/O status block.When you specify the iosb argument, $GETJPI sets the quadword to 0 upon request initiation. Upon request completion, a condition value is returned to the first longword; the second longword is reserved for future use.
Though this argument is optional, Digital strongly recommends that you specify it, for the following reasons:
- If you are using an event flag to signal the completion of the service, you can test the I/O status block for a condition value to be sure that the event flag was not set by an event other than service completion.
- If you are using the $SYNCH service to synchronize completion of the service, the I/O status block is a required argument for $SYNCH.
- The condition value returned in R0 and the condition value returned in the I/O status block provide information about different aspects of the call to the $GETJPI service. The condition value returned in R0 gives you information about the success or failure of the service call itself; the condition value returned in the I/O status block gives you information about the success or failure of the service operation. Therefore, to accurately assess the success or failure of the call to $GETJPI, you must check the condition values returned in both R0 and the I/O status block.
astadr
OpenVMS usage: ast_procedure type: procedure value access: call without stack unwinding mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit reference (VAX)
AST service routine to be executed when $GETJPI completes. The astadr argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of this routine.
Previous | Next | Contents | [Home] | [Comments] | [Ordering info] | [Help]
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
4527P037.HTM OSSG Documentation 22-NOV-1996 12:59:42.15Copyright © Digital Equipment Corporation 1996. All Rights Reserved.