![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
![[Digital logo]](../../IMAGES/DIGITAL-LOGO.GIF)
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the four access modes:
| Value | Symbolic Name | Access Mode |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | PSL$C_KERNEL | Kernel |
| 1 | PSL$C_EXEC | Executive |
| 2 | PSL$C_SUPER | Supervisor |
| 3 | PSL$C_USER | User |
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. The calling process can delete pages only if those pages are owned by an access mode equal to or less privileged than the access mode of the calling process.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The Delete Virtual Address Space service is a kernel mode service that can be called from any mode. This service deletes a range of addresses from a process's virtual address space. Upon successful completion of the service, the deleted pages are inaccessible, and references to them cause access violations. If any of the pages in the specified range have already been deleted or do not exist, the service continues as if the pages were successfully deleted.If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the return_va_64 and return_length_64 arguments. If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned address and returned length indicate the pages that were successfully deleted before the error occurred. If no pages were deleted, the return_va_64 argument will contain the value --1, and a value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed to by the return_length_64 argument.
Required Privileges
Required Quota
Related Services
$CREATE_REGION_64, $CRETVA_64, $CRMPSC_FILE_64, $CRMPSC_GFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $CRMPSC_PFN_64, $DELETE_REGION_64, $EXPREG_64, $MGBLSC_64, $MGBLSC_GPFN_64
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The return_va_64 argument or the return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the caller. SS$_IVREGID Invalid region ID specified. This condition value is returned if P0, P1, or P2 space is specified because these regions cannot be deleted, or if no region exists for the specified ID. SS$_LEN_NOTPAGMULT The length_64 argument is not a multiple of CPU-specific pages; or, for shared page table regions, is not a multiple of CPU-specific page table pages or does not include the last page in a memory-resident global section. SS$_PAGNOTINREG A page in the specified range is not within the specified region. SS$_PAGOWNVIO A page in the specified range is owned by an access mode more privileged than the access mode of the caller. SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN The start_va_64 argument is not a CPU-specific page table page aligned address; or, for shared page table regions, is not page table page aligned.
Dequeues (unlocks) granted locks; dequeues the sublocks of a lock; or cancels an ungranted lock request. The calling process must have previously acquired the lock or queued the lock request by calling the Enqueue Lock Request ($ENQ) service.On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$DEQ [lkid] ,[valblk] ,[acmode] ,[flags]
int sys$deq (unsigned int lkid, void *valblk, unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags);
lkid
OpenVMS usage: lock_id type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Lock identification of the lock to be dequeued. The lkid argument specifies this lock identification.Note that if you do not specify the lkid argument, you must specify the LCK$M_DEQALL flag in the flags argument.
When you specify the LCK$M_DEQALL flag in the flags argument, different values (or no value) for the lkid argument produce varying behavior:
- When you do not specify the lkid argument (or specify it as 0) and you do specify the LCK$M_DEQALL flag, $DEQ dequeues all locks held by the process, at access modes equal to or less privileged than the effective access mode, on all resources. The effective access mode is the least privileged of the caller's access mode and the access mode specified in the acmode argument.
- When you specify the lkid argument as a nonzero value together with the LCK$M_DEQALL flag, $DEQ dequeues all sublocks of the lock identified by lkid; it does not dequeue the lock identified by lkid. For this operation, $DEQ ignores the LCK$M_CANCEL flag if it is set. A sublock of a lock is a lock that was created when the parid argument in the call to $ENQ was specified, where parid is the lock ID of the parent lock.
If you omit the lkid argument (or specify it as 0) and the LCK$M_DEQALL flag is not set, the $DEQ service returns the invalid lock ID condition value (SS$_IVLOCKID).
valblk
OpenVMS usage: lock_value_block type: longword (unsigned) access: modify mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit reference (VAX)
Lock value block for the resource associated with the lock to be dequeued. The valblk argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit (on VAX systems) of the 16-byte lock value block. When you specify the LCK$M_DEQALL flag, you cannot use this argument.When a protected write (PW) or exclusive (EX) mode lock is being dequeued and you specify a lock value block in the valblk argument, the contents of that lock value block are written to the lock value block in the lock database. Further, if the lock value block in the lock database was marked as invalid, that condition is cleared; the block becomes valid.
acmode
OpenVMS usage: access_mode type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Access mode of the lock to be dequeued. The acmode argument is a longword containing the access mode.The acmode argument is valid only if the LCK$M_DEQALL flag of the flags argument is set. The $PSLDEF macro defines the following symbols for the four access modes.
Symbol Access Mode PSL$C_KERNEL Kernel PSL$C_EXEC Executive PSL$C_SUPER Supervisor PSL$C_USER User When dequeuing locks, $DEQ maximizes the access mode of the caller and the specified acmode argument. The maximized access mode is the less privileged of the caller's access mode and the acmode argument. If you do not specify the acmode argument, $DEQ uses the caller's access mode. Only those locks with an access mode that is equal to or less than the maximized access mode are dequeued.
flags
OpenVMS usage: mask_longword type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Flags specifying options for the $DEQ operation. The flags argument is a longword bit mask that is the logical OR of each bit set, where each bit corresponds to an option.Note that if you do not specify the lkid argument, you must specify the LCK$M_DEQALL flag in the flags argument.
A symbolic name for each flag bit is defined by the $LCKDEF macro. The following table describes each flag.
Flag Description LCK$M_DEQALL When you specify this flag, $DEQ dequeues multiple locks, depending on the value of the lkid argument. Refer to the description of the lkid argument for details. The acmode argument is ignored if the LCK$M_DQALL flag is not set. If you specify LCK$M_DEQALL, the LCK$M_CANCEL flag, if set, is ignored. LCK$M_CANCEL When you specify this flag, $DEQ attempts to cancel a lock request that was queued by $ENQ. You can cancel only a waiting request. When the request is canceled, $DEQ returns the condition value SS$_NORMAL. If you attempt to cancel a granted lock, the request fails and $DEQ returns the condition value SS$_CANCELGRANT. There are two types of waiting requests that can be canceled:
- A request for a new lock
- A request to convert an existing lock
When canceling a new lock request, the following action is taken:
- If a completion asynchronous system trap (AST) was requested, the AST is queued for delivery and SS$_ABORT is stored in the lock status block.
When canceling a request to convert an existing lock, the conversion request is canceled. The existing granted lock remains unchanged. The following specific actions are taken:
- The blocking AST address specified for the existing granted lock is queued for delivery if the granted mode of the existing lock is blocking other waiting requests.
- If a completion AST was specified by the conversion request, the completion AST is queued for delivery with SS$_CANCEL status stored in the lock status block that was specified by the conversion request.
If you specify the LCK$M_DEQALL flag, the LCK$M_CANCEL flag is ignored.
LCK$M_INVVALBLK When you specify this flag, $DEQ marks the lock value block, which is maintained for the resource in the lock database, as invalid. The lock value block remains marked as invalid until it is again written to. The Description section of the $ENQ service provides additional information about lock value block invalidation. This flag is ignored if (1) the lock mode of the lock being dequeued is not protected write or exclusive, or (2) you specify the LCK$M_CANCEL flag.
The Dequeue Lock Request service dequeues (unlocks) granted locks and waiting lock requests. The calling process must have previously acquired the lock or queued the lock request by calling the Enqueue Lock Request ($ENQ) service.Action taken by the $DEQ service depends on the current state (granted or waiting) and the type of lock request (new lock or conversion request) to be dequeued.
When dequeuing a granted lock, the $DEQ service returns the condition value SS$_NORMAL and the following specific action is taken:
- Any queued blocking ASTs that have not been delivered are removed from the process's AST queues.
There are two types of waiting requests that can be dequeued:
- A request for a new lock
- A request to convert an existing lock
When dequeuing a new lock request, the $DEQ service returns the condition value SS$_NORMAL and the following specific action is taken:
- If a completion AST was requested, the completion AST is queued for delivery with SS$_ABORT stored in the lock status block.
When dequeuing a lock for which there is a conversion request waiting, the existing lock and its conversion request are dequeued. The $DEQ service returns the condition value SS$_NORMAL and the following specific actions are taken:
- If a blocking AST was queued to the process, it is removed from the process's AST queue.
- If a completion AST was specified by the conversion request, the completion AST is queued for delivery with SS$_ABORT status stored in the lock status block that was specified by the conversion request.
When a protected write (PW) or exclusive (EX) mode lock is being dequeued and you specify a lock value block in the valblk argument, the contents of that lock value block are written to the lock value block in the lock database.
If you specify the LCK$M_INVVALBLK flag in the flags argument and the lock mode of the lock being dequeued is PW or EX, the lock value block in the lock database is marked as invalid whether or not a lock value block was specified in the valblk argument.
The $DEQ, $ENQ, $ENQW, and $GETLKI services together provide the user interface to the lock management facility. For additional information about lock management, refer to the descriptions of these other services and to the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
Required Access or Privileges
Required Quota
Related Services
$ENQ, $ENQW, $GETLKI, $GETLKIW
SS$_NORMAL The lock was dequeued successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The value block specified by the valblk argument cannot be accessed by the caller. SS$_CANCELGRANT The LCK$M_CANCEL flag in the flags argument was specified, but the lock request that $DEQ was to cancel had already been granted. SS$_ILLRSDM An illegal attempt to modify a value block was made. SS$_IVLOCKID An invalid or nonexistent lock identification was specified or the process does not have the privilege to dequeue a lock at the specified access mode. SS$_SUBLOCKS The lock has sublocks and cannot be dequeued.
Returns the names of all devices that match a specified set of search criteria.
SYS$DEVICE_SCAN return_devnam ,retlen ,[search_devnam] ,[itmlst] ,[contxt]
int sys$device_scan (void *return_devnam, unsigned short int *retlen, void *search_devnam, void *itmlst, struct _generic_64 *contxt);
return_devnam
OpenVMS usage: char_string type: character-coded text string access: write only mechanism: by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
Buffer to receive the device name. The return_devnam argument is the address of a character string descriptor pointing to a buffer into which $DEVICE_SCAN writes the name of the first or next device that matches the specified search criteria. The maximum size of any device name is 64 bytes.retlen
OpenVMS usage: word_unsigned type: word (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by reference
Length of the device name string returned by $DEVICE_SCAN. The retlen argument is the address of a word into which $DEVICE_SCAN writes the length of the device name string.search_devnam
OpenVMS usage: device_name type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
Name of the device for which $DEVICE_SCAN is to search. The search_devnam argument accepts the standard wildcard characters, the asterisk (*), which matches any sequence of characters, and the percent sign (%), which matches any one character. If the search_devnam argument does not include a wildcard character, an exact match is used for comparison. For example, to match all unit 0 DU devices on any controller, specify *DU%0. This string is compared to the most complete device name (DVI$_ALLDEVNAM). Only uppercase characters are accepted.
itmlst
OpenVMS usage: item_list_3 type: longword_unsigned access: read only mechanism: by reference
Item list specifying search criteria used to identify the device names for return by $DEVICE_SCAN. The itmlst argument is the address of a list of item descriptors, each of which describes one search criterion. The list of item descriptors is terminated by a longword of 0.The following diagram depicts the format of a single item descriptor.
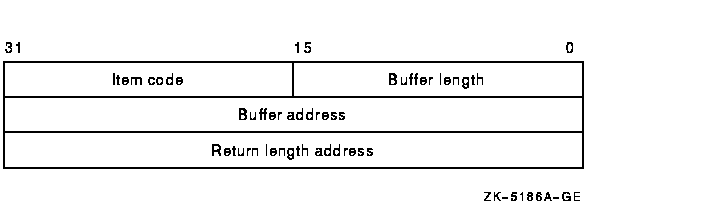
The following table defines the item descriptor fields.
Descriptor Field Definition Buffer length A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer from which $DEVICE_SCAN is to read the information. The length of the buffer needed depends upon the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor. Item code A word containing a user-specified symbolic code specifying the item of information that $DEVICE_SCAN is to return. The $DVSDEF macro defines these codes. Each item code is described in the Item Codes section. Buffer address A longword containing the address of the buffer from which $DEVICE_SCAN is to read the information. Return length address A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer from which $DEVICE_SCAN is to read the information. contxt
OpenVMS usage: quadword_unsigned type: quadword (unsigned) access: modify mechanism: by reference
Value used to indicate the current position of a $DEVICE_SCAN search. The contxt argument is the address of the quadword that receives this information. On the initial call, the quadword should contain 0.
DVS$_DEVCLASS
An input value item code that specifies, as an unsigned longword, the device class being searched. The $DCDEF macro defines these classes.The DVS$_DEVCLASS argument is a longword containing this number; however, DVS$_DEVCLASS uses only the low-order byte of the longword.
DVS$_DEVTYPE
An input value item code that specifies, as an unsigned longword, the device type for which $DEVICE_SCAN is going to search. The $DCDEF macro defines these types.The DVS$_DEVTYPE argument is a longword containing this number; however, DVS$_DEVTYPE uses only the low-order byte of the longword. DVS$_DEVTYPE should be used in conjunction with $DVS_DEVCLASS to specify the device type being searched for.
The Device Scan system service returns the names of all devices that match a specified set of search criteria. The names returned by $DEVICE_SCAN can then be passed to another service; for example, $GETDVI or $MOUNT.The device names are returned for one process per call. A context value is used to continue multiple calls to $DEVICE_SCAN.
$DEVICE_SCAN allows wildcard searches based on device names, device classes, and device types. It also provides the ability to perform a wildcard search on other device-related services.
$DEVICE_SCAN makes it possible to combine search criteria. For example, to find only RA82 devices, use the following selection criteria:
DVS$_DEVCLASS = DC$_DISK and DVS$_DEVTYPE = DT$_RA82To find all mailboxes with MB as part of the device name (excluding mailboxes such as NLA0), use the following selection criteria:
DVS$_DEVCLASS = DC$_MAILBOX and DEVNAM = *MB*Required Access or Privileges
Required Quota
Related Services
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The search_devnam, itmlst, or contxt argument cannot be read by the caller, or the retlen, return_devnam, or contxt argument cannot be written by the caller. SS$_BADPARAM The contxt argument contains an invalid value, or the item list contains an invalid item code. SS$_NOMOREDEV No more devices match the specified search criteria. SS$_NOSUCHDEV The specified device does not exist on the host system.
Marks an existing permanent global section for deletion. The actual deletion of the global section takes place when all processes that have mapped the global section have deleted the mapped pages.On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$DGBLSC [flags] ,gsdnam ,[ident]
int sys$dgblsc (unsigned int flags, void *gsdnam, struct _secid *ident);
flags
OpenVMS usage: mask_longword type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Mask indicating global section characteristics. The flags argument is a longword value. A value of 0 (the default) specifies a group global section; a value of SEC$M_SYSGBL specifies a system global section.gsdnam
OpenVMS usage: section_name type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor (VAX)
Name of the global section to be deleted. The gsdnam argument is the address of a character string descriptor pointing to this name string.For group global sections, the operating system interprets the group UIC as part of the global section name; thus, the names of global sections are unique to UIC groups.
ident
OpenVMS usage: section_id type: quadword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit reference (VAX)
Identification value specifying the version number of the global section to be deleted and the matching criteria to be applied. The ident argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) of a quadword structure containing three fields.The version number is in the second longword. The version number contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. Values for these fields can be assigned by installation convention to differentiate versions of global sections. If you specify no version number when creating a section, processes that specify a version number when mapping cannot access the global section.
Previous | Next | Contents | [Home] | [Comments] | [Ordering info] | [Help]
![[HR]](../../IMAGES/REDBAR.GIF)
4527P025.HTM OSSG Documentation 22-NOV-1996 12:59:22.02Copyright © Digital Equipment Corporation 1996. All Rights Reserved.